(Press-News.org) Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) continue to rank as the top killer in the modern world. This deadly disorder often starts with the buildup of lipid deposits or plaques within the blood vessel, silently setting the stage for atherosclerosis. Rupture of these atherosclerotic plaques, however, could clot blood vessels and lead to life-threatening conditions including heart attack or stroke.
Dyslipidemia, meaning having too much “bad” or atherogenic lipids in the blood, represents the most common cause of CVDs and is present in about 50% of the adult population. Accordingly, doctors often prescribe lipid-lowering medications (e.g. statins and proprotein convertase subtilisin/Kexin type 9 (PCSK9) inhibitors) for treating CVDs. These “block-buster” drugs, however, could only stabilize but were not able to reverse or eliminate the existing atherosclerotic plaques.
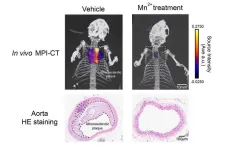
In two complementary studies, one published on Nature Cell Biology and the other on Life Metabolism, researchers have found a novel approach to achieve intensive lipid lowering, which enabled the reversal of atherosclerotic plaques in murine disease models. This potential therapy employs a previously unknown function of the essential element manganese. Increasing doses of extra manganese, even when conveniently provided to mice via diets, dramatically reduce blood lipids and clear out the atherosclerotic plaques that have already built up in the blood vessels (Figure 1).
Dr. Xiao Wang, one of the lead authors of the work, explains: “Manganese is considered as the least understood essential element, mainly playing supporting roles in enzymatic reactions. Yet, we’ve uncovered an active, signaling role of the manganese ion in controlling lipid delivery into the blood.”
Bulk lipids, including cholesterol and triglycerides, are transported into the blood via specialized carriers named lipoproteins. These lipid carriers are much larger and more complex compared to most of the other secretory factors in the blood. The researchers discovered that these lipid-ferrying lipoproteins rely on the biomolecular condensation of a common cellular machinery, known as the coat protein complex II (COPII) complex. Moreover, COPII condensation needs to be finely balanced at the right level to support bulk lipid delivery.
After dissecting a series of highly unexpected observations, the researchers further discovered that manganese ions could directly bind COPII and enhance its condensation. This in turn alters the fine balance in COPII regulation, resulting in a unique, bell-shaped regulation on blood lipid levels. The novel mechanism ultimately enabled the manganese-based therapy that could clear plaques in mice bearing CVDs.
“We are truly fascinated by manganese’s potential in both preventing and treating the biggest disease”, says Dr. Xiao-Wei Chen, the senior author of the work, “and we are enthusiastic to learn more about its efficacy and safety, as well as developing more efficient ways to harness this novel signaling function of manganese.”
END
A “manganese bullet” targeting the top killer?
2023-11-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New NUS study provides insights into early breast cancer development in individuals with BRCA2 mutations
2023-11-02
A pioneering study led by Professor Ashok Venkitaraman from the Cancer Science Institute of Singapore (CSI Singapore) at the National University of Singapore and Dr Mona Shehata from the University of Cambridge (UK) has uncovered vital insights into the distinct effects of BRCA2 mutations on breast tissue cells, shedding light on early breast cancer development in people with BRCA2 mutations. The research was published in the prestigious journal Nature Communications on 25 August 2023.
Breast cancer is a serious concern for individuals with BRCA2 mutations, ...
Clinical intervention directed at social risks does not increase experiences of discrimination
2023-11-02
A growing recognition of the health impact of social risks – such as food insecurity and homelessness – has prompted researchers, healthcare providers and policymakers to consider ways to address these risk factors as part of holistic clinical care. However, some healthcare providers worry the same interventions designed to help patients and families with social risks might also make them feel singled out or like they are otherwise stigmatized.
Now, new results of a rigorous study from the University of Chicago Medicine published October 2023 in JAMA Pediatrics suggest well-designed interventions that address social risks can be provided ...
$13M NIH grant funds research aimed at revitalizing immune systems of older adults
2023-11-02
University of Arizona Health Sciences researchers received a $13.1 million grant from the National Institute on Aging to continue studies aimed at rejuvenating the immune system of older people in order to improve health throughout the lifespan.
