(Press-News.org) INDIANAPOLIS -- Regenstrief Institute researchers are sharing the stage with other national aging research experts as they participate in the dissemination of scientific advances during the Gerontological Society of America (GSA) 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting on November 8-12 in Tampa, Florida.
The meeting provides aging researchers in a variety of disciplines a platform to share stimulating and high-level scholarship. This new and enriching knowledge will shape policy, practice and research for years to come.
At the meeting, Regenstrief’s Susan Hickman, PhD, will be inducted into the social research, policy and practice section of the GSA College of Fellows. See a related press release here.
The following is a list of Regenstrief conference presenters. All are research scientists with the Indiana University Center for Aging Research at Regenstrief Institute unless otherwise noted:
Symposium Presentations
Kathleen Unroe, M.D., MHA, M.S.: Utilizing Palliative Leaders in Facilities to Transform Care: The UPLIFT Clinical Trial Implementation.
Nicole R. Fowler, PhD, MHSA: Feasibility and Acceptability of Using Plasma Biomarkers for Diagnosing Alzheimer's Disease in Primary Care.
Poster Presentations
Susan Hickman, PhD; Edward Miech, EdD (Center for Health Services Research at Regenstrief Institute); Laramie Mack, B.S., CCRP, research coordinator; Wanzhu Tu, PhD; Kathleen Unroe, MD, MHA, M.S.: Conditions Associated with Successful Implementation of an Advance Care Planning Intervention in Nursing Homes.
Nicole R. Fowler, PhD, MHSA; Monica M. Williams-Farrelly, PhD: Racial Differences in the Relationship Between Loneliness and Cognition Among Older Adults in the Midwest.
Monica M. Williams-Farrelly, PhD; Nicole R. Fowler, PhD, MHSA: Loneliness and Quality of Life in Older Adult Primary Care Patients
Susan Hickman, PhD; Yvonne Yueh-Feng Lu, Regenstrief Affiliate Scientist: Daily Engagement in Meaningful Activity for home care patients with subjective cognitive decline and caregivers.
Papers
Alexander Floyd, Regenstrief Research Coordinator III; Kathleen Unroe, M.D., MHA, M.S.; Wanzhu Tu, PhD: Exploratory Factor Analysis of the Comfort Assessment in Dying With Dementia Scale.
Nicole R. Fowler, PhD, MHSA: Implementation of a Digital Cognitive Screening Program for Dementia in Primary Care.
About Regenstrief Institute
Founded in 1969 in Indianapolis, the Regenstrief Institute is a local, national and global leader dedicated to a world where better information empowers people to end disease and realize true health. A key research partner to Indiana University, Regenstrief and its research scientists are responsible for a growing number of major healthcare innovations and studies. Examples range from the development of global health information technology standards that enable the use and interoperability of electronic health records to improving patient-physician communications, to creating models of care that inform clinical practice and improve the lives of patients around the globe.
Sam Regenstrief, a nationally successful entrepreneur from Connersville, Indiana, founded the institute with the goal of making healthcare more efficient and accessible for everyone. His vision continues to guide the institute’s research mission.
END
Regenstrief research scientists participate in national conversation for advancement of aging research
2023-11-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
ISSCR and Cell Press renew publishing agreement for Stem Cell Reports
2023-11-06
The International Society for Stem Cell Research (ISSCR) and publisher Cell Press are extending their partnership to publish the ISSCR’s open access, peer-reviewed journal, Stem Cell Reports. For more than a decade, Stem Cell Reports has served as an important point of convergence for the stem cell research and regenerative medicine field.
“We are delighted to continue working with Cell Press to provide an outlet for our members and the community to publish impactful and high-quality science,” ...
New model adds human reactions to flood risk assessment
2023-11-06
Researchers at North Carolina State University have created a land change model that simulates interactions between urban growth, increased flooding and how humans adapt in response. The new model could offer a more realistic assessment of risk for urban planners, natural resource managers and other local government stakeholders.
“Traditional risk assessment typically involves overlaying inundation layers – areas that may flood – onto existing development or population distribution to identify areas and communities at risk,” says Georgina Sanchez, ...
Chicago community violence intervention program shown to reduce gun violence
2023-11-06
EVANSTON, Ill., --- New research shows large reductions in gun violence involvement for participants of a Chicago-based community violence intervention (CVI) program.
