(Press-News.org) PULLMAN, Wash. -- A new tool to rapidly grow cancer-killing white blood cells could advance the availability of immunotherapy, a promising therapy which harnesses the power of the body’s immune response to target cancer cells.
Washington State University researchers have developed a minifridge-sized bioreactor that is able to manufacture the cells, called T cells, at 95% of the maximum growth rate – about 30% faster than current technologies. The researchers report on their work in the journal Biotechnology Progress. They developed it using T cells from cattle, developed by co-author Bill Davis of WSU’s Veterinary College, and anticipate it will perform similarly on human cells.
In 2022, there were over 1,400 different types of therapies using T cells in development, with seven approved by the FDA for a variety of cancer treatments. Use of the therapy, called chimeric antigen receptor T cell (CAR-T), is limited, however, because of the cost and time needed to grow T cells. Each infusion treatment for a cancer patient requires up to 250 million cells.
“The manufacturing demand for this growing number of therapies is not being met, so there is a gap that needs to be filled in terms of biomanufacturing solutions,” said first author Kitana Kaiphanliam, a postdoctoral researcher in WSU’s Gene and Linda Voiland School of Chemical Engineering and Bioengineering. “At the end of the day, they need to be upscaled, so they can be used by more people.”
The bioreactor uses centrifugal force to act on the growing cells while they are suspended as a dense, cloud and continuously bathed by the inward flow of medium containing nutrients. The prototype comes out of four decades of research on designing a centrifugal bioreactor to rapidly densify and expand cells, led by Chemical Engineering Professor Bernie Van Wie, Kaiphanliam’s advisor and a co-author on the paper.
The most recent prototype is also self-contained within a sterile cabinet.
“It acts like a biosafety cabinet. It can be used in circumstances where clean manufacturing facilities are not available or easily accessible, so it can democratize these cell-based therapies,” said Kaiphanliam.
The researchers are working to improve the bioreactor. They hope to add multiple chambers and expect that they’ll eventually be able to produce enough cells in three days for three doses of a therapy. They also plan to start testing with human T cells and have begun communicating with cancer researchers on beta testing at Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center. Kaiphanliam and co-author Brenden Fraser-Hevlin have also started a company, Ananta Technologies Inc., with the idea of eventually producing and marketing the technology.
“I recognized the potential that this bioreactor could have on cell-based therapies and manufacturing for these therapies, and I didn’t want to see it stuck in an academic laboratory,” said Kaiphanliam. “I really hope having novel technologies to help with manufacturing reduces that financial barrier for these life-saving therapies.”
The work was predominately funded by a National Science Foundation Early-Concept Grant for Exploratory Research (EAGER) award. Additional support came from the WSU Office of Commercialization’s Gap Fund, the Palouse Club Cougar Cage pitch competition and the Washington Research Foundation. To protect the associated intellectual property and further enhance the commercial value of this technology, the Office of Commercialization has filed a U.S. patent application that is pending.
END
Machine can quickly produce needed cells for cancer treatment
2023-10-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
ERC synergy grant: Multidisciplinary research bridges physics and biology at ISTA and in France
2023-10-26
The Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA) receives its second generous ERC Synergy Grant. ISTA Professor Gašper Tkačik is one of three awarded researchers to join forces on unraveling the secrets of gene regulation during mammalian development.
Three research groups from Austria and France team up to crack open the black box of early mammalian development. Now endowed with a prestigious Synergy Grant from the European Research Council (ERC), Gašper Tkačik (ISTA), Thomas Gregor (Institut Pasteur), ...
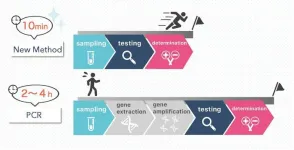
A new era for accurate, rapid COVID-19 testing
2023-10-26
Osaka, Japan – A rapid, accurate way of testing for COVID-19 infection would be a big step in overcoming the virus’ hold over our society. Now, in an article published in Lab on a Chip, Japanese researchers have developed a promising solution: a novel platform that couples nanopore technology with artificial intelligence.
What is a nanopore? A nanopore is a miniscule hole in a thin substrate, often a silicon wafer. A nanopore might range from several nanometers to several hundred nanometers in diameter — a scale small enough to work with SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes ...
