(Press-News.org) Experts in the Texas A&M University Department of Geography are teaming up with civil and chemical engineers and water resource, disaster recovery and public health researchers across the campus in a collaborative effort to better safeguard Texas Gulf Coast communities against climate-related emergencies, fueled by a three-year, $1.5 million grant from the National Academies Gulf Research Program (GRP).
The project, titled "Climate-LEAD: Climate Effects on Localized Environmental Health Disparities in Overburdened Texas Communities along Gulf Coast," is led by Texas A&M Assistant Professor of Geography Dr. Lei Zou and unites a diverse team of researchers from multiple departments within four Texas A&M colleges and schools — the College of Arts and Sciences, the College of Engineering, the School of Architecture and the School of Public Health. The interdisciplinary collaboration spans researchers at various career stages, including junior, mid-career and senior professionals
Zou, a faculty fellow in the Hazard Reduction and Recovery Center (HRRC), serves as principal investigator for the grant, one of four recently awarded by the GRP to advance the understanding of climate change effects on local health disparities. Collectively, these projects will create a series of models to better understand how environmental hazards influence human health outcomes and how those hazards will be affected by climate change under varying scenarios and time frames.
“Most models and data information products that identify vulnerable areas overburdened by pollution and susceptible to increased climate hazards are typically built on national datasets with limitations in data quality, coverage and scale resolution,” said Daniel Burger, senior program manager of the GRP’s Gulf Health and Resilience Board. “These awarded projects offer an opportunity to develop more robust models that incorporate localized data that enable community stakeholders, planners and decision-makers to fully understand current and future health risks to make the best decisions for their communities.”
Adverse conditions such as extreme heat, sea-level rise, flooding and extreme weather events are occurring more frequently and simultaneously, often interacting with non-climatic risks that threaten human health and well-being, such as heat-related stress and air and water pollution. Communities overburdened by these non-climatic risks are likely to experience more intense health impacts from climate change as adverse conditions compound, resulting in greater health disparities when compared to communities less exposed to environmental hazards. These disparities are particularly relevant to flood-prone communities in proximity to oil, gas and petrochemical facilities such as those located along the U.S. Gulf Coast.
Zou notes that the central goal of Texas A&M’s research is to anticipate and address the health consequences of climate change-induced air pollution and water insecurity in at-risk Texas communities situated near petrochemical facilities along the Gulf Coast. Through the seamless integration of recently established databases, localized models, web-based geographic information systems (webGIS), strategic frameworks, and community engagement, the project strives to formulate practical strategies that empower stakeholders to strengthen their ability to withstand evolving environmental pressures and safeguard public health.
“This project will pave the way for the development of state-of-the-art fine-scaled and localized databases, predictive models and innovative tools to combat environmental hazards under climate change,” Zou added.
Zou is joined by project co-principal investigators Dr. Wendy Jepson and Dr. Heng Cai from the Department of Geography, Dr. Qingsheng Wang from the Artie McFerrin Department of Chemical Engineering, Dr. Shankar Chellam and Dr. Qi Ying from the Zachry Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Dr. Michelle Meyer and Dr. Siyu Yu from the Department of Landscape Architecture and Urban Planning and the HRRC, and Dr. Natalie Johnson and Dr. Itza Mendoza-Sanchez from the School of Public Health.
Founded in 2013, the Gulf Research Program is dedicated to enhancing offshore energy safety, environmental protection and stewardship, and human health and community resilience in the Gulf of Mexico and other U.S. coastal regions.
END
Interdisciplinary research team works to mitigate climate change effects in Texas Gulf Coast communities
2023-10-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
An updated look at prostate cancer disparities
2023-10-27
Cedars-Sinai Cancer investigators have found that Black men respond as well as white men to systemic therapies for advanced prostate cancer when access to quality healthcare is equal, regardless of socioeconomic status. Their study, published today in the peer-reviewed Journal of Clinical Oncology, counters previous research suggesting that Black men receiving these therapies—which include hormone therapy, chemotherapy and immunotherapy—fare worse than white men do.
“We believe this is the most comprehensive look at this issue to date, and our findings suggest that, under the right conditions, Black men with metastatic ...
New battery technology could lead to safer, high-energy electric vehicles
2023-10-27
University of Maryland researchers studying how lithium batteries fail have developed a new technology that could enable next-generation electric vehicles (EVs) and other devices that are less prone to battery fires while increasing energy storage.
The innovative method, presented in a paper published Wednesday in the journal Nature, suppresses the growth of lithium dendrites—damaging branch-like structures that develop inside so-called all-solid-state lithium batteries, preventing firms from broadly commercializing the promising technology. But this new design for a battery “interlayer,” led by Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering ...
