Superdeep diamonds provide a window on supercontinent growth
Diamonds contain evidence of the mantle rocks that helped buoy and grow the ancient supercontinent Gondwana from below
2023-10-23
(Press-News.org) Washington, DC—Diamonds contain evidence of the mantle rocks that helped buoy and grow the ancient supercontinent Gondwana from below, according to new research from a team of scientists led by Suzette Timmerman—formerly of the University of Alberta and now at the University of Bern—and including Carnegie’s Steven Shirey, Michael Walter, and Andrew Steele. Their findings, published in Nature, demonstrate that superdeep diamonds can provide a window through space and time into the supercontinent growth and formation process.
For billions of years, Earth’s landmasses have been ripped apart and smashed back together by plate tectonics, periodically forming giant supercontinents. This formation process results from large-scale convection of the planet’s mantle. But the records of these events are poorly preserved, because the oceanic crust is young and continually sinks beneath the planet’s surface by a process called subduction, while the continental crust only provides a limited view of Earth’s deep workings.
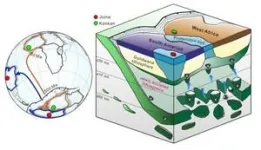
Surprisingly, the research team was able to show that superdeep diamonds that formed between 300 and 700 kilometers below Earth’s surface can reveal how material was added to the base of a once-mighty supercontinent.
“These diamonds allow us to see how deep plate tectonic processes relate to the supercontinent cycle,” Shirey said.
The supercontinent Gondwana is thought to have formed between 800 and 550 million years ago in Neoproterozoic times. Starting over the present-day location of the South Pole, it incorporated the landmasses that make up present day South America, Africa, the Middle East, India, and Australia.
“By revealing the geological processes that contributed to Gondwana’s growth, scientists can better understand the forces that shaped Earth’s history and phenomenon of continental stability, which is—of course—fundamental to the eventual success of life on our planet,” added Walter.
About 40 to 250 kilometers beneath the surface, geologic formations called mantle keels act as the foundation of the continental crust. The material that forms these keels thickened, stabilized, and cooled under the continental blocks to form strong, buoyant structures that can resist the relentless destructive forces of Earth’s tectonic activity.
Remnants of the mantle rocks that helped form the keel can be found in tiny silicate and sulfide inclusions hidden inside these superdeep diamonds. Typically flaws in normal gem diamonds, these inclusions are the best friends of a geoscientist. They were identified, isolated, studied crystallographically, and then radiometrically dated to determine their geologic ages.
This work was carried out by researchers at the University of Alberta and the Carnegie Institution for Science, as well as by other teams of diamond specialists at the Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam, University of Bristol, and the University of Padua. It required many steps, including shipping the diamonds around the world several times, and deployed some of the most precise mass spectrometers and X-ray diffractometers available.
“The study of such rare samples with a variety of measurement techniques required major teamwork. But even more remarkable is how careful analyses of such minute amounts of material can shed light on the evolution of Earth’s largest continental landmasses,” Timmerman explained.
“The age of these inclusions provides a record of when buoyant mantle was added to Gondwana from below, thereby scaffolding, underpinning, and growing the supercontinent” added Shirey.
Then, about 120 million years ago, the supercontinent once buoyed by the rocks that housed these diamonds started to break up and, eventually, 30 million years later—around 90 million years ago—the diamonds—and the inclusions trapped inside them—were brought to the Earth’s surface in violent volcanic eruptions of diamond-bearing kimberlite magma.
Now, by combining their lab analysis with existing models of tectonic movement and continent migration, the researchers can use these remarkably well-traveled diamonds to understand how material welds continental fragments together from below, stabilizing such a super-sized continental landmass.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-10-23
The American Cancer Society has awarded the University of Cincinnati Cancer Center an Institutional Research Grant.
Cancer Center member David Plas, PhD, is primary investigator for the grant, with members Maria Czyzyk-Krzeska, MD, PhD, and Kathryn Wikenheiser-Brokamp, MD, PhD, serving as co-principal investigators.
The American Cancer Society awards Institutional Research Grants to academic and nonprofit organizations that have a track record of outstanding cancer research and a pool of experienced researchers who can mentor junior faculty. The purpose is to support early-stage ...
2023-10-23
Washington, DC— As climate change warms the Earth, higher-latitude regions will be at greater risk for toxins produced by algal blooms, according to new research led by Carnegie’s Anna Michalak, Julian Merder, and Gang Zhao. Their findings, published in Nature Water, identify water temperatures of 20 to 25 degrees Celsius (68 to 77 degrees Fahrenheit) as being at the greatest risk for developing dangerous levels of a common algae-produced toxin called microcystin.
