(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, Nov. 21, 2023 – Forensic science has captured the public imagination by storm, as the profusion of “true crime” media in the last decade or so suggests. By now, most of us know that evidence left at a crime scene, such as blood, can often reveal information that is key to investigating and understanding the circumstances around a crime — and that scientific methods can help interpret that information.
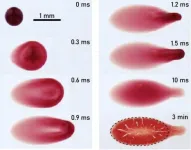
In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, a group of scientists from Boston University and the University of Utah demonstrated how bloodstains can yield even more valuable details than what is typically gathered by detectives, forensic scientists, and crime scene investigators. By examining the protrusions that deviate from the boundaries of otherwise elliptical bloodstains, the researchers studied how these “tails” are formed.
“These protrusions are typically only used to get a sense of the direction that the drop traveled, but are otherwise neglected,” said author James Bird.
In fact, previous studies have primarily focused on larger blood drops falling vertically on flat surfaces or on inclined surfaces where gravity can reshape and obscure the tails. By contrast, the new study involved a series of high-speed experiments with human blood droplets with diameters of less than a millimeter impacting horizontal surfaces at various angles.
“We show that the precise flow that determines the tail length differs from the flow responsible for the size and shape of the elliptical portion of the stain,” said Bird. “In other words, the tail lengths encompass additional independent information that can help analysts reconstruct where the blood drop actually came from.”
Indeed, the tail length can reflect information about the size, impact speed, and impact angle of the blood drop that formed the stain. When measured for several blood stains in a stain pattern, the trajectories of the drops can be backtracked to their presumed origin.
While their analysis employed only horizontal surfaces to examine impact velocity dynamics, Bird and his colleagues hope it triggers more studies that focus on the length of the tail in bloodstain patterns. They believe that incorporating tail length into standard bloodstain analyses will produce more robust evidentiary information.
“Knowing the origin of the blood stains at a crime scene can help detectives determine whether a victim was standing or sitting, or help corroborate or question a witness’s testimony,” said Bird.
###
The article “Bloodstain tails: Asymmetry aids reconstruction of oblique impact” is authored by Garam Lee, Daniel Attinger, Kenneth F. Martin, Samira Shiri, and James C. Bird. The article will appear in Physics of Fluids on Nov. 21, 2023 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0170124). After that date, it can be accessed at http://aip.scitation.org/doi/full/10.1063/5.0170124.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
Physics of Fluids is devoted to the publication of original theoretical, computational, and experimental contributions to the dynamics of gases, liquids, and complex fluids. See https://aip.scitation.org/journal/phf.
###
END
Written in blood
How bloodstain “tails” can point to significant, additional forensic details.
2023-11-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Unstable housing and mortality among veterans receiving dialysis
2023-11-21
About The Study: In this study of 25,000 veterans receiving dialysis, unstable housing experienced before starting dialysis was associated with increased risk of all-cause mortality, and risks increased with age. Further efforts are needed to understand the experiences of older adults with unstable housing and to estimate the scope of unstable housing among all individuals receiving dialysis.
Authors: Tessa K. Novick, M.D., M.S.W., M.H.S., of the University of Texas at Austin Dell Medical School in Austin, Texas is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit ...
Food insecurity, memory, and dementia among adults age 50 and older
2023-11-21
About The Study: In this study of 7,000 older U.S. residents, food insecurity was associated with increased dementia risk, poorer memory function, and faster memory decline. Future studies are needed to examine whether addressing food insecurity may benefit brain health.
Authors: Aayush Khadka, Ph.D., of the University of California, San Francisco, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.44186)
Editor’s ...
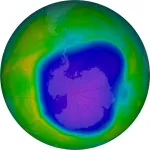
Study highlights need to keep an eye on the ozone hole
2023-11-21
Despite public perception, the Antarctic ozone hole has been remarkably massive and long-lived over the past four years, University of Otago researchers believe chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) aren’t the only things to blame.
In a study, just published in Nature Communications, the group analysed the monthly and daily ozone changes, at different altitudes and latitudes within the Antarctic ozone hole, from 2004 to 2022.
Lead author Hannah Kessenich, PhD candidate in the Department of ...
