(Press-News.org) Researchers from ICIQ in Spain have designed micromotors that move around on their own to purify wastewater. The process creates ammonia, which can serve as a green energy source. Now, an AI method developed at the University of Gothenburg will be used to tune the motors to achieve the best possible results.
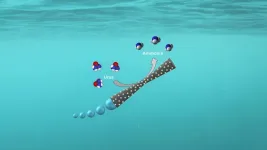
Micromotors have emerged as a promising tool for environmental remediation, largely due to their ability to autonomously navigate and perform specific tasks on a microscale. The micromotor is comprised of a tube made of silicon and manganese dioxide in which chemical reactions cause the release of bubbles from one end. These bubbles act as a motor that sets the tube in motion.
Researchers from the Institute of Chemical Research of Catalonia (ICIQ) have built a micromotor covered with the chemical compound laccase, which accelerates the conversion of urea found in polluted water into ammonia when it comes into contact with the motor.
Green energy source
“This is an interesting discovery. Today, water treatment plants have trouble breaking down all the urea, which results in eutrophication when the water is released. This is a serious problem in urban areas in particular,” says Rebeca Ferrer, a PhD student at Doctor Katherine Villa´s group at ICIQ.
Converting urea into ammonia offers other advantages as well. If you can extract the ammonia from the water, you also have a source of green energy as ammonia can be converted into hydrogen.
There is a great deal of development work to be done, with the bubbles produced by the micromotors posing a problem for researchers.
“We need to optimise the design so that the tubes can purify the water as efficiently as possible. To do this, we need to see how they move and how long they continue working, but this is difficult to see under a microscope because the bubbles obscure the view,” Ferrer explains.
Much development work remains
However, thanks to an AI method developed by researchers at the University of Gothenburg, it is possible to estimate the movements of the micromotors under a microscope. Machine learning enables several motors in the liquid to be monitored simultaneously.
“If we cannot monitor the micromotor, we cannot develop it. Our AI works well in a laboratory environment, which is where the development work is currently under way,” says Harshith Bachimanchi, a PhD student at the Department of Physics, University of Gothenburg.
The researchers have trouble saying how long it will be before urban water treatment plants can also become energy producers. Much development work remains, including on the AI method, which needs to be modified to work in large-scale trials.
“Our goal is to tune the motors to perfection,” Bachimanchi ends.
END
New water treatment method can generate green energy
2023-11-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
CPRIT recognized by TAMEST with Kay Bailey Hutchison Distinguished Service Award
2023-11-14
AUSTIN – TAMEST (Texas Academy of Medicine, Engineering, Science and Technology) is pleased to announce the Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas (CPRIT) as the recipient of the Kay Bailey Hutchison Distinguished Service Award.
TAMEST is recognizing CPRIT for their work improving the lives of Texans, advancing cancer research and prevention, and recruiting National Academy members to Texas. CPRIT’s success in attracting top-tier cancer scientists and companies to the state ...
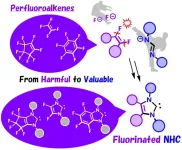
Converting PFAS “forever chemicals” into valuable compounds
2023-11-14
Osaka, Japan – Commonly known as “forever chemicals,” PFAS are notorious for persisting in the environment and in our bodies. Osaka Metropolitan University chemists may put an end to the “forever” life of PFAS with their simple yet innovative technique that converts these harmful substances into valuable compounds.
A research group led by Professor Masato Ohashi and Assistant Professor Kenichi Michigami of the Graduate School of Science at Osaka Metropolitan University has successfully synthesized ligands called fluorine-decorated ...
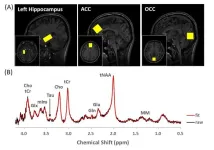
Women with depression have 20% lower taurine concentration in the hippocampus
2023-11-14
For the first time, a research team in Korea has discovered there is a significant relationship between depression and the taurine concentration in the hippocampus, an area of the brain responsible for memory and learning functions. This discovery provides the opportunity to publicize the role and importance of taurine in future prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of depression.
