(Press-News.org)
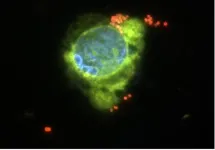
EL PASO, Texas (Nov. 17, 2023) – Could the solution to the decades-long battle against malaria be as simple as soap? In a new study published in PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases, scientists at The University of Texas at El Paso have made a compelling case for it.
The team has found that adding small quantities of liquid soap to some classes of pesticides can boost their potency by more than ten-fold.
The discovery is promising news as malaria-carrying mosquitoes display an increasing resistance to current insecticides, said Colince Kamdem, Ph.D., lead author of the study and assistant professor in UTEP’s Department of Biological Sciences.
“Over the past two decades, mosquitoes have become strongly resistant to most insecticides,” Kamdem said. “It’s a race now to develop alternative compounds with new modes of action.”
Both laboratory tests and field trials have shown that neonicotinoids, a special class of insecticide, are a promising alternative to target populations showing resistance to existing insecticides, said UTEP Research Assistant Professor Caroline Fouet, Ph.D., second author of the study. Neonicotinoids, however, do not kill some mosquito species unless their potency is boosted. In this case, Fouet said, soap is the boosting substance.
Malaria is a devastating mosquito-borne disease that is prevalent in sub-Saharan Africa, Asia and Latin America, causing fever, fatigue, headaches and chills; the disease can be fatal. In 2020, there were an estimated 241 million cases of malaria worldwide, according to the Centers for Disease Control, resulting in 627,000 deaths.
Prior to joining UTEP, Kamdem worked at Cameroon’s Centre for Research in Infectious Diseases (CRID); it was there that he first caught on to soap’s potency while conducting routine insecticide testing.
Current protocols from the World Health Organization (WHO) for testing mosquitoes’ susceptibility to some insecticides recommend adding a seed oil-based product to insecticide concoctions. Kamdem noticed when the compound was added, mosquito mortality increased from when the insecticide was used on its own.
“That compound belongs to the same class of substances as kitchen soap,” Kamdem said. “We thought, ‘Why don’t we test products that have same properties?’
He and his team selected three low-cost, linseed-oil based soaps that are prevalent in sub-Saharan Africa — Maître Savon de Marseille, Carolin Savon Noir and La Perdrix Savon — and added them to four different neonicotinoids, acetamiprid, clothianidin, imidacloprid and thiamethoxam.
The hunch paid off. In all cases, the insecticides drastically enhanced potency, the team wrote in the study. “All three brands of soap increase mortality from 30 percent to 100 percent compared to when the insecticides were used on their own,” said Ashu Fred, first author of the study and Ph.D. student at Cameroon’s University of Yaoundé 1.
The team also tested the addition of soap to a class of insecticides known as pyrethroids. In those cases, however, they saw no benefits.
The team hopes to conduct additional testing to establish exactly how much soap is needed to enhance insecticides.
“We would love to make a soap-insecticide formulation that can be used indoors in Africa and be healthy for users,” Kamdem said. “There are unknowns as to whether such a formulation will stick to materials like mosquito nets, but the challenge is both promising and very exciting.”
Additional authors on the study are doctoral student Marilene M. Ambadiang of CRID and the University of Yaoundé 1; and Professor Veronique Penlap-Beng, Ph.D., of the University of Yaoundé 1.
The project was supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health.
About The University of Texas at El Paso
The University of Texas at El Paso is America’s leading Hispanic-serving university. Located at the westernmost tip of Texas, where three states and two countries converge along the Rio Grande, 84% of our 24,000 students are Hispanic, and more than half are the first in their families to go to college. UTEP offers 171 bachelor’s, master’s and doctoral degree programs at the only open-access, top-tier research university in America.
END
Using historical records from around Australia, an international team of researchers have put forward the most accurate prediction to date of past Antarctic ice sheet melt, providing a more realistic forecast of future sea level rise.
The Antarctic ice sheet is the largest block of ice on earth, containing over 30 million cubic kilometers of water.
Hence, its melting could have a devasting impact on future sea levels. To find out just how big that impact might be, the research team, including Dr Mark Hoggard from The Australian National University, turned to the past.
“If ...
