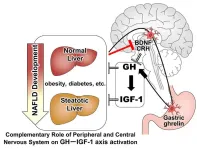
Niigata, Japan – The research group of Professor Kamimura in Niigata University have demonstrated the complementary role of peripheral and central nervous system on GH–IGF-1axis activation to prevent MASLD progression. IGF-1 ameliorates fatty infiltration in the liver. Its release is controlled by GH and GH activation is managed by peripheral or central nervous system. However, the role of this axis in MASLD developmental phase has not been well identified. Our study demonstrated that the GH–IGF-1 axis is significant in inhibiting the progression of MASLD. In addition to the peripheral autonomic nervous system activating gastric ghrelin to release GH, hypothalamic BDNF and CRH are keys in central nervous system for GH expression. “IGF-1 release by the nervous system is the key factor in maintaining the pathological homeostasis of MASLD, suggesting its therapeutic potential.” says Prof. Kamimura.
END
Involvement of brain peptide dynamics in the pathology of fatty liver disease
GH–IGF-1 axis and brain peptide in MASLD pathology
2023-11-03
(Press-News.org)
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How to measure improvement in Long COVID identified in an international consensus study
2023-11-03
Researchers have reached an agreement on how best to measure the severity and impact of Long COVID by identifying a “Core Outcome Measure Set” (COMS).
The research, published in Lancet Respiratory Medicine is co-led by the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience (IoPPN) at King’s College London and in collaboration with the World Health Organisation (WHO).
COMS are designed to help researchers and clinicians measure symptoms and impacts of disorders such as Long COVID in the same way, which optimises how data can be compared and summarised. Researchers say this will accelerate the understanding of, and the development ...
Human insulin less temperature-sensitive than previously thought
2023-11-03
A new Cochrane review has found that insulin can be kept at room temperature for months without losing potency, offering hope to people living with diabetes in regions with limited access to healthcare or stable powered refrigeration. This affects millions of people living in low- and middle-income countries, particularly in rural areas, as well as people whose lives have been disrupted by conflict or natural disasters.
Human insulin is a hormone produced by the body that helps turn food into energy and controls blood sugar levels. People with diabetes cannot make enough insulin and those with type 1 diabetes have to inject insulin several times a day, typically before every meal. ...
Study reveals untapped potential to increase eye donations needed for sight-restoring surgeries
2023-11-03
EMBARGOED: Not for Release Until 00:01 AM (UK Time) on Friday 3 November 2023
New research highlights the need for routine discussions about eye donation in end-of-life care clinical settings
Less than four per cent of eligible patients in end-of-life care settings were asked to consider eye donation
Patients had positive views about eye donation, but most did not know it could be an option for them
Staff need training and guidance to support discussing eye donation with patients
A new study has found there is significant scope to increase the number of eye donations from patients cared for in hospice and palliative care settings - donations which are desperately needed for ...
Penn Medicine researchers develop gene editing approaches for phenylketonuria treatment
2023-11-02
PHILADELPHIA— Phenylketonuria (PKU) is a rare newborn genetic disease that impacts between 1 in 10,000 to 1 in 20,000 people, depending on the individuals’ genetic ancestry. PKU causes an amino acid—called phenylalanine (Phe)—to build up in the bloodstream. Uncontrolled PKU can lead to intellectual disability, psychiatric issues, and seizures. While current therapies can partially improve outcomes, they require meticulous, lifelong compliance that is very difficult for most patients. ...
Mount Sinai researchers detail mechanism of a key protein implicated in age-related brain dysfunction
2023-11-02
Mount Sinai researchers have shed valuable light on the mechanism of a key protein that regulates the plasticity and function of the hippocampus, a key brain region involved in memory and learning, and that decreases with age in mice.
The team’s findings, published in Molecular Psychiatry, could pave the way for a better understanding of how the protein, known as tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 2 (TIMP2), could potentially be targeted in age-related disorders like Alzheimer’s disease to help restore ...
UH researcher tackles mysterious Z-RNA structure and its potential connection to diseases
2023-11-02
University of Houston Assistant Professor of Biology and Biochemistry Quentin Vicens has been awarded a $1.2 million grant from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences to unravel the mystery of Z-RNA – an enigmatic RNA structure within our cells that plays a critical role in immune response. This work is in collaboration with the laboratory of Beat Vögeli, associate professor at the University of Colorado and co-recipient of the award.
Vicens, Vögeli and their research teams are on a mission to understand how Z-RNA forms, how often it appears in our genetic material and what it means for ...
Different antibiotics’ effects on gut microbes may impact hypertensive organ damage
2023-11-02
Highlights
In a preclinical study, altering the intestinal microbiome with narrow-spectrum antibiotics affected organ damage associated with hypertension.
Results from the study will be presented at ASN Kidney Week 2023 November 1–November 5.
Philadelphia, PA (November 2, 2023) — New research in rodents indicates that altering gut microbes may affect the development of organ damage associated with hypertension. The findings will be presented at ASN Kidney Week 2023 November 1–November ...
Are sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors safe for patients with diabetes and cancer?
2023-11-02
Highlights
Investigators found that in patients with diabetes and cancer, sodium glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors were associated with a higher risk of diabetic ketoacidosis and fracture and a lower risk of acute kidney injury and urinary tract infection compared with glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists.
Results from the study will be presented at ASN Kidney Week 2023, November 1–November 5.
Philadelphia, PA (November 2, 2023) — Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) have heart- and kidney-related benefits for patients with and without diabetes ...
Wildfire air pollution may increase risks of hospitalization and death among patients on dialysis
2023-11-02
Highlights
Among individuals receiving in-center hemodialysis treatment in Washington, Oregon, and California, exposure to wildfire-related air pollution was associated with elevated risks of hospitalization and mortality.
Results from the study will be presented at ASN Kidney Week 2023 November 1–November 5.
Philadelphia, PA (November 2, 2023) — In analyses of data from western US states, increases in wildfire-related air pollution around dialysis clinics were linked to higher rates of hospitalizations and deaths among patients. The research will be presented at ASN Kidney Week 2023 ...
Simple automated tool prompts physicians to screen patients with diabetes for kidney disease
2023-11-02
Highlights
A tool that provides an automated prompt to physicians increased kidney disease screening in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Results from the study will be presented at ASN Kidney Week 2023 November 1–November 5.
Philadelphia, PA (November 2, 2023) — Investigators have implemented an automated health maintenance tool created by the National Kidney Foundation into electronic medical records to prompt primary care physicians to screen for chronic kidney disease (CKD) in adult patients ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
Microbial clues uncover how wild songbirds respond to stress
[Press-News.org] Involvement of brain peptide dynamics in the pathology of fatty liver diseaseGH–IGF-1 axis and brain peptide in MASLD pathology