Using ultra-high magnetic field 7T human MRI (7T MRI), researchers (Drs. Youngkyu Song, Jee-Hyun Cho and Chaejoon Cheong) in the Korea Basic Science Institute (KBSI, President Seong-Kwang Yang) Biochemical Analysis Team have confirmed ...
Genetic testing could greatly benefit patients with depression, save health system millions
2023-11-14
A special kind of genetic test that helps determine the best antidepressant for patients with moderate-to-severe depression could generate substantive health system savings and greatly improve patient outcomes, according to new research from the University of British Columbia.
The study, published today in CMAJ, shows that in B.C. alone, implementing pharmacogenomic testing could save the provincial public health system an estimated $956 million over 20 years.
“Pharmacogenomic testing aims to match patients with medications that are more likely to be effective and cause less side effects, based ...
Geese ‘keep calm and carry on’ after deaths in the flock
2023-11-14
Canada geese strengthen existing friendships and forge a few new connections after losing close associates from their flock, new research shows.
University of Exeter scientists observed flocks of Canada geese before and after a population-management cull in which about 20% of the birds were killed.
In such a situation, some animals species increase “social connectivity” – mixing with many new individuals – which can increase the transmission of infectious diseases.
But the geese in the study responded by strengthening existing relationships, only adding enough new associations to replace those they had lost.
“Our findings shows that Canada geese are very ...
Using eclipses to calculate the transparency of Saturn’s rings
2023-11-14
A Lancaster University PhD student has measured the optical depth of Saturn’s rings using a new method based on how much sunlight reached the Cassini spacecraft while it was in the shadow of the rings.
The optical depth is connected to the transparency of an object, and it shows how far light can travel through that object before it gets absorbed or scattered.
The research, led by Lancaster University in collaboration with the Swedish Institute of Space Physics, is published in the Monthly Notices ...
Researchers propose MOF modular customization strategy for efficient membrane separations
2023-11-14
Membrane separation technology offers great potential due to its low energy consumption and continuous operation availability. Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are promising in separation membranes due to their abundant species, high porosity, and precise regulation of pore architectures.
Recently, a research group led by Prof. YANG Weishen and Assoc. Prof. PENG Yuan from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) has proposed a new strategy of modular customization and non-destructive ...
Scientists test new method for identifying small microplastics
2023-11-14
Microplastics, from the beads that were once commonplace in cosmetics to the weathered and broken-down remnants of trash, are now ubiquitous in marine and inland waters around the world. To date, though, scientists have struggled to identify which plastics persist longest in the environment and measure their abundance, especially at the smaller end of the size range where they’re most likely to be consumed by foundational species near the bottom of the food web, like zooplankton.
Researchers from Bigelow Laboratory for Ocean Sciences and the University of Minnesota ...
Tandem single atom electrocatalyst realizes reduction of CO2 to ethanol
2023-11-14
The electrochemical CO2 reduction reaction (CO2RR) into carbon-based fuels provides a promising strategy to mitigate CO2 emission and promotes the utilization of renewable energy.
The Cn (n≥2) liquid products are desirable because of their high energy densities and ease of storage. However, manipulation of C-C coupling pathway remains a challenge due to the limited mechanistic understanding.
Recently, a research group led by Profs. ZHANG Tao and HUANG Yanqiang from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) has developed a Sn-based tandem electrocatalyst (SnS2@Sn1-O3G), which could reproducibly yield ethanol ...
Overdose prevention sites not associated with increase in crime, according to study
2023-11-14
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Overdose prevention centers, where individuals can consume illicit drugs under the observation of trained staff, are not associated with significant increases in crime, researchers found.
When the researchers compared syringe service programs in New York City with two programs that were recently sanctioned by city officials to offer supervised drug consumption, they found no significant increases in crimes recorded by the police or calls for emergency service in the surrounding neighborhoods.
The findings, which were published in JAMA Network Open, come as plans to open overdose prevention centers proceed in Rhode ...