(Press-News.org) Publications on sugarcane have increased exponentially since 2006 worldwide, and Brazil has had more articles published on the topic than any other country in the period, according to a review in BioEnergy Research.
The number of articles on the subject averaged about five per year between 1999 and 2006 but had reached 327 by 2021. Brazil has twice as many articles on sugarcane as the United States, which ranks first in the world for scientific publications in general. Brazil is also ahead of Australia, China and India, which are also major sugarcane growers.
According to the authors of the review, who are affiliated with the Laboratory of Plant Physiological Ecology (LAFIECO) at the University of São Paulo’s Institute of Biosciences (IB-USP), these statistics highlight Brazil’s importance to global sustainability efforts.
“Sugarcane is one of Brazil’s main tools for coping with climate change as ethanol from sugarcane is one of the most important renewable biofuels that can replace fossil fuels. However, there isn’t enough ethanol in the world. More needs to be produced, and this requires genetic improvement of sugarcane,” said Marcos Buckeridge, last author of the review and head of LAFIECO.
The study was funded by FAPESP via three projects (19/13936-0, 22/05524-7 and 22/00441-6).
The review also discusses the history of sugarcane genetic improvement in Brazil from the arrival of the Portuguese to the currently available varieties. “Despite all the improvement, the genetic engineering strategies applied to sugarcane need to advance further compared to other crops. Moreover, we’ve reached a limit in genetic terms: we’ll have to increase the number of cells or their size for the plant to store more sugar, and this requires sophisticated techniques. Big data, advanced analytical methods, bioinformatics and substantial computational resources, among others, are needed to help improve sugarcane’s physiological performance and yield without expanding crop acreage,” Buckeridge explained.
Challenges ahead
Scientists all over the world who aim to control the behavior of sugarcane with precision and leverage its potential to help cope with the extreme droughts and floods that are part of climate change face two challenges. The first is the need for better genome sequencing. In Brazil, this effort is being led by Diego Pachon, a researcher at the University of São Paulo’s Center for Nuclear Energy in Agriculture (CENA-USP).
Once precise whole genome sequencing of sugarcane is successfully obtained, the next step will be to develop techniques capable of making specific modifications in the genome. The main hope for most scientists resides in CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing, currently being tested by Marcelo Menossi, a researcher at the State University of Campinas’s Institute of Biology (IB-UNICAMP).
Progress has also been achieved in the field in recent years in other major sugarcane production and research centers, such as the United States, India and Australia.
The review of the literature conducted by LAFIECO was supported by INCT Bioethanol, one of the National Institutes of Science and Technology (known as INCTs, the Portuguese-language acronym) in São Paulo state funded by FAPESP and the National Scientific and Technological Development Council (CNPq) – and the Research Center for Greenhouse Gas Innovation (RCGI), an Engineering Research Center (ERC) established by FAPESP and Shell at the University of São Paulo’s Engineering School (POLI-USP).
About São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP)
The São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) is a public institution with the mission of supporting scientific research in all fields of knowledge by awarding scholarships, fellowships and grants to investigators linked with higher education and research institutions in the State of São Paulo, Brazil. FAPESP is aware that the very best research can only be done by working with the best researchers internationally. Therefore, it has established partnerships with funding agencies, higher education, private companies, and research organizations in other countries known for the quality of their research and has been encouraging scientists funded by its grants to further develop their international collaboration. You can learn more about FAPESP at www.fapesp.br/en and visit FAPESP news agency at www.agencia.fapesp.br/en to keep updated with the latest scientific breakthroughs FAPESP helps achieve through its many programs, awards and research centers. You may also subscribe to FAPESP news agency at http://agencia.fapesp.br/subscribe.
END
Review article shows key role of Brazil in research on sugarcane for bioenergy
The study by researchers at the University of São Paulo also shows that genetic engineering techniques need to be improved in order to increase ethanol production without expanding crop acreage, a strategy considered crucial to cope with climate change
2023-11-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Cellular postal service delivers messages from non-human cells, too
2023-11-27
Messenger bubbles produced by human cells can pick up bacterial products and deliver them to other cells, University of Connecticut researchers report in the Nov. 16 issue of Nature Cell Biology. The discovery may explain a key mechanism by which bacteria, whether friendly or infectious, affect our health.
Extra-cellular vesicles (EVs) are like a postal service for our cells. Cells produce the EVs, tiny bubbles with a water-resistant shell made of fatty substances called lipids, and send them into the bloodstream. When another cell comes across an EV, it takes it inside itself ...
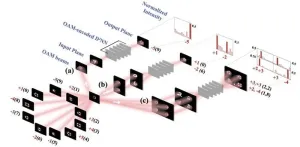
Orbital-angular-momentum-encoded diffractive networks for object classification tasks
2023-11-27
Deep learning has revolutionized the way we perceive and utilize data. However, as datasets grow and computational demands increase, we need more efficient ways to handle, store, and process data. In this regard, optical computing is seen as the next frontier of computing technology. Rather than using electronic signals, optical computing relies on the properties of light waves, such as wavelength and polarization, to store and process data.