Scientists take a step forward in understanding how to tackle chronic infections in cystic fibrosis patients
2023-11-21
Scientists have engineered a living material resembling human phlegm, which will help them to better understand how a certain kind of infection develops on the lungs of patients with cystic fibrosis.
The study, published in Matter, was led by Dr Yuanhao Wu and is a collaboration between Professor Alvaro Mata in the School of Pharmacy and Department of Chemical Engineering and Professor Miguel Cámara from the National Biofilms Innovation Centre in the School of Life Sciences at the University of Nottingham.
Biofilms are strong living 3D materials that play ...
BU study finds long-term acute care hospital closures associated with changes in hospital care practices
2023-11-21
EMBARGOED by JAMA Network Open until 11 am, ET, Nov. 21, 2023
Contact: Gina DiGravio, 617-358-7838, ginad@bu.edu
BU Study Finds Long-term Acute Care Hospital Closures Associated with Changes in Hospital Care Practices
(Boston)—Long-term acute care hospitals (LTCHs) are common sites of post-acute care for patients recovering from severe respiratory failure requiring long-term mechanical ventilation. Because of longer lengths of stay compared to regular, short-stay hospitals, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid (CMS) reimburses LTCHs at higher rates. However, since 2005, ...
How do we learn? Neuroscientists pinpoint how memories are likely to be stored in the brain
2023-11-21
What is the mechanism that allows our brains to incorporate new information about the world, and form memories? New work by a team of neuroscientists led by Dr Tomás Ryan from Trinity College Dublin shows that learning occurs through the continuous formation of new connectivity patterns between specific engram cells in different regions of the brain.
Whether on purpose, incidentally, or simply by accident, we are constantly learning and so our brains are constantly changing. When we navigate the world, interact with each other, or consume media content, our brain is grasping ...
Bone growth drug may reduce sudden infant death syndrome in children with common form of dwarfism
2023-11-21
A drug that boosts bone growth in children with the most common form of dwarfism, may also reduce their chances of sudden infant death syndrome, sleep apnoea and needing surgery, according to a new study.
The international research trial, led by Murdoch Children’s Research Institute (MCRI) and published in The Lancet Child & Adolescent Health, has showed for the first time that vosoritide treatment increases height, facial volume and the size of the foramen magnum, the hole at the base of the skull that connects the brain with the spinal cord, in children under five with achondroplasia.
MCRI is the largest vosoritide ...
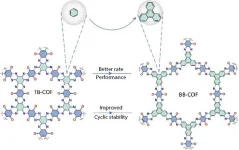
Density matters for better battery material performance, researchers find
2023-11-21
Zinc — cheap, abundant, environmentally friendly — may be the answer to better batteries, but there’s a major problem: Aqueous zinc ion batteries (AZIBs) cannot match lithium-ion batteries in terms of power output. To test what electrode material composition might be able to bring AZIBs up to par, a research team based in China developed two organic frameworks with the same constituents but arranged in different ways.
When put to the test, the framework with appropriate density of active sites — where the zinc ions gain electrons to recharge the ...
AHRI and BGI Genomics sign MoU to enhance public health outcomes in Ethiopia
2023-11-21
On October 13, 2023, in Addis Ababa, Armauer Hansen Research Institute (AHRI) and BGI Genomics signed a Memorandum of Understanding to enhance the Institute's genomics and precision medicine capabilities.
The Institute got its name from the Norwegian physician, Gerhard Henrik Armauer Hansen, who first described the leprosy bacillus (Mycobacterium leprae) and joined the Ethiopian Ministry of Health in 2004. Located in Addis Ababa, it serves as a biomedical hub for the region.
BGI Genomics provides ...
Unraveling autism spectrum disorder mechanisms through rigid-autonomous phase sequences
2023-11-21
This study delves into the behavioral complexities of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) by introducing the rigid-autonomous phase sequence (RAPS) formation concept. RAPS are may be responsible for the cognitive, sensory-motor, and memory-related challenges faced by individuals with ASD. By uniting these insights under a single theoretical framework, this research paves the way for innovative treatments, promising a brighter future for those with ASD.
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a complex neuropsychiatric condition, marked ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
[Press-News.org] Written in bloodHow bloodstain “tails” can point to significant, additional forensic details.