(Press-News.org) Dr. Marcia Rieke, principal investigator for the Near-Infrared Camera on NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope is the Astronomical Society of the Pacific’s (ASP) 2023 recipient of its most prestigious award. ASP’s Catherine Wolfe Bruce Gold Medal honors Rieke, a Regents Professor of astronomy and Elizabeth Roemer Endowed Chair, Steward Observatory, at the University of Arizona. Rieke’s award and achievements was recognized at the ASP Awards Gala on Saturday, Nov. 11, in Redwood City, California.
Groundbreaking Contributions
Rieke’s research has focused on infrared observations of the center of the Milky Way and high redshift galaxies in the early universe. Rieke is considered by many to be one of the “founding mothers of infrared astronomy,” and it is for her groundbreaking contributions to astronomical research at these wavelengths that she is being recognized and celebrated.
“I owe a debt of gratitude to my team that made all this possible. I am humbled that I’m on a list that includes the founders of infrared astronomy, Gerry Neugebauer and Frank Low,” said Rieke.
Rieke served as deputy principal investigator for the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) on NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope and co-investigator for the multiband imaging photometer on NASA’s retired Spitzer Space Telescope. Rieke was also involved with several infrared ground-based observatories, including the Multiple Mirror Telescope Observatory in Arizona.
Rieke’s nominators credit her leadership for the success of Webb’s Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam). As one of her nominators stated, “NIRCam was the Webb program’s most challenging instrument development effort. The instrument’s outstanding performance is due largely to the outstanding performance of its principal investigator. Marcia’s consistent focus, diligence, and ‘lead from the front’ approach under extremely difficult technical and programmatic circumstances presents an example for others to follow.”
Rieke has authored 310 refereed publications, which have over 30,000 citations. Her deep knowledge and expertise were put into service as vice chair for program prioritization for the Astro 2010 Decadal Survey Committee’s report, “New Worlds, New Horizons.” Her landmark contributions to astronomical research and instrument development, as well as her service to public policy and public outreach, have been recognized nationally. She was elected a fellow of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences in 2007, a fellow of the National Academy of Sciences in 2012, and a legacy fellow of the American Astronomical Society in 2020. Rieke has also been the recipient of numerous prestigious awards, including the NASA Distinguished Public Service Medal in 2023 for her contribution to the field of astronomy and key role in the development of cutting-edge instruments for Webb.
About the Catherine Wolfe Bruce Gold Medal
ASP is an international non-profit scientific and educational organization, founded in 1889, that works to increase understanding and appreciation of astronomy.
The Catherine Wolfe Bruce Gold Medal is the organization’s highest award given annually to a professional astronomer in recognition of a lifetime of outstanding achievement and contributions to astrophysics research. It was established by Catherine Wolfe Bruce, an American philanthropist and patroness of astronomy.
The James Webb Space Telescope is the world’s largest, most powerful, and most complex space science telescope ever built. Webb is solving mysteries in our solar system, looking beyond to distant worlds around other stars, and probing the mysterious structures and origins of our universe and our place in it. Webb is an international program led by NASA with its partners, ESA (European Space Agency) and the Canadian Space Agency.
For more information about NASA’s Webb telescope visit: www.nasa.gov/webb
END
Webb Telescope’s Marcia Rieke awarded Catherine Wolfe Bruce Gold Medal
2023-11-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Galactic ‘lightsabers’: Answering longstanding questions about jets from black holes
2023-11-14
The one thing everyone knows about black holes is that absolutely everything nearby gets sucked into them.
Almost everything, it turns out.
“Even though black holes are defined as objects from which nothing can escape, one of the astonishing predictions of Einstein’s theory of relativity is that black holes can actually lose energy,” says astrophysicist Eliot Quataert, Princeton’s Charles A. Young Professor of Astronomy on the Class of 1897 Foundation. “They ...
Researchers identify unexpected twist while developing new polymer-based semiconductors
2023-11-14
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — A new study led by chemists at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign brings fresh insight into the development of semiconductor materials that can do things their traditional silicon counterparts cannot – harness the power of chirality, a non-superimposable mirror image.
Chirality is one of nature’s strategies used to build complexity into structures, with the DNA double helix perhaps being the most recognized example – two molecule chains connected by a molecular “backbone” ...
Immigrants living in the U.S. have fewer preterm births
2023-11-14
Preterm birth predicts lifelong health outcomes
Worsening preterm birth rates in the U.S. represent a ‘key metric to target to improve overall societal health’
Study identifies key differences among Asian and Hispanic subgroups
Minority stress could contribute to inequities that begin at birth between populations in the U.S.
