(Press-News.org) Infants prenatally exposed to cannabis are more likely to be born preterm, have a low birth weight, and require neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) care than infants without prenatal cannabis exposure, according to a study published today in the scientific journal Addiction. However, cannabis-exposed infants are not at greater risk of birth defects or death within one year, including sudden unexpected infant death.
First author Ms. Maryam Sorkhou comments, “The global increase in cannabis use among women of reproductive age also extends to pregnant women. We know that THC, the main psychoactive constituent in cannabis, can cross the placenta from mother to fetus and bind to receptors in the fetal brain. Our study adds to that knowledge by showing that prenatal exposure to cannabis heightens the risk of several adverse birth outcomes.”
This meta-analysis (a synthesis of past studies) pooled the results of 57 prior studies with a total of 12,901,376 infant participants, 102,835 of them exposed to cannabis.
Twenty of the studies measured the association between intrauterine cannabis exposure and risk of preterm delivery. In these, the combined results show that mothers using cannabis were over one and a half times more likely to have a preterm delivery compared with mothers not using cannabis during pregnancy.
Eighteen of the studies measured the risk of low birth weight. In these, the combined results show that mothers using cannabis during pregnancy were more than twice as likely to have a low-birth-weight baby compared with mothers not using cannabis during pregnancy.
Ten of the studies measured the risk of requiring NICU admission. In these, the combined results show that newborns with intrauterine cannabis exposure were more than twice as likely to require NICU admission than nonexposed newborns.
The studies included in this meta-analysis were published between 1984 and 2023 in a broad range of countries.
-- Ends –
For editors:
This paper is available to read online for one month after the embargo has lifted ( https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/add.16370), or you may request a copy from Jean O’Reilly, Editorial Manager, Addiction, jean@addictionjournal.org.
To speak with the lead author Ms. Maryam Sorkhou, please contact her at the Institute of Medical Science, University of Toronto by email (maryam.sorkhou@mail.utoronto.ca) or telephone (+1 (416) 535-8501 x 36225).
Full citation for article: Sorkhou M, Singla DR, Castle DJ, and George TP. Birth, Cognitive, and Behavioral Effects of Intrauterine Cannabis Exposure in Infants and Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Addiction. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1111/add.16370.
Funding: This work was supported by a grant from the CAMH Foundation and NIDA Grant R21-DA043949 to Dr. George.
Declaration of interests: None to declare.
Addiction is a monthly international scientific journal publishing peer-reviewed research reports on alcohol, substances, tobacco, gambling, editorials, and other debate pieces. Owned by the Society for the Study of Addiction, it has been in continuous publication since 1884.
END
Cannabis use during pregnancy is associated with adverse birth outcomes
2023-11-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Landmark blood test to detect silent, lethal cancer
2023-11-16
Research that could lead to the first early detection blood test for pancreatic cancer has received critical funding from PanKind, The Australian Pancreatic Cancer Foundation.
Pancreatic cancer is one of Australia’s biggest killers, with poor survival rates marred by a lack of distinct symptoms and screening tools needed to detect the disease in its initial stages.
It’s hoped the test will, for the first time, accurately identify patients with early stages of pancreatic cancer – a crucial step towards improving survival ...
A better way to study Parkinson’s disease in the lab could lead to earlier diagnosis
2023-11-16
A recent study published in Progress in Neurobiology and led by researchers at the University of Arizona College of Medicine – Tucson has developed an improved method to study Parkinson’s disease in the lab. Along the way, researchers also uncovered clues that may help scientists figure out how to detect Parkinson’s earlier and point the way toward better treatments.
Around a million Americans are living with Parkinson’s disease, a neurological disorder that causes difficulty in movement, balance and cognition. Symptoms worsen until tasks like ...
Night-time radiative warming using the atmosphere
2023-11-16
Warming has played a crucial role in various industrial and agricultural processes throughout history. Night-time warming, however, presents a distinct challenge due to the absence of solar radiation. During the night, direct radiative heat loss to outer space through the atmospheric transparent window (8-14 μm) can cause temperature to drop below freezing, posing significant threats to agriculture (crops), transportation (outdoor cables), and more.
