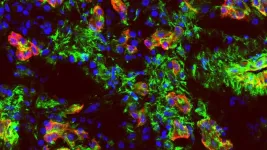
(Press-News.org) Recent findings at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) shine a new light on pancreatic cancer.
More than 90% of pancreatic cancer cases are attributed to an aggressive, deadly form of the disease called pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, or PDAC. Researchers have a poor understanding of how our immune system interacts with PDAC. So, coming up with treatments is tricky. It’s thought patients do not show a natural immune response to the cancer because the tumor environment somehow prevents that response. Many are unconvinced that PDAC interacts with the immune system at all.
CSHL scientists have now confirmed that pancreatic cancer does trigger a response in our immune system. However, the T cells that help fight off most diseases have a hard time infiltrating PDAC tumors. These findings could help guide future efforts for developing treatments.
For this study, CSHL Professor Douglas Fearon worked with a team including lead author Min Yao, Professor Matthew Weiss from the Zucker School of Medicine, and CSHL Partners for the Future program participant Sophia Shen from Cold Spring Harbor High School. They first set out to find a new antigen present only in PDAC tumors and not in normal tissue. The body makes cells called antibodies that recognize specific antigens and help destroy them. Identifying a new PDAC antigen could help explain why some patients have better outcomes than others.
The team sequenced plasma cells in pancreatic tumor samples taken from seven Northwell Health patients. They then created synthetic antibodies based on that sequence. The idea was that the synthetic antibodies would point the team toward the new PDAC antigen behind the body’s immune response. But they didn’t find the one they were looking for. Instead, they found 25 antibodies that responded to antigens from cancer cells and normal cells produced in the body. These antibodies were consistent across patients.
“I was surprised at the clarity of the data, that we had a number of antibodies react with the same antigen from multiple patients,” Fearon says.
Previously, researchers had believed that pancreatic cancer suppresses immunity. Some have even explored vaccination as a possible solution. Based on his team’s findings, Fearon says that strategy likely isn’t needed.
“Pancreatic cancer is not immunologically silent. That’s the message," explains Fearon. "Pancreatic tumors are already immunogenic. We have a challenge in allowing the immune response to attack the cancer.”
Now that scientists better understand the problem, they can try to develop workable solutions. For the pancreatic cancer community, that’s real progress and a welcome development unto itself.
END
Can we crack this cancer’s immune response?
2023-11-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Building blocks for life could have formed near new stars and planets
2023-11-29
While life on Earth is relatively new, geologically speaking, the ingredients that combined to form it might be much older than once thought. According to research published in ACS Central Science, the simplest amino acid, carbamic acid, could have formed alongside stars or planets within interstellar ices. The findings could be used to train deep space instruments like the James Webb Space Telescope to search for prebiotic molecules in distant, star-forming regions of the universe.
It has long been hypothesized that one of the building blocks for life, amino acids, could have formed during reactions in the “primordial ...
Uttam Superrhiza named as winner of Applied Microbiology International Product of the Year 2023
2023-11-29
Mycorrhiza biofertilizer Uttam Superrhiza has been named as the winner of the Applied Microbiology International Product of the Year 2023.
The prestigious prize recognizes a commercial product derived from microbiology research, with special consideration given to those products that have addressed the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals.
Uttam Superrhiza, marketed by Chambal Fertilizers and Chemicals Limited in India, is manufactured by the not-for-profit institute, The Energy and Resources Institute (TERI).
Disruptive mycorrhiza
A disruptive ...
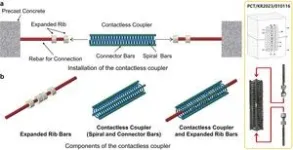
Contactless Coupler, the innovation and advancement in the connection of precast concrete member
2023-11-29
The Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology (KICT, President Kim, Byung-Suk) has developed a new Contactless Coupler that can efficiently improve the constructability of precast concrete (hereinafter referred to as PC).
