(Press-News.org) URBANA, Ill. – Over the past decades, Brazil has become the world’s leading soybean producer, as well as the leading consumer of pesticides. Despite concerns about potential public health consequences, little is known about the effects of pesticide exposure in the general population. A new study from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign in collaboration with the University of Denver and University of Wisconsin-Madison looks at how soy expansion and increased pesticide use in Brazil’s Cerrado and Amazon biomes correlate with increased childhood cancer mortality.
“The Brazilian Amazon region is undergoing a transition from low-input cattle production to intensified soy culture with high use of pesticides and herbicides. The expansion has happened really quickly, and it appears educational efforts and training for pesticide applicators didn’t match the growth in pesticide use. When not used properly, there are health implications,” said Marin Skidmore, assistant professor in the Department of Agricultural and Consumer Economics, part of the College of Agricultural, Consumer and Environmental Sciences (ACES) at U. of I. Skidmore is lead author on the paper, published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
“As this transition was happening, there were documented cases of pesticide poisoning of agricultural workers and evidence of chemicals in the blood and urine samples of non-agricultural workers in the surrounding communities,” Skidmore said. “This indicates that this rollout had happened in a potentially dangerous way that was leaving people exposed.”
The researchers investigated public health consequences of exposure to pesticides, focusing on children as the most vulnerable population. They specifically looked at deaths from acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), the most common childhood bloodborne cancer.
Their study drew from data on health outcomes, land use, surface water, and demographics in the Amazon and Cerrado biomes. The sample primarily consisted of areas that are classified as “rural” and have at least 25% of land cover in agriculture.
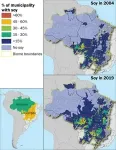
Soy production in the Cerrado area tripled from 2000 to 2019, and in the Amazon region there was a 20-fold increase, from 0.25 to 5 million hectares. Pesticide use in the study region increased between three- and ten-fold during the period as well. Brazilian soy farmers apply pesticides at a rate 2.3 times higher per hectare than the United States.
“Our results show a significant relationship between Brazil’s soy expansion and childhood deaths from ALL in the region,” Skidmore said. “Results suggest that about half of pediatric leukemia deaths over a ten-year period may be linked to agricultural intensification and exposure to pesticides.”
Skidmore and her colleagues show that a 10-percentage point increase in soy production is associated with an additional 0.40 deaths from ALL of children under 5 and an additional 0.21 deaths under 10 per 10,000 population. In total, they estimate that 123 children under 10 died from ALL associated with pesticide exposure between 2008 and 2019, out of a total of 226 reported deaths from ALL in the same period.
Skidmore emphasized that the study doesn’t provide a direct, causal link between pesticide exposure and cancer deaths, but the researchers take a number of steps to rule out other potential explanations. They found no correlations between ALL deaths and soy consumption, changes in socioeconomic status, or prevalence of crops with lower rates of pesticide applications.
The researchers also investigated contamination of water sources as a primary method of pesticide exposure.
“We looked for evidence of pesticide application upstream, in the watershed that flows into a region, and we found it is related to leukemia outcomes in the downstream region. This indicates that pesticide runoff into surface water is a likely method of exposure,” Skidmore explained.
“About 50% of the rural households in this region had a well or cistern at the time of the 2006 agricultural census, which left the other 50% reliant on surface water as a source of drinking water. If the surface water is contaminated, pesticides used in soy production upstream can reach children living downstream through waterways.”
“Our concern is that our results are only the tip of the iceberg. We measured one small, very precise outcome. Pesticide exposure may also result in non-fatal cases of leukemia, and there is a risk of impacts on the adult and teenage community,” she said.
ALL is a highly treatable disease, but it requires access to quality medical care. In the entire Amazon region, the researchers identified only two high-complexity pediatric oncology centers, although other facilities can also provide treatment. They found that the increase in observed pediatric ALL deaths following soy expansion was limited to municipalities that were more than 100 kilometers from a treatment center.
“Our results indicate that there are several ways to mitigate the relationship between pesticide exposure and ALL deaths,” Skidmore said. “This includes training and education for agricultural workers, smart regulations for pesticide use, and access to health care. We certainly are not advocating for a wholesale stop of using these inputs. They are important and valuable technologies, but they need to be handled safely and with some checks in place.”
Brazil is currently developing a certification program that requires pesticide applicators to undergo safety training and education. Such programs exist in many countries, including the United States, where pesticide applicators are required to be licensed and participate in an annual pesticide safety education and testing program.
“I think there is a strong awareness that safe use of pesticides is what's best both for agricultural productivity and for the communities. This soy expansion and boom are in many ways a huge win for Brazil's economy,” Skidmore stated.
“We want to highlight that when changes happen fast, there are risks associated with that, and this is not isolated to Brazil. There is a lot of focus on agricultural intensification for global food security around the world. We need to find a balance where we get the productive benefits while mitigating any potential risks. When there is rapid rollout of these technologies in a new region, often an underdeveloped or poor region, how do we ensure there are guardrails in place to prevent another case like this?”
END
Soy expansion in Brazil linked to increase in childhood leukemia deaths
2023-10-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Amazon deforestation linked to long distance climate warming
2023-10-30
Deforestation in the Amazon causes land surfaces up to 100 kilometres away to get warmer, according to a new study.
The research, by a team of British and Brazilian scientists, led by Dr Edward Butt at the University of Leeds, suggests that tropical forests play a critical role in cooling the land surface - and that effect can play out over considerable distances.
It is known that when tropical forests are cleared, the climate in the immediate vicinity gets warmer.
In this latest study, the researchers wanted to know if deforestation in the Amazon was resulting in climate warming further afield, and the study examined the impact of forest loss on sites up to ...