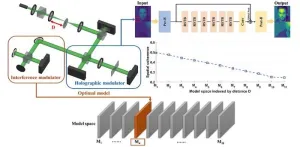
Clear holographic imaging in turbulent environments
2023-10-27
Holographic imaging has always been challenged by unpredictable distortions in dynamic environments. Traditional deep learning methods often struggle to adapt to diverse scenes due to their reliance on specific data conditions.
To tackle this problem, researchers at Zhejiang University delved into the intersection of optics and deep learning, uncovering the key role of physical priors in ensuring the alignment of data and pre-trained models. They explored the impact of spatial coherence and turbulence on holographic ...
$76,000 in grants awarded to entrepreneurs addressing health disparities in local communities
2023-10-27
DALLAS, October 27, 2023 — Approximately 50 million people in the United States are at higher risk for heart disease and/or stroke because they lack the most basic needs — healthy food, clean air and drinking water, quality education, employment, housing and access to health care. Historically, people of color -- including Black and Hispanic/Latino people, are at even higher risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) for these same reasons. Through the American Heart Association’s 2023 EmPOWERED to Serve Business Accelerator™, three local social entrepreneurs ...
Mechanics of breast cancer metastasis discovered, offering target for treatment
2023-10-27
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — The most lethal feature of any cancer is metastasis, the spread of cancer cells throughout the body. New research led by Penn State reveals for the first time the mechanics behind how breast cancer cells may invade healthy tissues. The discovery, showing that a motor protein called dynein powers the movement of cancer cells in soft tissue models, offers new clinical targets against metastasis and has the potential to fundamentally change how cancer is treated.
“This discovery marks a paradigm shift in many ways,” said Erdem Tabdanov, assistant professor of pharmacology at Penn State and a lead co-corresponding author on the study, recently published ...
Cold War spy satellite imagery reveals Ancient Roman forts
2023-10-27
Two-thousand years ago, forts were constructed by the Roman Empire across the northern Fertile Crescent, spanning from what is now western Syria to northwestern Iraq.
In the 1920s, 116 forts were documented in the region by Father Antoine Poidebard, who conducted one of the world's first aerial surveys using a WWI-era biplane. Poidebard reported that the forts were constructed from north to south to establish an eastern boundary of the Roman Empire.
A new Dartmouth study analyzing declassified Cold War satellite ...
Call for Papers: JMIR Neurotechnology
2023-10-27
JMIR Neurotechnology, published by JMIR Publications, welcomes submissions from researchers, clinicians, caregivers, and technologists that explore novel diagnostic and treatment tools for neurological disorders, particularly those leveraging the potential of neurotechnology.
The scope of the journal includes but is not limited to:
Neuroradiology
Advancements in neurosurgery
Innovative diagnostic tools and techniques
Cutting-edge neurotechnology for therapeutics
Data sharing and open science in neurotechnology
Code ...
fMRI study finds correlated shifts in brain connectivity associated with overthinking in adolescents
2023-10-27
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A new study from The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center and College of Medicine, University of Utah and University of Exeter (UK) substantiates previous groundbreaking research that rumination (overthinking) can be reduced through an intervention called Rumination-focused Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (RF-CBT). In addition, the use of fMRI technology allowed researchers to observe correlated shifts in the brain connectivity associated with overthinking.
Study findings are published online in the journal Biological Psychiatry Global Open Science.
“We know adolescent ...
Meltwater flowing beneath Antarctic glaciers may be accelerating their retreat
2023-10-27
A new Antarctic ice sheet modeling study from scientists at UC San Diego’s Scripps Institution of Oceanography suggests that meltwater flowing out to sea from beneath Antarctic glaciers is making them lose ice faster.
The model’s simulations suggest this effect is large enough to make a meaningful contribution to global sea-level rise under high greenhouse gas emissions scenarios.
The extra ice loss caused by this meltwater flowing out to sea from beneath Antarctic glaciers is not currently accounted for in the models generating major sea-level ...
Underwater robot finds new circulation pattern in Antarctic ice shelf
2023-10-27
ITHACA, N.Y. – More than merely cracks in the ice, crevasses play an important role in circulating seawater beneath Antarctic ice shelves, potentially influencing their stability, finds Cornell University-led research based on a first-of-its-kind exploration by an underwater robot.
The remotely operated Icefin robot’s climb up and down a crevasse in the base of the Ross Ice Shelf produced the first 3D measurements of ocean conditions near where it meets the coastline, a critical juncture known as the grounding zone.
The robotic survey revealed a new circulation pattern – a jet funneling water sideways through the crevasse – in addition to rising and sinking currents, ...