Increasing high-temperature strength of materials through collaborative efforts of AI and materials researchers
Optimizing thermal aging schedules by analyzing the unconventional AI-driven outcomes
2023-11-27
(Press-News.org)
1. A materials research team consisting of NIMS and Nagoya University has designed a novel two-step thermal aging schedule (i.e., non-isothermal aging or unconventional heat treatment) capable of fabricating nickel-aluminum (Ni-Al) alloys that are stronger at high temperatures than Ni-Al alloys fabricated using conventional thermal aging processes. This was achieved by using artificial intelligence (AI) techniques to identify several dozen different thermal aging schedules potentially effective in increasing alloys’ high-temperature strength. The mechanisms behind these schedules were then elucidated through detailed analysis. These results suggest that AI can be used to generate new insights into materials research.
2. Ni-Al alloys are composed of a γ/γ´ (gamma/gamma prime) two-phase microstructure. Increasing the high-temperature strength of these alloys requires optimizing both the size and volume fraction of the γ´ phase formed within the alloy during the thermal aging process. These two parameters are determined by the conditions under which alloys are thermally aged (i.e., temperatures used and periods during which they are maintained). There is an enormous number of possible temperature-duration combinations. For example, dividing a thermal aging process into 10 equal intervals with nine predetermined aging temperatures results in approximately 3.5 billion (910) possible temperature-duration combinations. Because of this vast number of possible combinations, previous efforts to determine optimum thermal aging schedules had been limited to using constant temperatures. This research team previously succeeded in significantly reducing the time and cost needed to evaluate these combinations by shifting their approach from experiments to computational simulations. Still, the team found it unrealistic to simulate all 3.5 billion combinations.
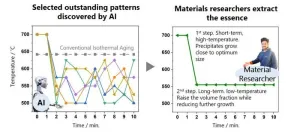
3. The research team recently adopted a Monte Carlo tree search (MCTS) system—an AI algorithm capable of streamlining a huge number of potential combinations into a smaller number of optimum ones. Using the MCTS algorithm, the team identified 110 thermal aging schedule patterns able to produce better results than conventional isothermal aging processes. The team initially found these patterns to be complicated and completely different from conventional isothermal aging, as shown in the figure. However, detailed analysis revealed the underlying mechanisms behind these patterns: initially aging a sample at a high temperature for a short period of time allows γ´ precipitates to grow until they reach near-optimum sizes, and subsequent low-temperature aging for a long period of time increases their volume fraction while preventing them from growing too large. Based on this discovery, the team designed a two-step thermal aging schedule—short-duration high-temperature aging to start followed by long-duration low-temperature aging. This schedule was proven to produce Ni-Al alloys that were stronger at high temperatures than those produced using any of the thermal aging patterns identified to be effective by the AI algorithm.
4. In future research, the research team hopes to increase the high-temperature strength of more complex nickel-based superalloys already in practical use in gas turbines using this AI-based technique, thereby improving their efficiency.
***
5. This project was carried out by Masahiko Demura (Director, Research Network and Facility Services Division (RNFS), NIMS), Satoshi Minamoto (Materials Data Platform Deputy Director, RNFS, NIMS), Vickey Nandal (Postdoctoral Researcher, NIMS), Sae Dieb (Researcher, NIMS), Toshio Osada (Principal Researcher, Research Center for Structural Materials (RCSM), NIMS), Dmitry S. Bulgarevich (Special Researcher, RCSM, NIMS) and Toshiyuki Koyama (Professor, Nagoya University).
This work—conducted under the structural materials DX-MOP framework—was supported in part by an SIP (Cross-ministerial Strategic Innovation Promotion Program) project entitled “Materials integration for revolutionary design system of structural materials.”
6. This research was published in Scientific Reports (Vol. 13, article number 12660) on August 4, 2023.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-11-27
Auburn, AL – Richard Feynman famously stated, “Everything that living things do can be understood in terms of the jigglings and wigglings of atoms.” This week, Nature Nanotechnology features a groundbreaking study that sheds new light on the evolution of the coronavirus and its variants of concern by analyzing the behavior of atoms in the proteins at the interface between the virus and humans. The paper, titled “Single-molecule force stability of the SARS-CoV-2–ACE2 interface in variants-of-concern,” is the result of an international collaborative ...
