(Press-News.org) 20 October 2023, Brussels, Belgium – At this critical junction for EU chemicals legislation, the independent scientific voice took centre stage at the 5th Annual Forum on Endocrine Disruptors. Together with an impressive number of concerned stakeholders, they called for the immediate adoption implementation of better EU legislation. While a restriction on per-and polyfluoroalkaline substances (PFAS) is ongoing, it risks being watered down by the massive volume of industry submissions to the public consultation. In addition, the European Commission’s legislative proposal on a revision of the main chemicals legislation REACH is still noticeably absent and is unlikely to still be published during the current term of the European Commission and Parliament.
The Forum brought together policy makers, scientists, industry leaders, and civil society to discuss the most pressing topics in the area of endocrine disruptors, including the most recent scientific developments in the field. The European Society of Endocrinology (ESE) once again took an active part in the Forum organised by the European Commission on October 19-20, 2023, and several of ESE’s affiliated experts were invited to present their research and voice their concerns on behalf of the European endocrine community.
This year’s conference put the adverse health effects of PFAS and the links with endocrine disruption at the heart of the agenda and discussed ongoing national and regional initiatives in Europe aimed at reducing exposure to endocrine disruptors.
Prof. Tina Kold Jensen, CPPEM, Environmental Medicine, University of Southern Denmark, described PFAS’ impact on children’s development by showing data from a child cohort. “The data is clear –PFAS continues to hamper the health of our children including their neurological function, fertility and overall development, stricter EU regulation is needed now to eradicate the presence of PFAS in our environment”, said Prof Jensen.
PFAS differ from other EDCs by their highly persistent and bio-accumulative nature, which leads to contemporary exposures having effects on human and animal health as well as our environment far into the future for generations to come. Extensive peer reviewed literature has described the many adverse health outcomes linked to exposure to PFAS, including altered reproductive function in men and women, abnormalities in reproductive organs, early puberty, immune system disruption, cancers, neuroendocrine tumours, respiratory problems, diabetes, obesity, cardiovascular conditions, altered nervous system development and function, and learning disabilities.
The need for strict regulation on PFAS and other Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals (EDCs) was stressed multiple times in the event by the different participating stakeholders.
“I wonder how long it will take for policy makers to catch up with the science and put in place an EU framework that will effectively protect us from PFAS and other EDCs” said Prof. Aleksandra Buha-Djordjevic, Department of Toxicology, University of Belgrade, Faculty of Pharmacy, Serbia.
ESE remains ready to share its expertise to further the regulation of harmful substances and looks forward to continuing to work with the European Commission and other stakeholders to address the issue of endocrine disruptors.
**** ENDS ****
To find out more please visit www.ese-hormones.org.
Follow us on X (formerly Twitter) @ESEndocrinology,
Facebook @EuropeanSocietyofEndocrinology
and LinkedIn: linkedin.com/company/european-society-of-endocrinology.
Contact:
Victoria Withy
European Society of Endocrinology
Phone: + 44 7761 80 08 55
Email: victoria.withy@ese-hormones.org
About the European Society of Endocrinology
The European Society of Endocrinology (ESE) provides a platform to develop and share leading research and best knowledge in endocrine science and medicine. By uniting and representing every part of the endocrine community, we are best placed to improve the lives of patients. Through the 51 National Societies involved with the ESE Council of Affiliated Societies (ECAS) ESE represents a community of over 22,000 European endocrinologists. We inform policy makers on health decisions at the highest level through advocacy efforts across Europe.
To learn more about the Society, visit our website at Home | ESE (ese-hormones.org). Follow us on X (formally Twitter) at @ESEndocrinology.
END
A team from the University of Cordoba has designed a model, based on fuzzy logic, that predicts the performance of online education students, dividing them into 4 categories and helping professors give more personalized assistance to each student, tailored to their situations
Distance education has democratized access to knowledge, overcoming problems of time and space. The flexibility and accessibility of this type of system has increased the number of people educated via online platforms. However, due to its large ...
Often introduced unintentionally by human activities, invasive alien species can outcompete and overwhelm native flora and fauna, driving species to the brink of extinction and disrupting the balance of ecosystems. Understanding why exactly they establish in new locations and how they got there in the first place is crucial if we are to mitigate their destructive effects. Unfortunately, there isn’t enough research on this, and the answers might not always be straightforward.
