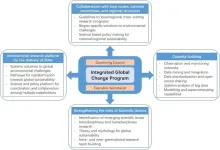
(Press-News.org) The global change program Future Earth is an international alliance of organizations and agencies that was launched by the UN in June 2012. The Future Earth 2025 Vision identified eight global challenges for scientific research to accelerate progress in sustainability, improve collaboration, and mobilize resources.
After more than a decade of this global change program, researchers are analyzing the challenges Future Earth has faced and the path forward. Discussion presented in a recently published paper reviews these challenges faced by the coalition and proposes solutions to help these programs meet the many needs of the global community.
The paper was published on November 15 in Ecosystem Health and Sustainability.
"The current global change program Future Earth has been modest in inspiring ground-breaking research to address major sustainability issues. In this article, we reflect on the UN request for global science to promote the delivery of sustainable development goals, giving our perspective with a focus on the future development of the global change program," said Yonglong Lu, a Chair Professor at Xiamen University in Fujian, China.
Three major challenges faced by the global change program were identified. The authors first point to a lack of visibility for Future Earth among the global science community. They attribute this to a lack of engagement with disciplinary scientific unions, which often drive and promote research and collaboration. This lack of engagement makes it difficult for Future Earth to inspire the groundbreaking research needed to meet its goals.
Because of this lack of engagement with the international science community, Future Earth developed a "top-down approach" to developing priorities and programming. This approach neglects the local communities that are impacted by sustainability programs and prevents Future Earth from responding nimbly to communities' needs.
The final challenge presented by the paper is that the global South is underrepresented in Future Earth. "In fact, there are tremendous opportunities in the global South to tackle emerging scientific issues, such as water security, environmental pollution, food safety, and human health, resulting from rapid economic and societal transformation," said Lu.
Finally, the paper provides specific recommendations to help make a stronger, integrated global change program to achieve the goals set forth in the UN 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. These five recommendations range from using the integrated global change program as a major international research platform to shifting focus to translating research and science into policy.
"In order to address the global grand challenges and act as an international authoritative source of knowledge, an integrated global change program should be more active and agile in order to respond to the large-scale, complex, and urgent issues that the global society is facing, while recognizing the dynamic interactions among coupled human-natural systems," said Lu.
Researchers also highlighted the importance of involving the global South and a variety of stakeholders, from global industry to business to national, state, and local governments.
Looking ahead, researchers emphasize that any new integrated global change program will need to bring together stakeholders and foster collaboration.
"We need to build a collaborative sustainability science alliance across geopolitical divides. This program will help develop and implement global and national science, technology, and innovation for sustainable development goals roadmaps, share science and knowledge to address the human needs for water, health, quality education, sanitation, and food security while maintaining the global ecosystem and planetary health," said Lu.
Other contributors include Prof. Bojie Fu of the Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences at the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Beijing, China, Prof. Tandong Yao at the Institute of Tibetan Plateau Research at the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Beijing, China, and Prof. Dahe Qin at the North-western Institute of Eco-Environment and Resources at the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Lanzhou, China. All the authors have been involved in the initiation and review process of Future Earth and the previous global environmental change programs.
The National Natural Science Foundation of China, the International Partnership Program by the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the Fundamental Research Fund for the Central Universities supported this research.
END
The Future of Future Earth: How global science programs can navigate the complex, shifting challenges in sustainability science
2023-11-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Georgetown Global Health Center launches first open-access wildlife disease database
2023-11-15
WASHINGTON (November 15, 2023) – Georgetown University Medical Center’s Center for Global Health Science and Security (GHSS) today announces the launch of a first-of-its-kind wildlife disease database -- a system for collecting records of viruses, bacteria, fungi, parasites, etc. -- designed to support an early warning system for potential viral emergence. The Pathogen Harmonized Observatory, or PHAROS, is open to the global community and free to access.
Scientists in GHSS’ Verena program, a collaborative ...
University of Basel delivers first biological implants for treatment of cartilage lesions and osteoarthritis in humans
2023-11-15
The Department of Biomedicine at the University of Basel and the University Hospital Basel, today announced that it delivered the first surgical procedure to treat Osteoarthritis (OA) in humans. The procedure called Nasal Chondrocyte Tissue-Engineered Cartilage, or N-TEC, provides an innovative alternative to cure confined knee cartilage lesions as well as to address degenerative OA cases that have to date required knee joint replacements – prosthetics that routinely need replacing after 15-20 years.
The team at Basel is spearheading the next-generation human clinical trials that will ...
