(Press-News.org) Golden retrievers are one of the most popular breeds of dogs. But research shows they have up to a 65% chance of dying from cancer. In a new study, University of California, Davis, researchers set out to find if certain genetic factors could help their survival rate. But instead of searching for genes associated with a cancer diagnosis in the breed, they instead chose to look for genes associated with longer life.
The gene they found is in a family of proteins long known to be important in human cancers. Specific versions or variants of the gene were associated with an increased lifespan of nearly two years. The study was published in the journal GeroScience.
“We assume that the majority of golden retrievers have a genetic predisposition to cancer, but if some of them are living to be 14, 15 or 16, we thought there could be another genetic factor that is helping to mitigate the bad genes, and the gene that popped out for us is HER4,” said co-corresponding author Robert Rebhun, Maxine Adler Endowed Chair in oncology at the UC Davis School of Veterinary Medicine.
HER4, also known as ERBB4, is a member of the family of human epidermal growth factor receptors. It is the same family of genes in humans as HER2, a gene well-known for making cancer cells grow quickly. Rebhun said dogs get many of the same kinds of cancers as humans, which could make this discovery important for humans, as well.
“If we find that this variant in HER4 is important either in the formation or progression of cancer in golden retrievers, or if it can actually modify a cancer risk in this cancer predisposed population, that may be something that can be used in future cancer studies in humans,” he said.
Hope for golden retrievers
More than 300 golden retrievers were part of the study. Researchers compared the DNA from blood samples of golden retrievers that were alive at 14 years of age to those that died before age 12. They found that dogs with certain variants of the gene survived longer, on average 13.5 years compared to 11.6 years.
“Almost two years is a significant difference in a dog’s life,” said co-corresponding author Danika Bannasch, Maxine Adler Endowed Chair in genetics with the UC Davis School of Veterinary Medicine. “Wouldn’t we all want our beloved pets to live another two years? Two years in goldens is about a 15-20% increase in lifespan, the equivalent of 12-14 years in humans.”
Bannasch said the finding is still one small piece to the complex puzzle of what could cause a golden retriever to get cancer.
“There are going to be many genes involved, but the fact that the gene associated with longevity is also a gene involved in cancer was really interesting to us.”
The study also found the gene variant seemed to be most important to the longevity of female dogs compared to male dogs. HER4 has been shown to interact with hormones such as estrogen and may also play a role in processing environmental toxins. Rebhun said the next step is to enroll a larger population of golden retrievers in a study to see if they can reproduce these results and discover how this genetic variant may impact expression or function of the gene.
Co-authors include Daniel York, Michael Kent, Madison Luker, Flora MD De Graaf, Kevin Batcher, Stephanie Ryan, Paula Yoon, and Jamie Peyton of UC Davis, and Joshua A. Stern of North Carolina State University.
The study was funded in part by the UC Davis Center for Companion Animal Health, Maxine Adler Endowed Chair Funds, and private donor funds specifically designated for longevity studies in golden retrievers.
END
Can golden retrievers live longer?
UC Davis researchers find gene associated with longevity in the breed
2023-10-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
University of Cincinnati researcher joins pediatric immunotherapy network
2023-10-19
Each year, approximately 200 to 300 children in the United States are diagnosed with diffuse midline gliomas (DMG), a tumor that begins in the brain or spinal cord.
The tumors cannot be removed through surgery due to their location in the brain, and current treatments are not effective and lead to a nearly zero percent survival rate.
The University of Cincinnati’s Timothy Phoenix is part of a multi-investigator collaborative team with St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital’s Stephen Mack, PhD, and Giedre Krenciute, PhD, that received a nearly $4 million National Cancer Institute (NCI) ...
New study provides ‘genetic fingerprint’ indicating disease spread by sand flies may be gaining firm foothold in the United States
2023-10-19
CHICAGO (October 19) — Scientists have new evidence that a tropical disease once seen almost exclusively in returning travelers is now being detected in the United States in people with no international travel history — and caused by a Leishmania parasite strain that’s distinctly different from “imported” cases, according to an analysis from researchers at the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) presented today at the Annual Meeting of the American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene (ASTMH).
The study, led by CDC scientist Marcos de Almeida, emerged from a curious rise of domestic infections over the last 10 years, ...
Researchers design a pulsing nanomotor
2023-10-19
An international team of scientists headed by the University of Bonn has developed a novel type of nanomotor. It is driven by a clever mechanism and can perform pulsing movements. The researchers are now planning to fit it with a coupling and install it as a drive in complex machines. Their findings have now appeared in the journal Nature Nanotechnology.
