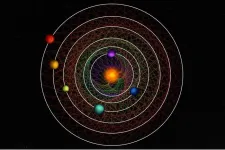
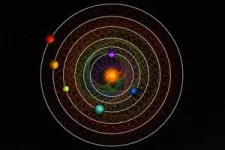
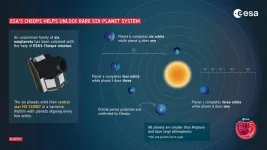
(Press-News.org) Scientists have discovered a rare sight in a nearby star system: Six planets orbiting their central star in a rhythmic beat. The planets move in an orbital waltz that repeats itself so precisely it can be readily set to music.
A rare case of an “in sync” gravitational lockstep, the system could offer deep insight into planet formation and evolution.
The analysis, led by UChicago scientist Rafael Luque, will be published Nov. 29 in Nature.
“This discovery is going to become a benchmark system to study how sub-Neptunes, the most common type of planets outside of the solar system, form, evolve, what are they made of, and if they possess the right conditions to support the existence of liquid water in their surfaces,” said Luque.
A rare resonance
The six planets orbit a star known as HD110067, which lies around 100 light-years away in the northern constellation of Coma Berenices.
In 2020, NASA’s Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) detected dips in the star’s brightness that indicated planets were passing in front of the star’s surface. Combining data from both TESS and the European Space Agency’s CHaracterising ExOPlanet Satellite (Cheops), a team of researchers analyzed the data and discovered a first of its kind configuration.
While multi-planet systems are common in our galaxy, those in a tight gravitational formation known as “resonance” are observed by astronomers far less often.
In this case, the planet closest to the star makes three orbits for every two of the next planet out – called a 3/2 resonance – a pattern that is repeated among the four closest planets. Among the outermost planets, a pattern of four orbits for every three of the next planet out (a 4/3 resonance) is repeated twice.
And these resonant orbits are rock-solid: The planets likely have been performing this same rhythmic dance since the system formed billions of years ago, the scientists said.
Formation stories
Orbitally resonant systems are extremely important to find because they tell astronomers about the formation and subsequent evolution of the planetary system. Planets around stars tend to form in resonance but can be easily perturbed. For example, a very massive planet, a close encounter with a passing star, or a giant impact event can all disrupt the careful balance. As a result, many of the multi-planet system known to astronomers are not in resonance but look close enough that they could have been resonant once. However, multi-planet systems preserving their resonance are rare.
“We think only about one percent of all systems stay in resonance, and even fewer show a chain of planets in such configuration,” said Luque. That why HD110067 is special and invites further study: “It shows us the pristine configuration of a planetary system that has survived untouched.”
More precise measurements of these planets’ masses and orbits will be needed to further sharpen the picture of how the system formed.
END
Scientists discover rare 6-planet system that moves in strange synchrony
Study led by UChicago astronomer Rafael Luque may tell us about how planets form
2023-11-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Disruptive ideas rely on old fashioned meetings
2023-11-29
A marvel of modernity is the ability to collaborate with others regardless of location. Researchers can work with a colleague, maybe the only person who has a specialized skill, even if they are halfway across the globe. They can pull together a powerhouse team with a dozen of the brightest minds in the field.
Yet, according to research from the lab of Lingfei Wu, assistant professor in Pitt’s School of Computing and Information, these collaborative teams are producing fewer truly disruptive ideas or radical innovations than ...
An astronomical waltz reveals a sextuplet of planets
2023-11-29
An international collaboration between astronomers using the CHEOPS and TESS space satellites, including NCCR PlanetS members from the University of Bern and the University of Geneva, have found a key new system of six transiting planets orbiting a bright star in a harmonic rhythm. This rare property enabled the team to determine the planetary orbits which initially appeared as an unsolvable riddle.
CHEOPS is a joint mission by ESA and Switzerland, under the leadership of the University of Bern in collaboration with the University of Geneva. Thanks to a collaboration with scientists ...
Final call for Awards Nominations 2024 of the World Cultural Council
2023-11-29
The World Cultural Council (WCC) is now accepting nominations for the “Albert Einstein” World Award of Science and the “Leonardo da Vinci” World Awards of Arts.
Nominations must be submitted by 26 January, 2024. NOMINATE NOW: To nominate online or for further details of the awards visit the WCC website Nominations page.