2023-11-27
ORLANDO, Nov. 27, 2023 – Three research projects from the University of Central Florida have been selected for NASA Minority University Research and Education Project Partnership Annual Notification (MPLAN) awards. The grants, worth up to $50,000 each, are designed to connect and promote research collaborations between Minority Serving Institutions and NASA Mission Directorates.
A total of 18 projects received Phase I funding across 15 universities. UCF received the most awards, with all three housed within the College of Engineering and Computer Science. Dean Michael Georgiopoulos ...
2023-11-27
An innovative stem cell-based treatment for Type 1 diabetes can meaningfully regulate blood glucose levels and reduce dependence on daily insulin injections, according to new clinical trial results from the University of British Columbia (UBC) and Vancouver Coastal Health (VCH).
“This is a significant step toward a functional cure for Type 1 diabetes,” said Dr. David Thompson, principal investigator at the Vancouver trial site, clinical professor of endocrinology at UBC and director of the Vancouver General Hospital Diabetes Centre. ...
2023-11-27
A new form of wave devouring propulsion (WDP) could power ships and help to cut greenhouse gas emissions in the maritime industry.
Academics from Cranfield University have worked on the concept of using wave energy for propulsion, and designed an inventive method of achieving greater thrust from the power of the waves by harnessing a vessel’s submerged flapping foils in an innovative way.
Inspiration from whale fins
Taking inspiration from the power of a whale's fins, the team studied the structure and movement of the tail fin to unravel how it effectively uses wave energy for propulsion. Through simulations and experiments, they developed ...
2023-11-27
Recommender systems are machine learning applications in online platforms that automate tasks historically done by people. In the news industry, recommender algorithms can assume the tasks of editors who select which news stories people see online, with the goal of increasing the number of clicks by users, but few studies have examined how the two compare.
A new study examined how users of an online news outlet in Germany reacted to automated recommendations versus choices made by human editors. On average, the algorithm outperformed the person, but the person did better under certain conditions. The study’s authors suggest a combination of human curation and automated recommender ...
2023-11-27
(Boston)—Breast density information aims to increase awareness of breast density and its risks and inform future breast screening decisions. Breast density notifications (BDN) advise women to discuss breast density with their clinicians, but prior research shows less than half of women in the general population have those conversations and little is known about the content of conversations that do occur.
A new study by researchers from Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School ...
2023-11-27
Scientists have simulated conditions that allow hazy skies to form in water-rich exoplanets, a crucial step in determining how haziness muddles observations by ground and space telescopes.
The research offers new tools to study the atmospheric chemistry of exoplanets and will help scientists model how water exoplanets form and evolve, findings that could help in the search for life beyond our solar system.
“The big picture is whether there is life outside the solar system, but trying to answer that kind of question requires really detailed modeling of all different types, specifically in planets with lots of water,” said co-author ...
2023-11-27
Scientists have made a surprising discovery that sheds new light on the role that oceanic deoxygenation (anoxia) played in one of the most devastating extinction events in Earth’s history. Their finding has implications for current day ecosystems – and serves as a warning that marine environments are likely more fragile than apparent.
New research, published today in leading international journal Nature Geosciences, suggests that oceanic anoxia played an important role in ecosystem disruption and extinctions in marine environments during the Triassic–Jurassic mass extinction, ...
2023-11-27
Antibodies—proteins that are produced by our immune system to protect us—are crucial for recognizing and getting rid of unwanted substances, or antigens, in our body. Although their role is universal, antibody structure varies in different animals. In a new study, researchers have analyzed the antibody Immunoglobulin M in rainbow trout to shed some light on why these proteins may have evolved over time.
In humans, IgM consists of five repeating units that are held together by a joining chain, resulting in a star shape. Consequently, IgM can bind to multiple antigens at the ...
2023-11-27
ITHACA, N.Y. – Bitcoin mining is often perceived as environmentally damaging because it uses huge amounts of electricity to power its intensive computing needs, but a new study demonstrates how wind and solar projects can profit from bitcoin mining during the precommercial development phase — when a wind or solar farm is generating electricity, but has not yet been integrated into the grid.
The findings suggest some developers could recoup millions of dollars to potentially invest in future renewable energy projects.
The ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Increasing high-temperature strength of materials through collaborative efforts of AI and materials researchers
Optimizing thermal aging schedules by analyzing the unconventional AI-driven outcomes