Harmful algal blooms result when bodies of water get overloaded with nitrogen and phosphorus ...
2023-10-23
The Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine (ABM) has released new literature-based recommendations related to breastfeeding in the setting of substance use and substance use disorder (SUD) treatments. The new clinical protocol is published in the peer-reviewed journal Breastfeeding Medicine. Click here to read the article now.
Miriam Harris, MD and Elisha Wachman, MD, from Boston Medical Center, and coauthors, provide breastfeeding recommendations in the setting of non-prescribed opioid, stimulant, sedative-hypnotic, alcohol, nicotine, and cannabis use, and SUD treatments. They also offer guidance on the use of toxicology testing in breastfeeding ...
2023-10-23
A new study leverages the NASA Exoplanet Archive and planetary system simulations to make narrowband SETI searches more efficient.
October 23, 2023, Mountain View, CA -- In a new study published in the Astronomical Journal, researchers used the known population of exoplanets and extrapolated to the much larger, unknown population of exoplanets to set better thresholds for planetary effects on signals from ETIs (extraterrestrial intelligences). The prior recommendation for the threshold “drift rate” contribution, caused by a planet’s motion around its host star, was 200 nHz. In this work, lead ...
2023-10-23
Lisbon, Portugal – 23 October, 2023
The International Society of Microbiota (ISM) is proud to present the 14th International Conference on Skin Ageing & Challenges 2023. This monumental event will unfold at the Altis Grand Hotel in Lisbon, Portugal, and virtually, on November 9-10, 2023.
Skin ageing, a multifaceted issue combining both basic research, mechanistic, clinical aspects and health concerns, is gaining significant attention in the scientific community.
This year’s conference promises to be a beacon of innovation, ...
2023-10-23
Certain gut-dwelling fungi flourish in severe cases of COVID-19, amplifying the excessive inflammation that drives this disease while also causing long-lasting changes in the immune system, according to a new study led by investigators at Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork-Presbyterian. This discovery identifies a group of patients who may benefit from specialized, but yet-to-be determined treatments.
Utilizing patient samples and preclinical models, the research team determined that the growth of fungi in the intestinal ...
2023-10-23
Before modern humans settled definitively in Europe, other human populations left Africa for Europe beginning approximately 60,000 years ago, albeit without settling for the long term. This was due to a major climatic crisis 40,000 years ago, combined with a super-eruption originating from the Phlegraean Fields volcanic area near current-day Naples, subsequently precipitating a decline in ancient European populations. To determine who the first modern humans to settle definitively in Europe were, a team led by CNRS scientists1 analysed the genome of two skull ...
2023-10-23
Alem & Narayanan Advancing Infectious Disease Capabilities Through Biomedical Research Laboratory Core Support
Farhang Alem, Interim Director of the Biomedical Research Laboratory, Institute for Biohealth Innovation, and Aarthi Narayanan, Professor, Biology, received funding for the project: "Advancing Infectious Disease Capabilities through BRL Core Support."
As part of this project, Alem and Narayanan will: 1) implement a comprehensive BSL-3 facilities preventative maintenance and upgrade plan to ensure continuity of operations, compliance with federal regulations, and a safe and secure facility; 2) enhance safety ...
2023-10-23
Ramseur To Receive Funding For APA Fellowship - APA Minority Fellowship Program (MFP)
Kevin Ramseur, II, a Mason doctoral student studying clinical psychology, is set to receive funding for: "APA Fellowship – APA Minority Fellowship Program (MFP)."
Ramseur will receive $27,144 from the American Psychological Association on a subaward from the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA). This funding will begin in Oct. 2023 and will end in late Sept. 2024.
###
About George Mason University
George Mason ...
2023-10-23
Doebel Innovating Developmental Science With An Online, Scalable Meta-Science Platform For Investigating Cognitive Development During Early Childhood
Sabine Doebel, Assistant Professor, Psychology, received $2,784 from the University of Texas at Dallas on a subaward from the National Science Foundation for: "Subaward Project GARDEN: Innovating Developmental Science with an Online, Scalable Meta-Science Platform for Investigating Cognitive Development During Early Childhood."
Regarding the importance of the project, Doebel said, "Project GARDEN will leverage online methodologies to gather data from a large, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Superdeep diamonds provide a window on supercontinent growth
Diamonds contain evidence of the mantle rocks that helped buoy and grow the ancient supercontinent Gondwana from below