Older adults are disproportionally affected by infection, cancer and certain types of autoimmune disease. This is influenced by the fact that as a person ages, their body produces fewer T cells and gets less proficient at maintaining them. T cells are a type of white blood cell essential to the immune ...
Study provides preliminary evidence in favor of a new type 1 diabetes treatment
2023-11-02
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease that causes the body's immune system to attack and destroy insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. Traditional management of type 1 diabetes has primarily involved replacing the missing insulin with injections which, though effective, can be expensive and burdensome. A new study led by researchers at the University of Chicago Medicine and Indiana University suggests that an existing drug could be repurposed to treat type 1 diabetes, potentially reducing dependence on insulin as the sole treatment.
The research centers on a medication known as α-difluoromethylornithine (DFMO), which inhibits an enzyme that plays a key role in cellular ...
New branch of oncology, cancer neuroscience, offers hope for hard-to-treat brain tumors
2023-11-02
Cancer cells hijack normal biological processes, allowing them to multiply. For example, tumors spur construction of new blood vessels, building themselves “highways” to supply nutrients.
Researchers have known about cancer’s blood vessel infiltration for decades, but it was only in the past few years that Stanford Medicine scientists and their colleagues discovered that tumors don’t just tap the body’s highway system; they can also infiltrate and exploit its “telecommunications.”
To ...
Less physical activity in adolescence likely rooted in biology
2023-11-02
AURORA, Colo. (Nov. 1, 2023) – The slowdown of physical activity during adolescence is not likely caused by lifestyle and environment but by energy demands placed on the body as it grows and sexually matures, according to a new study by researchers at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus.
The study, published today in the Proceedings of the Royal Society B, examined the lifestyles of the physically active Tsimane people, an indigenous population of forager-horticulturalists in lowland Bolivia, to see similarities and differences to adolescents living in post-industrialized nations.
“We wanted to look at the role of environment and the role of biology,” ...
Adult coral can handle more heat and keep growing thanks to heat-evolved symbionts
2023-11-02
Adult fragments of a coral species can better tolerate bleaching and recover faster when treated with tougher heat-evolved symbionts, new research from the Australian Institute of Marine Science (AIMS) and the University of Melbourne indicates.
The study also found that treatment with the heat-evolved symbionts did not compromise the coral’s ability to grow. This differs from previous studies on Great Barrier Reef corals which found that naturally heat tolerant symbionts could enhance heat resistance in adult corals, but at a cost to its growth.
Symbionts are the tiny cells of algae that live inside the coral tissue, providing corals with energy to grow. The survival ...
Stronger, stretchier, self-healing plastic
2023-11-02
An innovative plastic, stronger and stretchier than the current standard type and which can be healed with heat, remembers its shape and partially biodegradable, has been developed by researchers at the University of Tokyo. They created it by adding the molecule polyrotaxane to an epoxy resin vitrimer, a type of plastic. Named VPR, the material can hold its form and has strong internal chemical bonds at low temperatures. However, at temperatures above 150 degrees Celsius, those bonds recombine and the material can be reformed into different shapes. Applying heat and a solvent breaks VPR down into its raw components. Submerging it in seawater ...
Brain health in over 50s deteriorated more rapidly during the pandemic
2023-11-02
rain health in over 50s deteriorated more rapidly during the pandemic, even if they didn’t have COVID-19, according to major new research linking the pandemic to sustained cognitive decline.
Researchers looked at results from computerised brain function tests from more than 3,000 participants of the online PROTECT study, who were aged between 50 and 90 and based in the UK. The remote study, led by teams at the University of Exeter and the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience (IoPPN) at King’s ...
Low Emission Zones improve air quality, health, and people’s well-being – new policy brief
2023-11-02
The introduction of London's Low Emission Zone (LEZ) in 2008 and subsequent Ultra-Low Emission Zone (ULEZ) from 2019 has significantly improved air quality, benefiting Londoners’ physical and mental health, according to new analysis from the Department of Economics at the University of Bath.
A new Institute for Policy Research (IPR) policy brief, presenting research from health economists at the University, indicates that the introduction of the LEZ helped to reduce particulate matter (PM10) in Greater London by 13% between 2008-13, compared to pre-LEZ levels (2003-07).
The ULEZ has had an even more substantial impact, ...