From 2018 to 2022, eating disorder claim lines increased 65 percent nationally as a percentage of all medical claim lines
2023-11-15
NEW YORK, NY—November 15, 2023—From 2018 to 2022, eating disorder claim lines increased 65 percent nationally as a percentage of all medical claim lines.[1] All eating disorders studied increased during this period, but at different rates: avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder (ARFID) by 305 percent,[2] binge-eating disorder by 81 percent, anorexia nervosa (anorexia) by 73 percent and bulimia nervosa (bulimia) by 3 percent. These and other findings on eating disorders are reported in a FAIR Health white paper released today: Spotlight on Eating Disorders: An Analysis of Private Healthcare Claims.
Eating ...
NTU Singapore’s strength in research excellence sees it ranked 22nd globally and first in Singapore with most number of highly cited researchers
2023-11-15
Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) is up one spot to 22nd globally in this year’s Highly Cited Researchers list by Clarivate, a United Kingdom-based data company.
For the sixth year running, the University has the largest number of influential scientists among Singapore institutions recognised, with 42 NTU researchers that have significant and broad influence in their fields of research named.
These 42 scientists account for 44 mentions in the list, with two individuals recognised more ...
New study finds association between insecticide exposure and lower sperm concentration in adult men
2023-11-15
EMBARGOED until November 15, 2023
Contact: Michelle Thompson
George Mason University
mthomp7@gmu.edu
703-993-3485
New study finds association between insecticide exposure and lower sperm concentration in adult men
Comprehensive systematic review of 25 studies over nearly 50 years reveals consistent evidence of associations between insecticide exposure and lower sperm concentration
FAIRFAX, Va – Melissa J. Perry, Sc.D., MHS, dean of the George Mason University ...
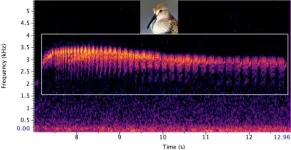
New deep learning AI tool helps ecologists monitor rare birds through their songs
2023-11-15
Researchers have developed a new deep learning AI tool that generates life-like birdsongs to train bird identification tools, helping ecologists to monitor rare species in the wild. The findings are presented in the British Ecological Society journal, Methods in Ecology and Evolution.
Identifying common bird species through their song has never been easier, with numerous phone apps and software available to both ecologists and the public. But what if the identification software has never heard a particular bird before, or only has a small sample of recordings to reference? This is a problem facing ...
Study finds increasingly popular oral nicotine pouches do little to curb smokers’ cravings
2023-11-15
Oral nicotine pouches, a tobacco-leaf-free product marketed as an alternative to cigarettes, do little to curb current smokers’ nicotine cravings, according to a new study. Public health scientists with The Center for Tobacco Research at The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center – Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital and Richard J. Solove Research Institute report these findings in the medical journal Addiction.
Nicotine pouches are small pre-portioned bags filled with nicotine powder, flavorings, artificial sweeteners and other chemicals that extend shelf life. Marketed ...
More than 10% of samples from a stool-based colorectal cancer test may be unsatisfactory
2023-11-15
Bottom Line: Over 10% of fecal immunochemical tests (FIT) used for routine colorectal cancer (CRC) screening in a safety-net health system contained unsatisfactory samples that could not be processed.
Journal in Which the Study was Published: Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR)
Authors: Rasmi Nair, MBBS, PhD, an assistant professor at the Peter O’Donnell Jr. School of Public Health of UT Southwestern Medical Center, and Po-Hong Liu, MD, a gastroenterology fellow at UT Southwestern Medical Center
Background: ...
Underworld marketplace exposed: Fake IDs for sale on the dark web
2023-11-15
Counterfeit Australian identity documents, especially driver’s licences, rank among some of the most frequently listed and sold identity documents on anonymous dark web marketplaces, according to new research from the Centre of Forensic Science at the University of Technology Sydney (UTS).
These documents are used by crime rings, terrorist organisations and other criminals for a wide range of illicit activities, including identity crime, money laundering, human and drug trafficking, illegal immigration, scams and ...
Shark fear: Just when you thought it was safe to get back in the water…
2023-11-15
It’s one of the most famous taglines in film history, immortalising sharks as ruthless predators. But beyond the horror generated by Spielberg’s Jaws series, a persistent fear of sharks remains, with consequences that extend into reality.
Following human-shark interactions in South Australia, this fear has prompted the Education Department’s ban on school-based sea activities for at least the remainder of the term. And while safety is at the core of such decisions, we should be cautious of scaremongering, says UniSA shark ...