(Press-News.org) Women who receive a false positive mammography result are more likely to develop breast cancer over the subsequent 20 years, report researchers from Karolinska Institutet in a study published in JAMA Oncology. The risk is highest for women aged between 60 and 75 and who have low breast density.
In global terms, breast cancer is the most common form of cancer among women, and screening is an important tool for catching women with a tumour at the earliest possible stage. In Sweden, all women between 40 and 74 are invited for screening at 18 to 24-month intervals.
At each screening visit, approximately three per cent of the women who undergo screening have a false positive result, which means that they are recalled for further examination without any cancer diagnosis. False-positive mammography results can cause psychological anxiety and influence screening attendance. Previous studies indicated that false-positive mammography results were associated with a short-term increased risk of breast cancer.
The new study shows that women with false-positive results are more likely to develop breast cancer than other women over the subsequent 20 years, facing, on average, a 60 per cent increased risk, suggesting the increased risk is long-term. In this study, the researchers identified 45,213 women with an initial false positive result and 452,130 women of the same age who were not recalled, all of whom attended the mammography screening program in Stockholm. Additionally, the researchers included 12,243 women with information on mammographic density from the Karolinska Mammography Project for Risk Prediction of Breast Cancer (KARMA) study.
“The elevated risk was higher in women in the 60–75 age-bracket than in the 40–49 age-bracket, and in women with low rather than high mammographic density,” says Xinhe Mao, postdoctoral researcher at the Department of Medical Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Karolinska Institutet in Sweden. “The risk was also highest in the four to six years following a false positive result.”
“It’s important to accentuate a long-term awareness of breast cancer in women who get false positive mammography results,” says Mao. “It might be beneficial to draw up personal monitoring programmes for these women with careful follow-ups over the years immediately following.”
The study formed part of Xinhe Mao’s doctoral thesis, and she will now continue her research with the aim to motivate more women to undergo regular mammography screening.
“Radiology and breast cancer screening are currently in a phase of rapid development, partly thanks to the use of AI,” says the study’s last author Professor Kamila Czene at the Department of Medical Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Karolinska Institutet. “Our published paper is part of the general efforts to achieve better screening results and increase the screening programme uptake.”
The study was financed by the Swedish Research Council, the Swedish Cancer Society, Region Stockholm, the Swedish Research Council for Health, Working Life and Welfare (FORTE) and the China Scholarship Council. The researchers report no conflicts of interest.
Publication: “Breast cancer incidence after a false-positive mammography result”. Xinhe Mao, Wei He, Keith Humphreys, Mikael Eriksson, Natalie Holowko, Haomin Yang, José Tapia, Per Hall, Kamila Czene, online 2 November 2023, doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2023.4519
END
Higher risk of breast cancer in women with false positive mammography result
2023-11-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
PTSD symptoms and cardiovascular and brain health in women
2023-11-02
About The Study: In this study of 274 midlife women, greater posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) symptoms were associated with higher carotid atherosclerosis and, among women who were APOEɛ4 carriers, greater brain small vessel disease and poorer cognitive performance. These findings point to the adverse implications of PTSD symptoms for cardiovascular and neurocognitive health among women in midlife, particularly for women who are APOEɛ4 carriers.
Authors: Rebecca C. Thurston, Ph.D., of the University of Pittsburgh, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed ...
Breast cancer incidence after a false-positive mammography result
2023-11-02
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that the risk of developing breast cancer after a false-positive mammography result differs by individual characteristics and follow-up. These findings can be used to develop individualized risk-based breast cancer screening after a false-positive result.
Authors: Xinhe Mao, M.Sc., of the Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2023.4519)
Editor’s Note: Please ...
Practicing mindfulness can help people make heart-healthy eating choices
2023-11-02
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Practicing mindfulness focused on healthy eating can be good for the heart, a new study shows, because it improves self-awareness and helps people stick to a heart-healthy diet.
When people who had elevated blood pressure participated in an eight-week mindfulness-based blood pressure reduction program for the study, they significantly improved their scores on measures of self-awareness and adherence to a heart-healthy diet compared to a control group. The results were published in JAMA Network Open.