Recently, Off-site Construction (OSC) has been actively used worldwide to solve the problems at complex construction sites. The OSC method minimizes on-site work by prefabricating parts of the structure and then simply assembling and constructing them on-site. In particular, Korean construction sites are promoting OSC to solve the problem of aging skilled workers and labor shortages.
The PC method, one of the representative OSC methods, is a method ...
Swapping blood for spit — for convenient at-home health monitoring
2023-11-29
Blood tests are a common, yet often painful, step in health care. But what if we could skip the needles altogether? Saliva and blood contain many of the same biomarkers, and collecting spit is as simple as drooling into a container. Researchers reporting in ACS Sensors have developed a device that detects glucose and adenosine monophosphate (AMP) biomarkers in saliva with high sensitivity, which could help make at-home health monitoring easier and without a poke.
Blood tests provide critical information about a person’s health. But they also rely on uncomfortable procedures, ranging from collecting small blood samples through frequent finger pricks to blood draws from ...
Conscientious personalities less at risk of dementia diagnosis
2023-11-29
People with personality traits such as conscientiousness, extraversion and positive affect are less likely to be diagnosed with dementia than those with neuroticism and negative affect, according to a new analysis by researchers at the University of California, Davis and Northwestern University. The difference was not linked to physical damage to brain tissue found in dementia patients, but more likely to how certain personality traits help people navigate dementia-related impairments.
The work is published Nov. ...
AI may aid in diagnosing adolescents with ADHD
2023-11-29
CHICAGO – Using artificial intelligence (AI) to analyze specialized brain MRI scans of adolescents with and without attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), researchers found significant differences in nine brain white matter tracts in individuals with ADHD. Results of the study will be presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
ADHD is a common disorder often diagnosed in childhood and continuing into adulthood, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. In the U.S., an estimated 5.7 million children and adolescents between the ages of 6 and 17 have been diagnosed with ADHD.
“ADHD often ...
Common headaches tied to neck inflammation
2023-11-29
CHICAGO – Researchers have identified objective evidence of how the neck muscles are involved in primary headaches, according to a study being presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA). The findings could lead to better treatments.
The distinct underlying causes of primary headaches are still not fully understood. The most common primary headaches are tension-type headaches and migraines.
“Our imaging approach provides first objective evidence for the very frequent involvement of the neck muscles in primary headaches, such as neck pain ...
AI model predicts breast cancer risk without racial bias
2023-11-29
CHICAGO – A deep learning artificial intelligence (AI) model that was developed using only mammogram image biomarkers accurately predicted both ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and invasive carcinoma, according to research being presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA). Additionally, the model showed no bias across multiple races.
Traditional breast cancer risk assessment models use information obtained from patient questionnaires, such as medical and reproductive history, to calculate a patient’s future risk of developing breast cancer.
“In ...
Coronary heart disease before age 45 may increase risk of dementia later in life
2023-11-29
Research Highlights:
People diagnosed with coronary heart disease had a significantly increased risk of developing dementia later in life, according to an analysis of data for more than 430,000 people from the UK Biobank.
Participants who had coronary heart disease before age 45 had a 36% increased risk of developing dementia, a 13% increased risk of developing Alzheimer’s and a 78% greater risk of developing vascular dementia compared with participants who did not have coronary heart disease.
Men and women diagnosed with coronary heart disease before age 45 were significantly more likely to develop dementia than their counterparts who ...
One in seven male gym goers consider impact on fertility
2023-11-29
Young male gym users are largely unaware of the risks of their lifestyle on their fertility, a new study shows.
New results from a survey of 152 gym enthusiasts, published in Reproductive BioMedicine Online found that men were largely unaware of the risks to their fertility from aspects of gym lifestyle including protein supplements, which can contain high levels of estrogen, used by 79% of male respondents.
When questioned about their concern about fertility, more than half (52%) of male participants said that they had thought about their ...