Traditionally, achieving night-time warming ...
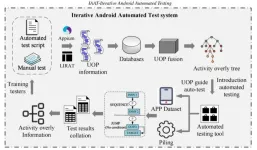
A bi-directional iterative approach to Android automated testing
2023-11-16
With the benefits of reducing time-cost and human efforts, automated testing has been widely used for quality assurance of mobile applications (apps). However, in complex interactive activities, manual testing can achieve higher coverage. However, the effectiveness of manual testing is highly dependent on the vital User Operation Process (UOP) of experienced testers.
To solve the problems, a research team led by Zhenyu CHEN and Chunrong FANG published their new research on 15 Oct 2023 in Frontiers of Computer Science co-published ...
Oregon State researchers receive $2M to look for new ways to prevent organic potatoes from spoiling
2023-11-16
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Oregon State University researchers have been awarded $2 million from the U.S. Department of Agriculture to develop improved ways of preventing stored potatoes from sprouting, particularly in the organic sector.
This research is pivotal given the rapid rise of the organic market in U.S. agriculture, the scientists note.
“The organic potato industry cannot depend on traditional chemical anti-sprouting treatments since synthetic chemicals are banned in certified organic,” said Valtcho Jeliazkov of OSU’s College of Agricultural ...
Why it’s important to improve communication of unanticipated genomic findings to patients with late-stage cancer
2023-11-16
New research conducted by City of Hope and supported by the American Cancer Society focuses on developing scalable educational interventions to support informed patient decision making and consent, such as online tools and applications that include visual aids or interactive multimedia.
FINDINGS
Cancer genomics experts at City of Hope®, one of the largest cancer research and treatment organizations in the United States, conducted a qualitative study that underscored the importance of properly preparing patients for unanticipated, inheritable genetic findings prior to receipt of ...
New studies of brain activity explain benefits of electroconvulsive therapy
2023-11-16
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), formerly known as electroshock therapy, involves inducing a brief seizure in the brain using controlled doses of electricity. While ECT is highly effective for certain mental illnesses, particularly depression, the reasons for its efficacy have long puzzled the fields of psychiatry and neuroscience.
Now, researchers from University of California San Diego may have an answer. In two new studies published November 16, 2023 in Translational Psychiatry, they propose a new hypothesis that ECT alleviates depression symptoms by increasing aperiodic activity, a type of electrical activity in the brain that doesn’t follow a consistent pattern ...
McWilliams School of Biomedical Informatics researchers awarded $31M in grants for medical artificial intelligence innovation research
2023-11-16
McWilliams School of Biomedical Informatics at UTHealth Houston reached a funding landmark with 15 faculty members awarded 16 different grants totaling more than $31 million between August and October 2023. Each grant has a focus on medical artificial intelligence (AI) innovations and advancements in research or health care.
“This is an incredible achievement for McWilliams School of Biomedical Informatics; these grants play a key role in advancing informatics research while also expanding on the important role technology continues to play in medicine,” said Jiajie Zhang, PhD, dean and Glassell Family Foundation Distinguished Chair in ...
The BMJ investigates concerns over informed consent for pregnant women in Pfizer’s RSV vaccine trial
2023-11-16
A debate has broken out over whether Pfizer should have told pregnant women taking part in its maternal respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) vaccine trial that a trial of a similar GSK vaccine was stopped over a safety signal around preterm birth, an investigation by The BMJ can reveal.
Pfizer’s vaccine, called Abrysvo, was recently approved for use in the US and the European Union, but is not yet authorised in the UK.
Some experts have criticised Pfizer for not informing participants, while others believe notification would have been premature and caused unnecessary anxiety, reports freelance investigative journalist Hristio ...
No one-size-fits-all solution for the net-zero grid, Surrey research demonstrates
2023-11-16
As power generation from sources like solar and wind increases, along with the introduction of devices such as heat pumps and batteries, a new optimisation tool created at the University of Surrey will help the UK plan for a greener electricity network.
The researchers developed an algorithm to model how these smaller networks distributed electricity – factoring in how local grids could become unbalanced by adding too many heat pumps in a single area or generating more electricity than the grid could accept.
The Surrey team found that it was generally more efficient ...