Diffractive deep neural networks (D2NN) utilize various properties of light waves to perform tasks like image and object recognition. Such networks consist of two-dimensional pixel arrays as diffractive layers. Each pixel serves as an adjustable ...
Gig workers saw greater financial hardship during COVID-19 compared to other workers
2023-11-27
Many gig workers experienced financial hardships during the COVID-19 pandemic, including food insecurity and trouble paying bills, according to a recent study published in Work and Occupations.
“In a nutshell, our study shows gig workers were harmed more by the COVID-19 pandemic than any other workers,” said Dr. Mathieu Despard, a co-author on the paper and faculty member in UNC Greensboro’s Department of Social Work.
Despard – who collaborated closely with first author Daniel Auguste ...
CU Anschutz scientists create patch that may successfully treat congenital heart defects
2023-11-27
AURORA, Colo. (Nov. 27, 2023) – Using laboratory engineered tissue, scientists at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus have created a full thickness, biodegradable patch that holds the promise of correcting congenital heart defects in infants, limiting invasive surgeries and outlasting current patches.
The findings were published this week in the journal Materials Today.
“The ultimate goal is to make lab-grown heart tissue from a patient’s own cells that can be used to restructure the heart to correct for heart defects,” said the ...
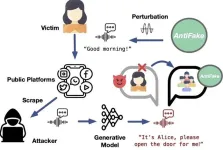
Defending your voice against deepfakes
2023-11-27
Recent advances in generative artificial intelligence have spurred developments in realistic speech synthesis. While this technology has the potential to improve lives through personalized voice assistants and accessibility-enhancing communication tools, it also has led to the emergence of deepfakes, in which synthesized speech can be misused to deceive humans and machines for nefarious purposes.
In response to this evolving threat, Ning Zhang, an assistant professor of computer science and engineering at the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University ...
Revolutionizing cancer treatment through programmable bacteria
2023-11-27
What if a single one-dollar dose could cure cancer?
A multi-university team of researchers, supported by federal funding, is developing a highly efficient bacterial therapeutic to target cancer more precisely to make treatment safer through a single $1 dose.
Traditionally, cancer therapies have been limited in their efficacy in treating patients. Some, like radiation and chemotherapy, cause harmful side effects, while others tend to result in low patient responsiveness, not to mention the cost it takes to receive treatment. Findings from the American Cancer Society Cancer Action Network recorded ...
One protein is key to the spread of lung cancer. Now, a new study has found a way to stop it
2023-11-27
A new study by Tulane University has uncovered a previously unknown molecular pathway that could be instrumental to halting lung cancer in its tracks.
Lung cancer is one of the most common cancers and the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the world. The research, published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, could lead to the development of a new anti-cancer drug and more personalized lung cancer treatment, said senior study author Dr. Hua Lu, the Reynolds and Ryan Families Chair in Translational Cancer at the Tulane University School of Medicine.
The study found ...
Study: Spike in premature births caused by COVID, halted by vaccines
2023-11-27
MADISON, Wis. — COVID-19 caused an alarming surge in premature births, but vaccines were key to returning the early birth rate to pre-pandemic levels, according to a new analysis of California birth records.
“The effect of maternal COVID infection from the onset of the pandemic into 2023 is large, increasing the risk of preterm births over that time by 1.2 percentage points,” says Jenna Nobles, a University of Wisconsin–Madison sociology professor. “To move the needle on preterm birth that much is akin to a disastrous ...
Why does puberty trigger us to stop growing?
2023-11-27
All animals start out as a single-celled organism and then start growing. At some point, of course, they need to stop getting bigger, but the process by which this happens is poorly understood.
New research from Alexander Shingleton at the University of Illinois Chicago and colleagues identifies a potential trigger that makes fruit flies stop growing, which has implications for understanding human development. The research is published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
In humans, the body’s signal to stop growing happens around puberty, though it takes several more years before growth actually ceases. It is important to better ...
Maternal vaccination against COVID-19 lowered risk of preterm births, Stanford study finds
2023-11-27
During the first two years of the pandemic, a COVID-19 infection during pregnancy increased the risk of preterm birth and NICU hospitalizations. However, by 2022, when COVID-19 vaccines were readily available in the United States, this effect disappeared – suggesting that vaccination against the coronavirus may have prevented thousands of preterm births, according to a new study led by Stanford sociologist Florencia Torche.
The study’s findings, published Nov. 27 in the journal Proceedings of the National ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Review article shows key role of Brazil in research on sugarcane for bioenergyThe study by researchers at the University of São Paulo also shows that genetic engineering techniques need to be improved in order to increase ethanol production without expanding crop acreage, a strategy considered crucial to cope with climate change