(Press-News.org) Rochester Institute of Technology’s Lucia Carichino, assistant professor in the School of Mathematics and Statistics, has received a Launching Early-Career Academic Pathways in the Mathematical and Physical Sciences (LEAPS-MPS) award from the National Science Foundation (NSF).
The award funds Carichino’s research in computational modeling of the interaction between the eye and a contact lens. Specifically, Carichino is focusing on orthokeratology (ortho-k) lenses that help reduce myopic progression in kids and young adults. She aims to develop a mathematical model that will help predict how the eye will shape based on the use of a specific contact lens, and how the eye and lens will interact with each other.
For those individuals wearing ortho-k lenses, stiff contact lenses are worn that reshape the eye during the night. As the lenses are continuously worn, the eye reshapes itself to the shape of the lens. There are multiple shapes of lenses, so finding the correct lens for each person is an iterative process. Through trial and error, patients are evaluated using topographic mapping, and a reliable assessment is sometimes difficult, even for experienced eye doctors. Carichino’s work aims to reduce some of the trial and error and to help make the lenses more comfortable.
“The idea is that this computational tool could eventually aid the fitting process,” explained Carichino. “Given the shape of the eye and the shape of the lens, a theoretical prediction could be used ahead of time to see how the lens will fit on a particular eye.”
Carichino is joined in the project by Riley Supple, a RIT mathematical modeling Ph.D. student who is co-mentored by Kara Maki, associate professor in the School of Mathematics and Statistics.
The LEAPS-MPS award program has an emphasis to help launch the careers of pre-tenure faculty in mathematical and physical science fields, with an aim to broaden participation from groups historically excluded or underrepresented in the field. Carichino will accomplish the LEAPS-MPS goal of achieving excellence through diversity by collaborating with the diversity, equity, and inclusion initiatives for the College of Science and with the Undergraduates Research Training Initiative for Scientific Enhancement (U-RISE) of deaf and hard-of-hearing students program offered at the National Technical Institute for the Deaf.
This research project connects mathematics and science to find a solution that will help millions of people around the world who use contact lenses. Biomedical mathematics is a growing field as it helps simulate and predict experimental outcomes in both theoretical and practical research.
“Naturally, when people think of biology, they don’t necessarily think of all the mathematical components that are involved in it,” said Carichino.
The goal of the research is to help contact lens manufacturers and doctors anticipate the correct lens shape based on fit and performance, ultimately providing an easier, more comfortable result for the patient. The duration of the award is 24 months, with 32-48 awards distributed each year.
END
RIT’s Carichino receives National Science Foundation LEAPS-MPS award
The award funds Carichino’s research in computational modeling of the interaction between the eye and a contact lens
2023-11-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A closer look at rebel T cells
2023-11-10
LA JOLLA, CA—Scientists at La Jolla Institute for Immunology (LJI) are investigating a talented type of T cell.
Most T cells only work in the person who made them. Your T cells fight threats by responding to molecular fragments that belong to a pathogen—but only when these molecules are bound with markers that come from your own tissues. Your influenza-fighting T cells can't help your neighbor, and vice versa.
"However, we all have T cells that do not obey these rules," says LJI Professor and President Emeritus Mitchell Kronenberg, Ph.D. "One of these cell types is mucosal-associated invariant ...
Low-intensity fires reduce wildfire risk by 60%, according to study by Columbia and Stanford researchers
2023-11-10
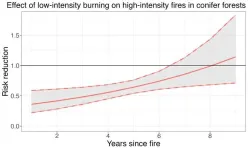
There is no longer any question of how to prevent high-intensity, often catastrophic, wildfires that have become increasingly frequent across the Western U.S., according to a new study by researchers at Stanford and Columbia universities. The analysis, published Nov. 10 in Science Advances, reveals that low-intensity burning, such as controlled or prescribed fires, managed wildfires, and tribal cultural burning, can dramatically reduce the risk of devastating fires for years at a time. The findings – some of the first to rigorously quantify the value of low-intensity fire – come while Congress is reassessing the U.S. Forest Service’s ...
Unlocking the secrets of spin with high-harmonic probes
2023-11-10
Deep within every piece of magnetic material, electrons dance to the invisible tune of quantum mechanics. Their spins, akin to tiny atomic tops, dictate the magnetic behavior of the material they inhabit. This microscopic ballet is the cornerstone of magnetic phenomena, and it's these spins that a team of JILA researchers—headed by JILA Fellows and University of Colorado Boulder professors Margaret Murnane and Henry Kapteyn—has learned to control with remarkable precision, potentially redefining the future of electronics and data storage.
