(Press-News.org) Global warming caused by climate change could exacerbate the burden of inpatient mortality from respiratory diseases during the warm season. This is the main conclusion of a study led by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported by the "la Caixa" Foundation, and published in The Lancet Regional Health - Europe. The results could help health facilities adapt to climate change.
The research team analysed the association between ambient temperature and in-hospital mortality from respiratory diseases in the provinces of Madrid and Barcelona between 2006 and 2019. In both locations, the number of hospital admissions (including those resulting in death) was higher in the cold season and lower in the warm season, with a peak in the month of January and a minimum in the month of August. In contrast to hospital admissions, which were higher during the cold season, the maximum incidence of inpatient mortality occurred during the summer and was strongly associated with high temperatures.
To calculate the association between ambient temperature and hospital mortality, the team used data on daily hospital admissions, weather (temperature and relative humidity) and air pollutants (O3, PM2,5, PM10 and NO2). Although it is well established that daily exposure to heat and cold is associated with a higher risk of hospital admission from a range of respiratory diseases such as pneumonia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma, no study had focused on the proportion of hospital admissions that result in death, and therefore, the more severe cases.
The link between high temperatures and mortality
In terms of attributable burden, summer temperatures accounted for 16% and 22.1% of overall fatal hospitalisations from respiratory diseases in Madrid and Barcelona, respectively. The heat effect was immediate, with most of the impact occurring within the first three days of exposure to high temperatures.
“This suggests that the increase in acute respiratory outcomes during heat is more related to the aggravation of chronic and infectious respiratory diseases than to the spread of new respiratory infections, which usually take several days to cause symptoms," says Hicham Achebak, first author of the study and researcher at Inserm and ISGlobal, who holds a Marie Skłodowska-Curie Postdoctoral Fellowship from the European Commission.
The results of the study showed an effect of heat on acute bronchitis and bronchiolitis, pneumonia and respiratory failure. Neither relative humidity nor air pollutants played a statistically significant role in the association of heat with mortality in patients admitted for respiratory disease. The research also showed that women were more vulnerable to heat than men. “This is most likely due to specific physiological differences in thermoregulation. Women have a higher temperature threshold above which sweating mechanisms are activated, and a lower sweat output than men, which results in less evaporative heat loss, and therefore greater susceptibility to the effects of heat," explains Joan Ballester, ISGlobal researcher and last author of the study.
Adapting to climate change in hospital centres
The study shows that high temperatures contributed to an increase in the risk of fatal hospital admissions, especially in Barcelona, whereas low temperatures were not associated with this variable. According to the research team, this might have to do with the fact that health services are increasingly prepared to deal with winter peaks in respiratory diseases.
In this sense, the findings have important implications for health adaptation policies to climate change, and for projections of the impact of climate change on human health. “Unless effective adaptation measures are taken in hospital facilities, climate warming could exacerbate the burden of inpatient mortality from respiratory diseases during the warm season," says Hicham Achebak.
Reference
Achebak H, Garcia-Aymerich J, Rey G, Chen Z, Méndez-Turrubiates RF, Ballester J. Ambient temperature and seasonal variation in inpatient mortality from respiratory diseases: a retrospective observational study. Lancet Regional Health - Europe. Oct 2023. 10.1016/j.lanepe.2023.100757
END
Risk of dying in hospital from respiratory causes is higher in the summer than in the winter
A study analyzes the association between ambient temperature and hospital mortality from respiratory diseases in the provinces of Madrid and Barcelona
2023-11-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Poetry can help people cope with loneliness or isolation
2023-11-07
Reading, writing and sharing poetry can help people cope with loneliness or isolation and reduce feelings of anxiety and depression, a new study shows.
Research by the University of Plymouth and Nottingham Trent University, funded by the Arts and Humanities Research Council, found that many people who took to sharing, discussing and writing poetry as a means to deal with the COVID-19 pandemic experienced “demonstrable positive impact on their wellbeing”.
The findings are based on a survey of 400 people which showed that poetry helped those experiencing common mental health symptoms as well as those suffering from grief.
It was carried out with registered users of the ...
French love letters confiscated by Britain finally read after 265 years
2023-11-07
UNDER STRICT EMBARGO UNTIL 19:01 (US ET) ON MONDAY 6TH NOVEMBER 2023 / 00:01AM (UK TIME) ON TUESDAY 7TH NOVEMBER 2023
Over 100 letters sent to French sailors by their fiancées, wives, parents and siblings – but never delivered – have been opened and studied for the first time since they were written in 1757-8.
The messages offer extremely rare and moving insights into the loves, lives and family quarrels of everyone from elderly peasants to wealthy officer’s wives.