Ideal candidates for the “Albert Einstein” World Award of Science are scientists whose achievements can serve as an inspiration for future generations. This award is granted each year. Consideration will be given to ...
BU/VA researcher awarded funding to prevent intimate partner violence
2023-11-29
(Boston)—Casey Taft, PhD, professor of psychiatry at Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine, has been approved for a five-year, $2.8 million funding award from the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) for his research study “A Randomized Controlled Trial to Evaluate a Trauma-Informed Partner Violence Intervention Program.”
Taft, who also is a staff psychologist at the National Center for PTSD in the VA Boston Healthcare System, is conducting a randomized controlled trial of the Strength at Home program to prevent and end intimate partner violence (IPV) in Rhode Island. Strength at Home ...
The act of saying "no" under the linguistic magnifying glass
2023-11-29
FRANKFURT. Prof. Bernhard Brüne, Vice President Research, Early Career Researchers and Transfer at Goethe University Frankfurt, congratulated the researchers involved in the successful application: "Anyone who establishes a major project like a Collaborative Research Center must have both creative and viable research ideas as well as a strong network. To discover new things about language and thinking, the new CRC 1629 not only makes use of Goethe University’s structures, and the combination of philology with philosophy and didactics. It also cooperates with partner universities in Göttingen and Tübingen. Aside that, I am of course delighted that ...
Insilico Medicine showcases latest AI drug discovery platform breakthroughs
2023-11-29
Insilico Medicine (“Insilico”), an artificial intelligence (AI)-driven, clinical stage biotechnology company and leader in AI drug discovery platform technology, is hosting three webinars unveiling its latest technology breakthroughs Nov. 28-30, 2023. These new features are part of the expansion of the Company’s end-to-end Pharma.AI platform and include chat functionality, off-target screening tools, enhanced knowledge graphs and more. They represent major steps forward in the advancement of AI drug discovery.
The company is an early ...
New astrophysics model sheds light on additional source of long gamma-ray bursts
2023-11-29
Cutting-edge computer simulations combined with theoretical calculations are helping astronomers better understand the origin of some of the universe’s most energetic and mysterious light shows — gamma-ray bursts, or GRBs. The new unified model confirms that some long-lasting GRBs are created in the aftermath of cosmic mergers that spawn an infant black hole surrounded by a giant disk of natal material.
Astronomers previously thought that black holes that generate long GRBs typically form when massive ...
Brain scans of former NFL athletes show a repair protein in place long after initial injury
2023-11-29
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
In a new study using brain scans of former NFL athletes, Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers say they found high levels of a repair protein present long after a traumatic brain injury such as a concussion takes place. The repair protein, known as 18 kDa translocator protein (TSPO), is known to be present in the brain at high levels in the immediate aftermath of brain injury as part of the inflammatory response and to facilitate repair. The new findings, published Oct. 30 in JAMA Network Open, suggest that brain injury and repair processes persist for years after players end collision sports careers, and lead to long-term cognitive ...
Long-live quantum entanglement goes to distance
2023-11-29
Quantum technologies are currently maturing at a breath-taking pace. These technologies exploit principles of quantum mechanics in suitably engineered systems, with bright prospects such as boosting computational efficiencies or communication security well beyond what is possible with devices based on today’s 'classical' technologies. As with classical devices, however, to realise their full potential, quantum devices will need to be networked. In principle, this can be done using the fibre-optic networks employed for classical telecommunications. But practical implementation requires that the information ...
To build better tuberculosis vaccines, Saint Louis University researchers develop a new model by leveraging an old vaccine
2023-11-29
ST. LOUIS – Each year, tuberculosis (TB) kills more people than any other infectious disease, falling out of the top spot only temporarily during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Despite TB’s wide reach and some lost progress during the COVID-19 pandemic, researchers believe it is possible to eradicate TB through advances in vaccine development and public health. To cross the finish line, scientists must find ways to test new vaccines rapidly to prevent TB infections more effectively.
In a paper published in the Journal of Infectious Diseases, Daniel Hoft, M.D., Ph.D., ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
[Press-News.org] Scientists discover rare 6-planet system that moves in strange synchronyStudy led by UChicago astronomer Rafael Luque may tell us about how planets form