Researchers from Northwestern University evaluated outcomes for the Chicago CRED (Create Real Economic Destiny) program and found that those who completed the full program were more than 73% less likely to have an arrest for a violent crime in the two years following enrollment compared to individuals who did not participate.
Analyzing program participation, the researchers ...
New study sheds light on Adélie penguins' reliance on declining sea ice during molt
2023-11-06
EMBARGOED UNTIL: 6, NOVEMBER, 2023, 3 PM US EASTERN
A groundbreaking study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences underscores the pivotal role that seasonal Antarctic sea ice plays in the annual molting periods of Adélie penguins. Despite the relatively large amount of sea ice still available in the Ross Sea, researchers have discovered a potential bottleneck in the penguins’ annual cycle, which could be exacerbated as the climate continues to change.
Unlike most penguin species, the majority of Adélie penguins are thought to carry out their annual molt ...
450-million-year-old organism finds new life in Softbotics
2023-11-06
PITTSBURGH—Researchers in the Department of Mechanical Engineering at Carnegie Mellon University, in collaboration with paleontologists from Spain and Poland, used fossil evidence to engineer a soft robotic replica of pleurocystitid, a marine organism that existed nearly 450 million years ago and is believed to be one of the first echinoderms capable of movement using a muscular stem.
Published today in The Proceedings of the National Academy of Science (PNAS), the research seeks to broaden modern perspective of animal design and movement by introducing a new a field of study - Paleobionics - aimed at using Softbotics, robotics ...
City and highway lights threaten mountain lion habitats
2023-11-06
City lights shine all night amid the bustling traffic, businesses and neighborhoods of Southern California, one of the most populated areas that mountain lions call home.
A study from the University of California, Davis, found that mountain lions avoid places with artificial light, even during the day. The finding adds to the list of challenges faced by the big cats in the region, where scientists have warned they may face extinction within decades.
The new study, published in the journal Philosophical ...
Prostate cancer drug candidate developed at University of Tennessee Health Science Center goes to first clinical trial
2023-11-06
A drug candidate developed by researchers at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center for advanced metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer is now in its first clinical trial.
Ramesh Narayanan, PhD, deputy director of the Center for Cancer Research and the Muirhead Endowed Professor in the College of Medicine at UTHSC, and Duane Miller, PhD, Professor Emeritus in the Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences at UTHSC, have worked for more than a decade on therapies involving the hormone receptors that influence cancer progression. Their drug candidate, a molecule designed as a treatment for ...
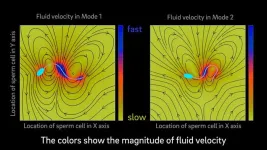
Model suggests that mammalian sperm cells have two modes of swimming
2023-11-06
A new mathematical model predicts that mammalian sperm cells have two distinct swimming modes. This prediction opens new questions about potential connections between sperm cells’ motor activity and their transitions to hyperactivation phases that may play an important role in fertilization. The finding is part of a larger effort to use math and fluid dynamics to describe how mammalian sperm move. The research is led by a team of engineers at the University of California San Diego. The new work is published in the journal Physical ...
Ochsner Health hospitals and partners earn national recognition from The Leapfrog Group
2023-11-06
NEW ORLEANS, La. – Several Ochsner Health hospitals and partners across the Gulf South have earned an ‘A’ Leapfrog Hospital Safety Grade for Fall 2023.The Leapfrog Group, a national nonprofit watchdog that sets standards for excellence in patient care, assigns a grade to general hospitals across the country based on more than 30 national performance measures reflecting errors, accidents, injuries and infections, as well as the systems hospitals have in place to prevent them.
The following Ochsner Health hospitals and partners received an ...
Neuromorphic computing will be great… if hardware can handle the workload
2023-11-06
Technology is edging closer and closer to the super-speed world of computing with artificial intelligence. But is the world equipped with the proper hardware to be able to handle the workload of new AI technological breakthroughs?
“The brain-inspired codes of the AI revolution are largely being run on conventional silicon computer architectures which were not designed for it,” explains Erica Carlson, 150th Anniversary Professor of Physics and Astronomy at Purdue University.
A joint effort between Physicists from Purdue University, University of California San Diego (USCD) and École ...