This novel type of motor is similar to a hand grip trainer that strengthens your grip when used regularly. However, the motor is around one million times smaller. Two handles are connected by a spring in a V-shaped structure.
In a hand grip trainer, ...
Lactate-producing bacteria inside tumors promote resistance to radiation therapy
2023-10-19
HOUSTON ― Researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center have discovered that lactate-producing intratumoral bacteria drives resistance to radiation therapy, suggesting that lactic acid-producing bacteria present in various cancers may serve as novel therapeutic targets.
The study, published today in Cancer Cell, reported that a particular bacterial species, Lactobacillus iners (L. iners), caused cancer cells to respond to radiation by rewiring metabolic signaling pathways to resist treatment. The researchers also found that L. iners was associated with poorer clinical outcomes in patients with cervical ...
Researchers document dramatic increase in advanced stage cervical cancer and deaths from cervical cancer in Appalachian Kentucky
2023-10-19
While the overall incidence and death rates from cervical cancer have dropped in the U.S., the opposite has been occurring in Appalachian Kentucky – a steady increase. The death rate from cervical cancer in Appalachian Kentucky is now twice that of the national rate.
A team of cancer population scientists from MUSC Hollings Cancer Center and the University of Kentucky Markey Cancer Center documented the increase through investigation of county-level data from 2000 through 2019. Their findings are published this month in JAMA Network Open.
“The rapidly growing disparities that we're ...
Researchers discover associations among PTSD, diet, and the gut microbiome
2023-10-19
Study suggests that adhering to a Mediterranean diet may alleviate or prevent posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) symptoms
The human gut microbiome has a significant impact on our health. Research has shown that it can influence the development and response of emotions, but the relationship between posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and the gut microbiome has been unexplored. PTSD is a fear-based mental health disorder that develops in some individuals who experience a disturbing and horrifying situation involving severe injury, actual or threat of death, or violence. A new study by investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare ...
COVID-19 vaccination willingness and reasons for vaccine refusal
2023-10-19
About The Study: The findings of this study that involved the use of data from Hong Kong and Singapore suggest that trust in health authorities was fundamental to overcoming COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy. As such, engendering trust in health care professionals, experts, and public health agencies should be incorporated into pandemic preparedness and response.
Authors: Michael Y. Ni, M.D., of the University of Hong Kong, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.37909)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article ...
Developmental trajectory of body weight in youths at risk for major mood disorders
2023-10-19
About The Study: In this study of 394 individuals, females with a family history of mood disorders were prone to weight gain starting around puberty and predating mood disorder onset. Early interventions aiming to prevent adverse mental and physical outcomes in this vulnerable group need to start in childhood.
Authors: Rudolf Uher, M.D., Ph.D., of Dalhousie University in Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.38540)
Editor’s ...
Soft optical fibers block pain while moving and stretching with the body
2023-10-19
Scientists have a new tool to precisely illuminate the roots of nerve pain.
Engineers at MIT have developed soft and implantable fibers that can deliver light to major nerves through the body. When these nerves are genetically manipulated to respond to light, the fibers can send pulses of light to the nerves to inhibit pain. The optical fibers are flexible and stretch with the body.
The new fibers are meant as an experimental tool that can be used by scientists to explore the causes and potential treatments for peripheral nerve disorders in animal models. ...
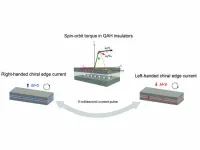
Electrical control of quantum phenomenon could improve future electronic devices
2023-10-19
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — A new electrical method to conveniently change the direction of electron flow in some quantum materials could have implications for the development of next-generation electronic devices and quantum computers. A team of researchers from Penn State developed and demonstrated the method in materials that exhibit the quantum anomalous Hall (QAH) effect — a phenomenon in which the flow of electrons along the edge of a material does not lose energy. The team described the work in a paper appearing today (Oct. 19) in the journal Nature ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
Microbial clues uncover how wild songbirds respond to stress
Researchers develop AI tools for early detection of intimate partner violence
Researchers develop AI tool to predict patients at risk of intimate partner violence
New research outlines pathway to achieve high well-being and a safe climate without economic growth
How an alga makes the most of dim light
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
Inside the light: How invisible electric fields drive device luminescence
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
[Press-News.org] Can golden retrievers live longer?UC Davis researchers find gene associated with longevity in the breed