In a new Science Advances ...
University of Minnesota Medical School researchers investigate cause of cardiomyopathy in coronary artery disease using cardiac MRI
2023-11-10
MINNEAPOLIS/ST. PAUL (11/10/2023) — Researchers from the University of Minnesota Medical School examining the cause of cardiomyopathy discovered one out of every six patients with coronary artery disease had non-ischemic or dual cardiomyopathy.
The findings of this study were published this week in the peer-reviewed journal Circulation, the flagship journal of the American Heart Association.
Cardiomyopathies are diseases of the heart muscle. Patients with coronary artery disease can have cardiomyopathy from heart muscle ...
Heart of Gold: Bath student team wins world Heart Hackathon competition
2023-11-10
Student engineers from the University of Bath are on top of the world after winning an international competition to design an artificial heart.
Team Bath Heart took top prize at the grand final of the first-ever Heart Hackathon, which was held in Texas at the end of October.
Six members of the team presented their device to global experts in artificial heart technologies, competing against teams from Australia, the United States, Sweden, New Zealand, Romania and Egypt.
The ‘total artificial heart’ ...
Cleveland Clinic research links sleep apnea to increased risk of atrial fibrillation
2023-11-10
New research from Cleveland Clinic has identified a link between sleep apnea and the development of atrial fibrillation, a common heart rhythm disorder.
Published in JAHA, the study of over 42,000 patients found that sleep-related hypoxia - or low oxygen levels during sleep - is associated with a higher risk of developing atrial fibrillation over time. The study found this risk persisted even after accounting for lung function, suggesting sleep-related hypoxia independently increases atrial fibrillation risk separate from any underlying lung disease.
Atrial fibrillation causes an irregular ...
New approach to pancreatic cancer treatment expands therapeutic possibilities, shows promise for increased survival
2023-11-10
Preclinical research published in the Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer points to a promising new treatment option for people with pancreatic cancer. Researchers from VCU Massey Comprehensive Cancer Center and the VCU Institute of Molecular Medicine (VIMM) suggest that when used in a form that can be delivered directly into the tumor cell, polyinosine–polycytidylic acid (pIC) suppresses tumor growth, induces cancer cell death and enhances survival in animal models with the most common form of pancreatic cancer.
Researchers also concluded that when used alone ...
UTHealth Houston partners with Mexican organizations for $5 million NIH grant to improve implementation of cancer control interventions in Mexico and Latin America
2023-11-10
A five-year, $5 million grant has been awarded by the National Cancer Institute (NCI) to the UTHealth Houston Institute for Implementation Science to support research and training in implementation science, with a focus on improving cancer control efforts in Mexico and Latin America.
The grant brings together researchers from UTHealth Houston, the Mexican National Institute of Public Health (INSP), the Mexican National Cancer Institute (INCan), and the University of California San Francisco (UCSF).
The grant will fund a new center, LISTOS for Cancer Control – Leveraging Implementation ...
Yucatán’s underwater caves host diverse microbial communities
2023-11-10
Cave divers collected 78 water samples throughout the complex web of underwater caves
Researchers found the cave system’s microbiome is distinct from the nearby sea
Microbial communities vary between cave systems forming distinct “neighborhoods”
EVANSTON, Ill. — With help from an experienced underwater cave-diving team, Northwestern University researchers have constructed the most complete map to date of the microbial communities living in the submerged labyrinths beneath Mexico’s Yucatán Peninsula.
Although previous researchers have collected water and microbial samples from the ...
A catalyst for change: New research aims to design atomically efficient and selective catalysts
2023-11-10
Most of us understand that electrical engineering and mechanical engineering play a key role in running our washing machines or our computers. But did you know that more than 80 percent of the products we use every day, such as fertilizers, cosmetics, fragrances, rubber and more, require some sort of chemical catalyst while being manufactured?
Catalysts are like turbochargers for chemical reactions. Until now, the process of designing a catalyst for chemical reactions has been mostly trial ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
[Press-News.org] RIT’s Carichino receives National Science Foundation LEAPS-MPS awardThe award funds Carichino’s research in computational modeling of the interaction between the eye and a contact lens