CHICAGO --- Preterm birth rates are an important marker in assessing a country’s overall health. And the United States isn’t fairing very well.
Individuals born in the U.S. had an overall higher rate (9.7%) of giving birth prematurely compared to U.S. immigrants (9%), a new Northwestern Medicine ...
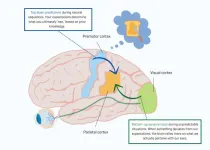
When we see what others do, our brain sees not what we see, but what we expect
2023-11-14
When we see what others do, our brain sees not what we see, but what we expect
When we engage in social interactions, like shaking hands or having a conversation, our observation of other people’s actions is crucial. But what exactly happens in our brain during this process: how do the different brain regions talk to each other? Researchers at the Netherlands Institute for Neuroscience provide an intriguing answer: our perception of what others do depends more on what we expect to happen than previously believed.
For some time, researchers have been trying to understand how our brains process other people’s ...
Great results with emergency care adapted for pregnant women
2023-11-14
Increased vigilance for high blood pressure and diffuse stomach pain. These are some of the characteristics of emergency care adapted for pregnant women and new mothers. The model, which could become clinical routine throughout Sweden, is described in a thesis at the University of Gothenburg.
The aim of the thesis was to reduce morbidity and mortality among pregnant women and new mothers seeking emergency care. Sweden has relatively low rates of pregnancy-related morbidity and mortality, but pregnant women and new mothers do not currently receive ...
Vegan diet fosters changes in gut microbiome that reduce hot flashes by 95%, finds new study
2023-11-14
A low-fat vegan diet that includes soy fosters changes in the gut microbiome that decrease postmenopausal vasomotor symptoms, or hot flashes, overall by 95%, according to a new study by the Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine. A vegan diet also eliminated severe hot flashes, led to a 96% decrease in moderate-to-severe hot flashes, and reduced daytime and nighttime hot flashes by 96% and 94%, respectively. Participants also lost 6.4 pounds on average.
“Women who want to fight hot flashes should feed the bacteria in their gut a vegan diet rich in fruits, vegetables, grains, and beans, which also leads to weight loss and protects against heart disease and type 2 diabetes,” ...
Drug that kills off sleeping bone cells could treat lower back pain
2023-11-14
An existing drug that targets senescent, or sleeping cells could provide the answer to treating lower back pain, according to a new study.
The research, published today as a Reviewed Preprint in eLife, advances our understanding of the role of senescent osteoclasts – cells that break down and remove damaged bone tissue – in the development of lower back pain, which affects 8 in 10 people at some point in their lives. eLife’s editors say the study provides compelling evidence that an existing drug, Navitoclax, can eliminate senescent osteoclasts in mice and, in doing so, markedly reduce spinal pain.
Osteoclasts resorb ...
Inflammation and loss of protective mechanisms in the brain linked to suicide risk
2023-11-14
GRAND RAPIDS, Mich. (Nov. 14, 2023) — A first-of-its-kind study has identified overactive inflammation and loss of critical protection mechanisms in the brain as potential contributors to suicide risk.
The findings support further exploration of anti-inflammatory medications to reduce risk, especially in situations where suicidal ideation can be ascertained early.
The study was published in the journal Molecular Psychiatry and led by Van Andel Institute’s Lena Brundin, M.D., Ph.D., Columbia ...
Another step toward the HIV-1 vaccine: Dynamics of neutralizing antibodies
2023-11-14
An international team has for the first time researched the longevity of neutralizing antibodies in HIV-1-infected people. Currently, it is assumed that an HIV-1 vaccine can only be effective if it produces these antibodies in vaccinated humans. The findings improve understanding of the dynamics of such antibodies and are an important building block for further research into an HIV-1 vaccine. Professor Dr Florian Klein, Director of the Institute of Virology at the University Hospital Cologne, and Dr Dr Philipp Schommers, Head of the Laboratory for Antiviral Immunity at Department ...
When languages collide, which survives?
2023-11-14
Language has the power to shape our perceptions and interactions with the world. Different languages can coexist, but their dynamics are shaped by the communities that speak them – and how those communities interact with each other. Shared beliefs, assumptions, and feelings toward specific language forms often determine whether a specific language will survive or disappear, especially within multilinguistic societies.
In Chaos, by AIP Publishing, researchers from the University of the Balearic Islands in Spain incorporate language ideologies, along with the impact of interaction between individuals with opposing preferences, on the language shift process.
“Our ...