NYU Abu Dhabi researchers reveal how common desert shrub efficiently harvests water from the air
2023-10-30
Abu Dhabi, UAE, October 2023: A team of scientists, led by Post-Doctoral Associate Marieh Al-Handawi and Professor of Chemistry Panče Naumov from NYU Abu Dhabi’s Smart Materials Lab and NYU Abu Dhabi Institute’s Center for Smart Engineering Materials (CSEM) has revealed the mechanism a desert plant native to the United Arab Emirates uses to capture moisture from the desert air in order to survive. The identification of this unique mechanism, in which the plant excretes salts to extract and condense water onto the surface of its leaves, has the potential to inspire ...
Royal Canadian Institute for Science recognizes the unsung heroes of science communication
2023-10-30
The Royal Canadian Institute for Science (RCIScience) awards the 2023 Sandford Fleming Medal for Excellence in Science Communication to independent science writer Terry Collins and the William Edmond Logan Award to the team behind CBC Radio's national weekly science program, Quirks & Quarks.
A knowledge translator for over 27 years, Terry Collins' reporting has been picked up by journalists in Canada and worldwide, awakening public interest in and deepening understanding of diverse sciences, fostering political will and mobilizing resources for change.
Nominator Dr. Peter A. Singer, former Special Advisor to the Director-General of the World Health Organization, ...
Institute for Systems Biology and NED Biosystems announce collaboration to show how cancer’s onset may be reversed
2023-10-30
SEATTLE – Leroy Hood, MD, PhD, co-founder of Seattle’s Institute for Systems Biology (ISB) and a pioneer in systems biology, and Rebecca Lambert, founder and CEO of NED Biosystems, Inc. (NED), a public benefit corporation that is developing the first oral “systems treatment” for cancer, have entered into a memorandum of understanding to collaborate on a clinical trial to show how cancer’s onset may be reversed.
NED’s cancer treatment, NED-170, takes a systems approach that combines repurposed, oral agents that are well documented in humans to affect critical cancer disease-driver processes at doses that lack customary toxicity and side effects.
“A ...
Women with physical disabilities are less likely to be screened for cervical cancer than women without disabilities
2023-10-30
Around 11,500 new cases of cervical cancer are diagnosed each year in the United States, according to the Centers for Disease Control (CDC). The CDC tracks cervical cancer rates by age, race, and ethnicity, but not by disability type. A 2022 study found that women with disabilities may encounter multiple social and economic barriers to accessing reproductive health care, and a lack of timely access to cervical cancer screening may lead to delayed diagnosis and treatment for cervical cancer.
According to research by Mason PhD in Public Health ...
Department of Energy announces $11.4 million for research on quantum information science for fusion energy sciences
2023-10-30
WASHINGTON, D.C. - Today, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) announced $11.4 million for six projects in quantum information science (QIS) with relevance to fusion and plasma science.
The Fusion Energy Sciences (FES) program supports fundamental research to expand the understanding of matter at very high temperatures and densities and to build the scientific foundation needed to develop a fusion energy source. The QIS portfolio within FES supports research opportunities outlined in the 2018 Fusion Energy Sciences Roundtable on Quantum Information Science report. It includes science and technology thrusts where QIS might have a transformative impact on FES ...
RIT scientists receive grant to expand work on a sign language lexicon for chemistry
2023-10-30
A team of scientists at Rochester Institute of Technology will expand its work after receiving a large grant from the National Science Foundation to make chemistry more accessible for students who rely on American Sign Language interpreters in class.
Christina Goudreau Collison, professor in the School of Chemistry and Materials Science; Jennifer Swartzenberg, senior lecturer in the National Technical Institute for the Deaf’s Department of Science and Mathematics; Lea Michel, professor in the School of Chemistry and Materials Science; and Pepsi Holmquist, visiting assistant professor in NTID’s Department of Science and Mathematics, have been awarded nearly $380,000 ...
Canine cuddles can comfort equally across all genders
2023-10-30
While there are a number of studies demonstrating that dog therapy programs can improve a person’s social and emotional wellbeing, many typically have a disproportionate number of female participants.
Recent research led by Dr. John-Tyler Binfet, an Associate Professor in UBC Okanagan’s School of Education and Director of Building Academic Retention through K9s (BARK), evaluated if there are gender differences in wellbeing by setting up separate dog therapy sessions for those who identified as female, male and gender diverse participants.
Dr. Binfet has conducted numerous studies on the benefits of canine therapy, but to his knowledge, ...
Protein eIF4A emerges as a potential Achilles’ heel for triple-negative breast cancer
2023-10-30
Improving treatments for triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), an aggressive tumor with very poor prognosis and limited therapeutic targets, has been challenging. Responding to this need for better treatments, researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and collaborating institutions have investigated potential vulnerabilities in TNBC that could lead to novel therapies and improved outcomes for this devastating condition.
The team reports in The Journal of Clinical Investigation that in diverse TNBC animal models, targeting protein eIF4A with the ...
Novel Rett syndrome variant shines light on new screening strategies for therapies
2023-10-30
Rett syndrome is a rare devastating neurological disorder that primarily affects young girls and manifests as an impaired ability to walk and talk, along with characteristic ‘hand-wringing’ movements, seizures, and cognitive disability. This incurable condition results from mutations in the methyl-CpG binding protein 2 (MECP2) gene that impairs the role of the MeCP2 protein in regulating the activity of many genes in brain cells.
A new MECP2 gene variant (G118E) was recently characterized by a research team led by Dr. Huda Zoghbi, a distinguished service professor at Baylor College of Medicine and the founding director of the Jan and Dan Duncan Neurological ...