“Participants ...
Infirmary Health partners with Ochsner Accountable Care Network to improve health outcomes for seniors across the Gulf Coast
2023-11-02
NEW ORLEANS, LA- Ochsner Health, the leading healthcare system in the Gulf South, and Infirmary Health, Alabama's largest private non-profit healthcare provider, are proud to announce a landmark partnership with Ochsner Accountable Care Network, a top-performing accountable care organization (ACO) in both clinical performance and healthcare savings for the Medicare population. The partnership aims to improve health outcomes for seniors across the Gulf Coast region.
Infirmary Health's hospitals and acute care facilities are recognized as national leaders in innovative and compassionate care for ...
Imaging advance poised to provide new insights into reproduction and infertility
2023-11-02
WASHINGTON — Researchers have developed a new optical coherence tomography (OCT) approach that can directly image coordination of tiny hair-like structures known as motile cilia in their natural environment. The ability to observe cilia dynamics in living organisms gives researchers a powerful new tool to investigate how these structures move cells and substances through the female reproductive system, as well as other functions of cilia throughout the body.
“Our new method has the potential to answer the longstanding question about cilia's ...
New study sheds light on the molecular mechanisms underlying lipid recycling within cells
2023-11-02
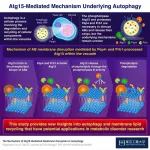
Recycling is just as essential in cells as in our more familiar macroscopic world. Cells continuously generate waste products and accumulate damaged components while performing regular functions. Various recycling mechanisms have evolved to ensure efficient use of these resources and help maintain homeostasis, with autophagy being one of the most well-preserved among countless animal, plant, and fungal lineages.
In the main form of autophagy, materials floating in the cell are transported to specialized organelles, such as lysosomes or vacuoles, within small capsule-like structures called ...
Researchers identify the mutations that drive resistance to PI3K inhibitors in breast cancer that can be overcome by next generation agents
2023-11-02
Mutations in the PIK3CA gene that lead to elevated production of the PI3Ka protein are among the most frequent alterations found in cancer, including in approximately 40% of hormone receptor–positive breast cancers.
Alpelisib, the first drug targeting PI3Ka, was approved for use in the United States four years ago, but cancers with mutated PIK3CA eventually develop resistance to the medication.
A team led by investigators at the Mass General Cancer Center, a member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, recently identified that resistance in some cases can be caused by secondary mutations in the PIK3CA gene itself. This leads ...
Scientists discussed the key questions of solar wind–moon interaction
2023-11-02
As the nearest celestial body to Earth, Moon’s space environment is distinctive to Earth’s mainly because of lack of a significant atmosphere/ionosphere and a global magnetic field. From a global perspective, solar wind can bombard its surface, and the solar wind materials cumulated in the soil record the evolution of the Solar System. Many small-scale remanent magnetic fields are scattered over the lunar surface and, just as planetary magnetic fields protect planets, they are believed to divert the incident solar wind and shield the local lunar surface beneath, thus producing ...
Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine launches Institute for Glial Sciences
2023-11-02
CLEVELAND—Case Western Reserve University has established an Institute for Glial Sciences to advance research of glial cells and their critical role in the health and diseases of the nervous systems, including multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer’s, pediatric leukodystrophies, Autism spectrum disorders, Parkinson’s disease and cancer.
Housed within the Case Western Reserve School of Medicine’s Department of Genetics and Genome Sciences, the new institute will be directed by Paul Tesar, the Dr. Donald and Ruth Weber Goodman Professor of Innovative ...
Researchers launch first study of a vaginal film that dissolves in 30 days to assess its acceptability as a potential HIV prevention method for women
2023-11-02
PITTSBURGH – November 2, 2023 – A vaginal film designed to slowly dissolve over the course of 30 days is being put to the test for the first time in a study launched this week that aims to determine its feasibility and acceptability as a potential HIV prevention method for women.
The study, which is being conducted in the United States and Africa by MATRIX, a United States Agency for International Development (USAID)-funded project focused on the early research and development of innovative HIV prevention products for women, will help inform the final design of a monthly film containing the antiretroviral (ARV) ...