(Press-News.org) Highlights:
Gonorrhea is difficult to treat, and there is no approved vaccine.
AI can help researchers search through banks of potential proteins to use in a vaccine.
In a new study, researchers used AI to identify 26 potential new antigens.
A combination of 2 novel antigens elicited antibodies that killed Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacteria in lab experiments and reduced gonococcal colonization in mouse models.
The group has now partnered with a South African company to develop an experimental mRNA vaccine using the antigens.
Washington, D.C.—Gonorrhea, a sexually transmitted bacterial infection that affects more than 80 million people worldwide every year, has become resistant to almost all known antibiotics. That makes it notoriously difficult to treat, but left untreated, an infection could lead to serious or even fatal complications. It also increases a person’s risk of contracting HIV.
A new study suggests artificial intelligence (AI) may help identify a vaccine’s key ingredients. This week in mBio, an international collaboration between academic and commercial researchers reported the identification of 2 promising antigens as candidates for a gonorrhea vaccine. The researchers used an AI model called Efficacy Discriminative Educated Network, or EDEN, to identify the protective proteins.
They also used EDEN to generate scores that accurately predicted how well antigen combinations would reduce pathogenic bacterial populations of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, the microbe that causes gonorrhea.
“To the best of our knowledge, this correlation has not been shown before,” said infectious disease researcher Sanjay Ram, M.D., at the University of Massachusetts Chan Medical School, in Worcester. Ram, Sunita Gulati, D.Sc, and their colleagues tested the antigens identified by EDEN in lab and animal models.
The work began in 2008 when Andreas Holm Mattsson, in Denmark, mined published literature to assemble a large dataset of protective surface proteins from a variety of pathogenic bacteria. That same year, Mattsson founded Evaxion, an AI immunology startup, and wanted to design an AI-based system that could identify vaccine targets in infectious microbes.
For the new study, Mattsson and his colleagues applied this new AI model to the proteomes of 10 clinically relevant strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to predict a set of bacterial proteins that, in a vaccine, could help teach the body’s immune system to recognize and fend off the bacteria.
“EDEN uses a feature like face recognition to understand the difference among proteins,” said Mattsson.
Once they’d compiled the list, they sent it to Ram and Gulati in Massachusetts. “We tested and validated all of their candidates in mouse models,” Ram said. The group first tested combinations of 2 or 3 antigens in mice. That analysis identified 2 proteins involved in cell division as promising candidates, neither of which were previously known to be exposed on the surface of the cell.
In lab experiments, blood samples taken from mice immunized with these 2 proteins killed bacteria from multiple strains of gonorrhea in vitro. Those findings lined up with EDEN’s predictions. In additional experiments, immunized mice were infected with N. gonorrhoeae, and the vaccine decreased the bacterial burden.
“That really was a surprise,” Ram said. “Nobody would have predicted that these 2 proteins that were believed not to be surface exposed would work in vaccines, and other researchers reacted with skepticism.”
Given the efficacy of the individual tests, the Evaxion team then combined the proteins into a single chimeric protein, which induced an immune response that similarly showed efficacy in lab and animal models.
Ram noted that the investigation also revealed a mechanism critical to clearance of N. gonorrhoeae infection by this vaccine candidate. Whether such mechanisms of bacterial clearance occur in humans remains to be studied.
The researchers are now using EDEN to look for vaccine candidate proteins in other pathogenic microbes, including several bacteria for which EDEN has predicted high efficacy in mouse models.
They’re also thinking about how to move beyond the promise of preclinical work and see if the same proteins are protective in the human body. They recently partnered with a South African biotechnology company to develop an experimental mRNA vaccine based on the antigens.
###
The American Society for Microbiology is one of the largest professional societies dedicated to the life sciences and is composed of 36,000 scientists and health practitioners. ASM's mission is to promote and advance the microbial sciences.
ASM advances the microbial sciences through conferences, publications, certifications, educational opportunities and advocacy efforts. It enhances laboratory capacity around the globe through training and resources. It provides a network for scientists in academia, industry and clinical settings. Additionally, ASM promotes a deeper understanding of the microbial sciences to diverse audiences.
END
Researchers use AI to identify potential gonorrhea vaccine proteins
2023-10-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Jean-Laurent Casanova is recipient of 2023 Maria I. New International Prize for Biomedical Research
2023-10-31
New York, NY (October 30, 2023)—The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai will award its 2023 Maria I. New International Prize for Biomedical Research to Jean-Laurent Casanova, MD, PhD, for revolutionizing our understanding of human infectious diseases through the discovery of genetic and immunological determinants that underpin both rare and common infectious illnesses.
The prize honors medical pioneers in the tradition of Maria I. New, MD, a world-renowned researcher in pediatric genetic disorders with a special focus ...
NYU Tandon cuts a rug with new 3D video technology
2023-10-31
A groundbreaking research project spearheaded by NYU Tandon School of Engineering will bring cutting-edge immersive three-dimensional (3D) video to dance education, making learning the art form more available to a diverse range of students.