The messages were seized by Britain’s Royal Navy during the Seven Years’ War, taken to the Admiralty in London ...
First in human trial of new drug raises hopes for patients with relapsed blood cancer
2023-11-06
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A new targeted drug, studied by researchers at The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center – Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital and Richard J. Solove Research Institute (OSUCCC – James), may offer a new treatment option for patients with blood cancers, including chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) whose disease has stopped responding to standard treatments.
In the first clinical trial of this drug in humans, nemtabrutinib ...
A cutting-edge approach to tackling pollution in Houston and beyond
2023-11-06
With its notoriously hot and humid climate and robust industrial environment, Houston is one of the most ozone-polluted cities in the United States. Now, a University of Houston research team is integrating the power of machine learning (ML) with innovative analysis techniques to pinpoint the city’s air pollution sources more accurately.
While the ozone layer in the stratosphere protects the Earth, and us, from the harmful rays of the sun, it’s also a major pollutant that can be harmful to human health when it’s closer to the ground. Long-term exposure to surface ozone can cause difficulty breathing, worsen asthma and increase the ...
The last turn of ‘Ezekiel’s Wheel’ honors a Yale-affiliated fossil hunter
2023-11-06
New Haven, Conn. — The mystery of Ezekiel’s Wheel — the extinct sea creature, not the Biblical vision — may have taken its final turn, thanks to Yale paleontologists.
In so doing, the researchers have also finally put a scientific name to the favorite fossil of a beloved amateur fossil hunter.
Samuel J. Ciurca Jr., who died in 2021, was a curatorial affiliate of the Yale Peabody Museum for many years. He collected tens of thousands of fossils, primarily from the Silurian rocks of upstate New York and southern Ontario, Canada.
He donated more than 11,000 ...
STEM Career Days boost high school students’ career aspirations in STEM fields, MU study finds
2023-11-06
COLUMBIA, Mo. – A new study at the University of Missouri — in partnership with Harvard-Smithsonian researchers — shows that when colleges host ‘STEM Career Days,’ the students who attend are far more likely to pursue a career in a STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering and Math) related field.
The findings not only highlight the benefits of college recruiters introducing high school students to STEM-related opportunities, but they can also help increase and diversify ...
Ochsner Health and Chevron partner for a third consecutive year to offer smoking cessation and education program
2023-11-06
NEW ORLEANS, La. – Chevron and Ochsner Health continue to offer their Lung Cancer Awareness, Education and Prevention Program for a third consecutive year thanks to a $50,000 donation from Chevron. The program will be offered in Jefferson Parish for the first time and continue to reach community members in St. Tammany, East Baton Rouge, West Baton Rouge, Ascension, St. Charles, Terrebonne, and Lafourche parishes.
Ochsner Health and Chevron formed a key partnership for the Lung Cancer Awareness, Education and Prevention Program to improve lung health and overall wellness. ...
Patients more likely to lose weight if physicians offer advice using optimistic tone
2023-11-06
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 6 November 2023
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
----------------------------
1. Patients more likely to lose weight if physicians offer advice using optimistic tone
Abstract: ...
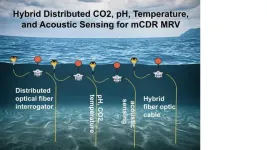
Deploying sensor nets to measure ocean CO2 and pH from the surface to the depths
2023-11-06
Researchers at the University of Pittsburgh Swanson School of Engineering, in collaboration with the National Energy Technology Laboratory, are among 11 projects in eight states selected to receive a combined $36 million to accelerate the development of marine carbon dioxide removal (mCDR) capture and storage technologies.
The funding from the U.S. Department of Energy Advanced Research Projects Agency-Energy (ARPA-E) is part of the ARPA-E Sensing Exports of Anthropogenic Carbon Through Ocean ...
Passion for vascular disease research yields $5 million in NIH funding for Yabing Chen
2023-11-06
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. – Yabing Chen, Ph.D., has been awarded two National Institutes of Health grants totaling more than $5 million to further her research into vascular diseases ranging from hardening of the arteries to dementia.
Vacuolar calcification, which leads to the hardening of blood vessels and increased vascular stiffness, is a hallmark of the aging process in the cardiovascular system. As early as the mid-1600s, physician Thomas Sydenham noted that “a man is as old as his arteries.” Chen expands that to include two different disease processes. “I like ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
[Press-News.org] Risk of dying in hospital from respiratory causes is higher in the summer than in the winterA study analyzes the association between ambient temperature and hospital mortality from respiratory diseases in the provinces of Madrid and Barcelona