75% of exclusive hardwood may be illegally harvested
2023-10-26
The tropical wood type ipê is popular for building exclusive wooden decks, and in North America and Europe, the demand for the material has increased sharply. Now, a study from Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, shows that more than three-quarters of all ipê from the top producing region in Brazil could have been harvested illegally. "The study reveals where in the chain the greatest risks lie. It can be a tool to counteract illegal logging," says Caroline S.S. Franca, PhD student at Chalmers.
Ipê is one of the world's hardest woods. It is therefore particularly suitable for building ...
Farmed wolffish could be on your plate in the future
2023-10-26
In the future, farmed wolffish could start appearing on fish counters. However, a new thesis from the University of Gothenburg shows that this fish, with its delicate, firm flesh, needs somewhat different farming conditions compared to salmon.
The salmon farms of today have created a steady supply of fish in our supermarkets. The nutritional content of salmon, its rapid growth and low cost, have made it a popular fish in many households. But only farming one species can create vulnerabilities in terms of food security. Today Sweden ...
MSU’s ‘Robin Hood’ approach for tracking biodiversity
2023-10-26
MSU has a satellite uplink/LTN TV studio and Comrex line for radio interviews upon request.
THIS STORY IS UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL OCT. 26 AT 12:01 A.M. EDT/05:01 A.M. U.K. TIME.
Images
Highlights:
Researchers at Michigan State University have developed a framework that can help scientists understand trends in biodiversity by using data from well-characterized species to provide insights on data-deficient species.
The framework is published in the Journal of Animal Ecology, which provides a how-to guide for researchers and practitioners to implement.
Roughly one in seven species are classified ...
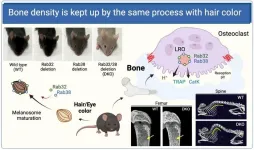
Bone density is kept up by the same process with hair color
2023-10-26
Osaka, Japan – Bone is maintained via delicate balance between formation and resorption, and its imbalance leads to bone related diseases like osteoporosis rheumatism and periodontitis. In studies published in scientific journals J Biol Chem and Cell Struct Funct, researchers led by Osaka University revealed proteins named Rab32 and Rab38 play pivotal roles in bone resorption in osteoclast, cell specialized in the process. These proteins are also crucial for pigmentation of hair and skins.
Bone ...
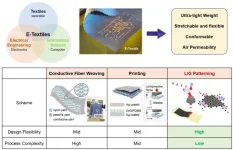
Multimodal graphene-based e-textiles for the realization of customized e-textiles have been developed for the first time in the world
2023-10-26
Multimodal* graphene-based electronic textiles (e-textiles) for the realization of customized e-textiles have been developed for the first time in the world.
* Multimodal means the process by which information is exchanged through various sensory interfaces such as visual sensation and auditory sensation.
The joint research team led by Principal Researcher Soongeun Kwon of the Department of Nano Manufacturing Technology of the Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials (President Sang-jin Park, hereinafter referred to as KIMM), an institute under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Science and ICT, and Professor Young-Jin Kim of the Department of Mechanical Engineering ...
Treating amphetamine use disorder with stimulants: an encouraging new approach
2023-10-26
A new study has found that it may be possible to use stimulants to treat stimulant use disorder. People with amphetamine-type stimulant use disorder who are treated with prescription psychostimulants such as methylphenidate and dextroamphetamine (commonly used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)) may lower both their craving and stimulant use, especially if such treatments are administered at high doses. This study was led by Dr. Jutras-Aswad, a researcher at the CHUM Research Centre and a professor of psychiatry and addictology at Université de ...
Does guideline-based treatment prevent racial disparities in cardiovascular outcomes?
2023-10-26
Philadelphia, October 26, 2023 – Cardiovascular disease remains the leading cause of death for women within most racial and ethnic groups in the United States. A new study in the Canadian Journal of Cardiology, published by Elsevier, characterizes the risk profile for black and nonblack women with obstructive coronary artery disease (CAD) enrolled in the Women’s Ischemia Syndrome Evaluation (WISE) cohort study. It concludes that racial and ethnic disparities in long-term cardiovascular outcomes were not observed among women ...
Genetic risks of autism and ADHD may be related to more screen time in children
2023-10-26
A team led by Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine in Japan has investigated screen time in autistic (ASD) and ADHD children. Screen time refers to the amount of time a person spends on a device with a screen, such as a smartphone, computer, television, or video game system. The researchers found that children with a genetic predisposition to ASD were more likely to use screens for longer periods. Meanwhile, children with ADHD gradually increased their screen time as they grew older, even if their initial screen use time was short. They published their results in the journal Psychiatry Research.
People ...