The project, supported by a new $1.2 million four-year grant from the National Science Foundation, aims to make Point-Cloud Video (PCV) technology suitable for streaming onto standard Internet-connected devices.
Developed over the past decade, PCV is a type of highly-detailed 3D video that allows viewers to “move” within an immersive video environment, observing objects and scenes from any angle or distance as if they ...
Using transcription factors to explore plant metabolites
2023-10-31
Plants produce a dizzying array of chemical compounds known as secondary metabolites, which help them flourish under fluctuating environmental conditions. Some of these metabolites defend against insect attack, while others help plants communicate, time life cycle events, or attract pollinators, among other functions. Humanity has long taken advantage of these bioactive natural products, using them as medicine, flavorings, dyes, perfumes, and even industrial materials. Production of secondary metabolites is typically controlled by transcription factors. Tsubasa Shoji and colleagues sought to identify unexplored secondary metabolites by manipulating these upstream regulators ...
Researchers observe wolves hunting and killing sea otters and harbor seals on Alaska’s Katmai coast
2023-10-31
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Firsthand observations of a wolf hunting and killing a harbor seal and a group of wolves hunting and consuming a sea otter on Alaska’s Katmai coast have led scientists to reconsider assumptions about wolf hunting behavior.
Wolves have previously been observed consuming sea otter carcasses, but how they obtain these and the frequency of scavenging versus hunting marine prey is largely unknown. Scientists at Oregon State University, the National Park Service and Alaska Department of Fish and Game are beginning to change that with a paper just published ...
Pilot awards to advance global brain health and dementia projects
2023-10-31
Today, the Alzheimer’s Association, Global Brain Health Institute (GBHI), and the UK-based Alzheimer’s Society announced the most recent awardees of the Pilot Awards for Global Brain Health Leaders, a competitive funding initiative dedicated to nurturing efforts and improving outcomes in the fields of brain health and dementia.
“The Alzheimer’s Association is proud to partner with GBHI and the Alzheimer’s Society to make these innovative grants,” said Heather M. Snyder, Ph.D., Alzheimer’s Association vice president of medical and ...
Anesthesia technology precisely controls unconsciousness in animal tests
2023-10-31
If anesthesiologists had a rigorous means to manage dosing, they could deliver less medicine, maintaining exactly the right depth of unconsciousness while reducing postoperative cognitive side effects in vulnerable groups like the elderly. But with myriad responsibilities for keeping anesthetized patients alive and stable, as well as maintaining their profoundly unconscious state, anesthesiologists don’t have the time without the technology.
To solve the problem, researchers at The Picower Institute for Learning and Memory ...
The limits of deplatforming
2023-10-31
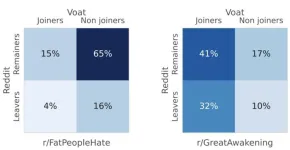
Social media can incubate communities that are so resilient that even banning them from the platform cannot destroy them. Michele Starnini and colleagues studied two online communities on the social media site Reddit: the far-right conspiracy theory subreddit GreatAwakening, which was banned in 2018, and the hate-speech subreddit FatPeopleHate, banned in 2015. Both communities decided amongst themselves to move to Voat, an unmoderated Reddit clone designed to serve those banned by Reddit. The authors estimate that less than 20% of FatPeopleHate users migrated to Voat, while more than 70% of GreatAwakening users migrated to the new platform. This result suggests that members ...
CCDC expands global talent pool with Ghana-based Orgmento
2023-10-31
· CCDC extends its partnership with Orgmento, a Ghanaian software engineering and data sciences company.
· The partnership, which started in 2021, has been strengthened by the shared commitment to engineering excellence from both organizations, and has now been extended for a further 3 years.
· Software engineering teams from the CCDC and Orgmento will build software to advance structural science.
Cambridge, UK. 31 October 2023
The Cambridge Crystallographic ...
DNA organization influences the growth of deadly brain tumors in response to neuronal signals
2023-10-31
A pioneering study at Umeå University, Sweden, has unveiled that the 3D organization of DNA can influence the progression of the aggressive brain tumour known as glioblastoma. Having identified the factors that glioblastoma uses to respond to neurons by growing and spreading, this discovery paves the way for further research into new treatments for brain tumours.
"We have now identified the most important factors behind how the tumour responds to nerve cells, thus becoming more dangerous. These findings offer hope in our long-term battle against this difficult-to-treat ...
Humans are disrupting natural ‘salt cycle’ on a global scale, new study shows
2023-10-31
The planet’s demand for salt comes at a cost to the environment and human health, according to a new scientific review led by University of Maryland Geology Professor Sujay Kaushal. Published in the journal Nature Reviews Earth & Environment, the paper revealed that human activities are making Earth’s air, soil and freshwater saltier, which could pose an “existential threat” if current trends continue.
Geologic and hydrologic processes bring salts to Earth’s surface over time, but human activities such as mining and land development are rapidly accelerating the natural “salt ...