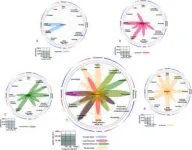
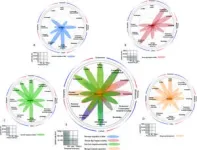
(Press-News.org) Transplanting gut microbes from an obesity-resistant shrew can improve microbiome diversity and decrease the weight of obese mice
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0293213
Article Title: Gut microbiota of Suncus murinus, a naturally obesity-resistant animal, improves the ecological diversity of the gut microbiota in high-fat-diet-induced obese mice
Author Countries: Japan, China
Funding: This work (PONE-D-23-21281) was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan (Nos. 19K07271). However, the funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. None of the authors received a salary from this grant
END
Transplanting gut microbes from an obesity-resistant shrew can improve microbiome diversity and decrease the weight of obese mice
2023-11-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
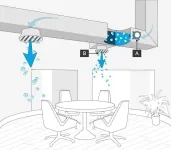
Airborne virus infectivity can be reduced by up to 99.98% by commercially available NPBI-based air purifiers, per experiment using real-world concentrations of COVID-19 strains, flu and RSV viruses
2023-11-22
Airborne virus infectivity can be reduced by up to 99.98% by commercially available NPBI-based air purifiers, per experiment using real-world concentrations of COVID-19 strains, flu and RSV viruses
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0293504
Article Title: Bipolar ionization rapidly inactivates real-world, airborne concentrations of infective respiratory viruses
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. All research and 3rd party laboratory testing was funded entirely by GPS Air. Edward Sobek is an employee of GPS Air ...
7 in 8 homicide victims in South Africa are male
2023-11-22
7 in 8 homicide victims in South Africa are male, with homicide rates peaking on weekends and holidays, and firearms and sharp items being the most common murder weapons, in analysis of almost 20,000 2017 post-mortems. END ...
In Nepalese survey, 1 in 5 men who have sex with men report having attempted suicide, with over 40 percent experiencing some suicidal ideation
2023-11-22
In Nepalese survey, 1 in 5 men who have sex with men report having attempted suicide, with over 40 percent experiencing some suicidal ideation.
####
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/globalpublichealth/article?id=10.1371/journal.pgph.0002348
Article Title: Suicidal ideation, plan, and attempt among men who have sex with men in Nepal: Findings from a cross-sectional study
Author Countries: Nepal, USA
Funding: RS received funding from the National Institute on Drug Abuse (Award Number: K01DA051346). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision ...
New tool to enable exploration of human-environment interactions
2023-11-22
Spurred by the current climate crisis, there has been a heightened attention within the scientific community in recent years to how past climate variation contributed to historic human migration and other behaviors.
Now, an international group of scientists — including archaeologists, historians, climate scientists, paleo-scientists, a volcanologist and others — are calling for a strengthened commitment to transdisciplinary collaboration to study past and present human-environmental interactions, which they say will advance our understanding of these complex, entangled histories. Their recommendations were published ...
Researchers pinpoint brain area where people who are blind recognize faces identified by sound
2023-11-22
WASHINGTON – Using a specialized device that translates images into sound, Georgetown University Medical Center neuroscientists and colleagues showed that people who are blind recognized basic faces using the part of the brain known as the fusiform face area, a region that is crucial for the processing of faces in sighted people.
The findings appeared in PLOS ONE on November 22, 2023.
“It’s been known for some time that people who are blind can compensate for their loss of vision, ...
Cognitive ability mattered in the UK’s vote for Brexit, University of Bath research shows
2023-11-22
Susceptibility to misinformation and disinformation likely to have played part in Leave vote
New research from the University of Bath’s School of Management finds that higher cognitive ability was strongly linked to voting to Remain in the 2016 UK referendum on European Union Membership.
The study shows that cognitive skills including memory, verbal fluency, fluid reasoning and numerical reasoning, were correlated with how people decided to vote.
Lead author Dr Chris Dawson, from the University of Bath’s School of Management, said: “This study adds to existing academic evidence showing that low ...
Autonomous excavator constructs a 6-meter-high dry-stone wall
2023-11-22
ETH Zurich researchers deployed an autonomous excavator, called HEAP, to build a six metre-high and sixty-five-metre-long dry-stone wall. The wall is embedded in a digitally planned and autonomously excavated landscape and park.
The team of researchers included: Gramazio Kohler Research, the Robotics Systems Lab, Vision for Robotics Lab, and the Chair of Landscape Architecture. They developed this innovative design application as part of the National Centre of Competence in Research for Digital Fabrication ...
Depression, anxiety, and stress frequently co-occur in Black pregnant individuals
2023-11-22
November 22, 2023 — Black pregnant individuals frequently experience more than one mental health concern, according to findings published by Susan Gennaro, PhD, RN, FAAN, Professor in the William F. Connell School of Nursing at Boston College, and colleagues in The Nurse Practitioner. They say prenatal screening and treatment for stress is warranted in addition to care of depression and anxiety. The Nurse Practitioner is part of the Lippincott portfolio of Wolters Kluwer.
"Prenatal interventions for Black people should aim to address mental health distress and treat high depression, anxiety, and stress," the research ...
UTA, DOE lab partner to prove new atomic cooling techniques
2023-11-22
The U.S. Department of Energy has awarded associate professor of physics Benjamin Jones a $540,000 grant to initiate a new collaborative research partnership between The University of Texas at Arlington and the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory in Richland, Washington. The project aims to prove a new atomic cooling approach required for the next generation of neutrino mass research.
Neutrinos are the most abundant particles with mass in the universe. Every time atomic nuclei come together (in the case of stars like the sun) or break apart (such as in nuclear ...
Low-pH-dependent RNA binding and oligomerization of SID-1 transmembrane family proteins: implications for their RNA transport activity
2023-11-22
In C. elegans, the protein SID1 plays a crucial role in the systemic RNA interference process by facilitating the transport of exogenous double-stranded RNA into the cytoplasm. Previously, Chen-Yu Zhang's group has already demonstrated that intact plant miRNA found in dietary sources can be absorbed through the mammalian digestive system and mediate cross-kingdom gene regulation. Mammalian SID-1 transmembrane family proteins, namely SIDT1 and SIDT2, have attracted considerable attention due to their role in facilitating the uptake of regulatory exogenous small RNAs, such as small interfering RNA (siRNA) and plant-derived ...