Policies that encourage landlords to evict tenants who have involvement with the criminal justice system do not appear to reduce crime, while increasing evictions among Black residents and people with lower incomes, according to a new RAND Corporation report.
Studying “crime-free housing policies” adopted by cities in California over a decade-long period, researchers found no meaningful statistical evidence that the policies reduce crime.
The study also found that crime-free housing policies significantly increased ...
This year’s European Antibiotic Awareness Day (EAAD) focuses on the targets outlined in the 2023 Council Recommendation to step up efforts in the European Union (EU) against antimicrobial resistance in a One Health approach. [1] Those recommendations formulate the 2023 goal to reduce total antibiotic consumption (community and hospital sectors combined) by 20%, using consumption data from 2019 as baseline.
Consumption of antibiotics in the community accounts for around 90% of the total use. This means, that a substantial and consistent decline in the use of antibiotics in this sector will be key on the way towards reaching ...
New Orleans, LA – The American Psychiatric Association (APA) Foundation has selected Rahn Baily, MD, DLFAPA, ACP, Professor and Chair of Psychiatry at LSU Health New Orleans School of Medicine, as the recipient of the 2024 Solomon Carter Fuller Award.
According to the APA Foundation, “The Solomon Carter Fuller Award—established in 1969 and named for Dr. Solomon Carter Fuller, recognized as the first Black psychiatrist in America—honors a Black citizen who has pioneered in ...
A team of scientists from the Institut Pasteur has used the database of the National Reference Center for Meningococci to trace the evolution of invasive meningococcal disease cases in France between 2015 and 2022, revealing an unprecedented resurgence in the disease after the easing of control measures imposed during the COVID-19 epidemic. Recently reported cases have mainly been caused by meningococcal serogroups that were less frequent before the pandemic, and there has been a particular uptick in cases among people aged 16 to 24. The results, published in the Journal of Infection and Public Health on October 12, ...
Researchers at the University of Wisconsin–Madison have identified a protein key to the development of a type of brain cell believed to play a role in disorders like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases and used the discovery to grow the neurons from stem cells for the first time.
The stem-cell-derived norepinephrine neurons of the type found in a part of the human brain called the locus coeruleus may enable research into many psychiatric and neurodegenerative diseases and provide a tool for developing ...
Migraine is more than just a headache. Often the pain is accompanied by nausea, vomiting, light sensitivity, and sound sensitivity. Chronic migraine can be disabling and may prevent many, especially women, from contributing to working life.
Still, it often takes a long time for migraine patients to find a treatment that works well for them. Researchers at the Norwegian Center for Headache Research (NorHead) have used data from the Norwegian Prescription Register to look at which medicines best prevent migraine in people in Norway:
“There has now been done a lot of research on this subject ...
University of B.C. researchers have uncovered startling connections between micronutrient deficiencies and the composition of gut microbiomes in early life that could help explain why resistance to antibiotics has been rising across the globe.
The team investigated how deficiencies in crucial micronutrients such as vitamin A, B12, folate, iron, and zinc affected the community of bacteria, viruses, fungi and other microbes that live in the digestive system.
They discovered that these deficiencies led to significant shifts in the gut ...
Researchers at the University of Pittsburgh and KU Leuven have discovered a suite of genes that influence head shape in humans. These findings, published this week in Nature Communications, help explain the diversity of human head shapes and may also offer important clues about the genetic basis of conditions that affect the skull, such as craniosynostosis.
By analyzing measurements of the cranial vault — the part of the skull that forms the rounded top of the head and protects the brain — the team identified 30 regions of the genome associated with different aspects of head shape, 29 of which have not been reported previously.
“Anthropologists ...
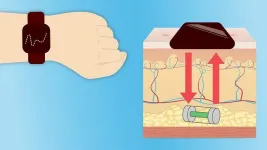
The first glucose self-monitoring system created in 1970 weighed three pounds, was initially designed only for physicians’ offices and needed a large drop of blood for a reading. Over 50 years later, researchers at Texas A&M University are working to create a fully injectable continuous glucose monitor (CGM) so small it rivals a grain of rice and can be used with an external optical reader to measure sugar levels at any given time.
While CGMs have advanced over the last 25 years, current models can still be a nuisance to the user and the required upkeep may discourage use. To address this issue, two faculty members from the Department of Biomedical Engineering ...