A research team from AgResearch and Better Border Biosecurity (B3) investigated the biological risk posed by ...
A huge step forward in the evolution of perovskite solar cells recorded by researchers at City University of Hong Kong (CityU) will have significant implications for renewable energy development.
The CityU innovation paves the way for commercialising perovskite solar cells, bringing us closer to an energy-efficient future powered by sustainable sources.
“The implications of this research are far-reaching, and its potential applications could revolutionise the solar energy industry,” said Professor Zhu Zonglong of the Department of Chemistry at CityU, who collaborated ...
They published their work on Oct. 18 in Energy Material Advances.
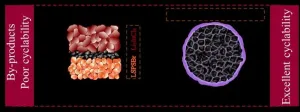
"Constructing a good interface between cathode and electrolyte is crucial for the development of all-solid-state battery," said Chuang Yu, a professor at the State Key Laboratory of Advanced Electromagnetic Technology at Huazhong University of Science and Technology. "Currently, strategies such as coating protect layer on cathode surface and isolating cathode/sulfide electrolyte by halide electrolyte layer are typical solutions to solve the problems at the interface between the cathode and the sulfide electrolytes, but it is not yet clear who is more suitable for sulfide-based all-solid-state ...
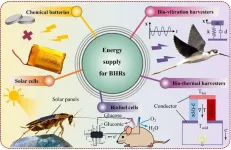
Bio-machine hybrid robots (BHRs) represent a new generation of micro-aerial vehicles that be controlled by building an interface between biological and artificial systems. In contrast to conventional bionic robots, they are free of complex mechanical structures, and due to the direct adoption of the animal body, they have superior moving characteristics and lower energy demand. Thus, the BHRs can be applied in many important scenarios, such as urban and wilderness rescue operations, environmental monitoring and hazardous area surveys.
To accomplish long mission endurance, the energy supply ...
Johns Hopkins researchers looking to develop a long-acting, injectable malaria preventive using atovaquone have shown in a new study that resistance may not be the challenge scientists thought it was, particularly when using atovaquone as a malaria preventive. Malaria parasites in infected patients being treated with atovaquone tend to develop a resistance to the drug. Because of this, atovaquone by itself is not used as a malaria treatment nor has not been seen as a strong candidate for use as a preventive.
The study, led by a team of researchers at the Johns Hopkins Malaria Research Institute and the Johns ...
New findings from researchers at UCLA Health suggest that measuring changes in how pupils react to light could help predict recovery from depression and personalize transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) treatment of major depressive disorder.
TMS is a safe, non-invasive therapy that uses magnetic fields to stimulate parts of the brain involved in mood regulation. While TMS is proven effective, not all patients respond equally well to the therapy. The ability to predict who will benefit most could allow doctors to better customize ...
Women with diets during middle age designed to lower blood pressure were about 17 percent less likely to report memory loss and other signs of cognitive decline decades later, a new study finds.
Led by researchers from NYU Grossman School of Medicine, the new findings suggest that a mid-life lifestyle modification – adoption of the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension, or DASH diet – may improve cognitive function later in life for women, who make up more than two-thirds of those diagnosed with Alzheimer’s disease, the most prevalent form of dementia.
The findings, published online today in ...
The winners of the Society’s prestigious annual Awards for 2024 have all contributed to improving knowledge and expertise in endocrinology and have helped drive innovation and progression across the field.
Each of these deserving winners will be presenting a plenary lecture at ESE’s annual Congress, the European Congress of Endocrinology (ECE) 2024, which will be held in Stockholm, Sweden from 11-14 May 2024.
The 2024 Geoffrey Harris Award is being presented to Jens C. Brüning (Germany). This Award recognises outstanding researchers in the field of neuroendocrinology. Jens Brüning is the Director of the Max Planck Institute for Metabolism Research ...
The more diverse species in your gut, the better it is for your health. Now an international team led by the Hudson Institute of Medical Research has found a way to determine which species are important and how they interact to create a healthy microbiome.
Understanding these relationships opens the door to a new world of medical opportunities for conditions from Inflammatory Bowel Disease to infections, autoimmune diseases and cancers.
Associate Professor Samuel Forster and his team at Hudson Institute of Medical Research, working with collaborators from the Institute for Systems Biology in ...