(Press-News.org) Biliary tract cancers (BTCs) including cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) and gallbladder cancer (GBC) are becoming more prevalent globally. An effective chemotherapeutic agent for the treatment of BTCs is gemcitabine. Other novel molecular targeted drugs have also been developed; however, they are only effective at treating a few cases of BTCs. In addition, very few drugs are effective against GEM-resistant BTCs. While surgery is the best option for the treatment of BTCs, many patients are diagnosed late, due to a lack of symptoms. Another challenge for physicians treating BTCs is identifying an appropriate treatment approach due to the complexity of the hepatobiliary-pancreatic system. Therefore, developing novel treatment strategies for BTCs, especially for GEM-resistant BTCs, is the need of the hour.
Nucleic acid-based therapies built around microRNAs (miRNAs) are the next frontier of cancer treatment. miRNAs play a role in gene expression, and their dysregulation is believed to contribute to cancer pathogenesis. Now, researchers from Japan are exploring the prospects of microRNA-451a (miR-451a), a miRNA identified in gallbladder tissue, as a viable targeted nucleic acid BTC therapy. The team, led by Assistant Professor Koichiro Tsutsumi, along with Dr. Taisuke Obata and Dr. Motoyuki Otsuka, all from the Department of Gastroenterology Okayama University Hospital, Japan, recently uncovered the mechanism of miR-451a’s antineoplastic effects. Their findings were published in Molecular Therapy: Nucleic Acids on 28 October 2023.
“Apart from gemcitabine, very few effective drugs are available for the treatment of BTCs. Therefore, there is an urgent need for new therapies. Additionally, we don’t know a lot about the miRNA targets that can be used to improve the prognosis of BTCs, especially in the context of resistance to GEM,” explains Dr. Tsutsumi while discussing his motivation behind this research.
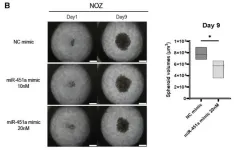
The team had evidence from previous experiments that miR-451a was downregulated in patients with GBC, and they decided to build on other research that showed that the miRNA inhibited cell proliferation when introduced into human GBC cells. They transfected miR-451a into GBC, gemcitabine-resistant GBC (GR-GBC), and gemcitabine-resistant CCA (GR-CCA) cells to understand its effects on tumor progression. They also studied the gene expression profile in these three groups following transfection, to gauge how cell-signaling pathways were altered by miR-451a.
“Under experimental conditions that mimicked those of the cancer environment, we found that miR-451a significantly diminished cell proliferation, induced cell death, and reduced the occurrence of chemoresistant cell types in GBC, GR-CCA, and GR-GBC cells,” says Dr. Tsutsumi. He adds, “One of the factors known to promote metastasis and chemoresistance was the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT pathway. This pathway was suppressed partially through the downregulation of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) after the transfection of miR-451a. These findings underpin miR-451a’s use as a replacement therapy for GEM-resistant BTCs.” miR-451a’s effects at the molecular level were reflected in 2D or 3D cell culture experiments where GR-CCA and GR-GBC cells were rendered less viable following treatment.
Dr. Tsutsumi is looking to the future, and the group is planning future studies to evaluate the effective delivery of miR-451a and validate its clinical application. He concludes, “Nucleic acid-based treatments are not mature enough to be considered first-line treatments for BTCs, so chemotherapy and immunotherapy still have their place. However, given miR-451a’s antineoplastic activity against GEM-resistant BTCs, I anticipate them to be mainstream alternatives with further developments.”
About Okayama University, Japan
As one of the leading universities in Japan, Okayama University aims to create and establish a new paradigm for the sustainable development of the world. Okayama University offers a wide range of academic fields, which become the basis of integrated graduate schools. This not only allows us to conduct the most advanced and up-to-date research, but also provides an enriching educational experience.
Website: https://www.okayama-u.ac.jp/index_e.html
About Assistant Professor Koichiro Tsutsumi from Okayama University, Japan
Dr. Koichiro Tsutsumi is an Assistant Professor in the Department of Gastroenterology at Okayama University Hospital. He earned his Doctor of Medicine from Tohoku University in 2001, and Doctor of Philosophy from Okayama University in 2013. His research explores themes across gastroenterology, tumor diagnostics and therapeutics. Dr. Tsutsumi has published over 120 peer-reviewed articles since 2003 and received the Japanese Biliary Society International Exchange Encouragement Award in 2016.
END
A novel targeted molecular therapy for drug-resistant biliary tract cancer
Researchers from Japan uncover the effects and mechanism of a microRNA that suppresses the progression of gemcitabine-resistant biliary tract cancers
2023-11-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Money to burn: Wealthy, white neighborhoods losing their heat shields
2023-11-30
White, wealthy neighborhoods in the LA area are about to start feeling the same heat that has plagued poorer, Hispanic neighborhoods for generations. A new study shows the protective effect of income has largely eroded over the past 40 years, as landscape plants can’t keep up with the pace of climate warming.
Published in the journal Urban Climate, the research cuts across neighborhoods, income levels, and race in the Los Angeles area between 1985 and 2021. It reveals a troubling forecast for city dwellers: it’s becoming unbearably hot, ...
Children who play baseball risk elbow injury
2023-11-30
CHICAGO – Youth baseball players are prone to elbow pain and injuries, including repetitive overuse changes and fractures, based on the maturity of their bones, according to a new study being presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
The repetitive motion and force of throwing a baseball places a large amount of stress on the growing bones, joints and muscles of the elbows of baseball players. Youth baseball players who have not yet reached skeletal maturity might be especially vulnerable to elbow pain and injuries.
“When we look at the forces that baseball players, even ...
Regular screening mammograms significantly reduce breast cancer deaths
2023-11-30
CHICAGO – Breast cancer mortality is significantly reduced when women regularly attend screening mammograms, according to research being presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Early detection of breast cancer, before symptoms are present, is key to survivability. According to the American Cancer Society, women between the ages of 45 and 54 should get mammograms every year. Women who are 55 years and older can switch to every other year or continue with annual mammograms. Skipping just one scheduled mammogram could result ...
Brain waves usually found in sleep can protect against epileptic activity
2023-11-30
Slow waves that usually only occur in the brain during sleep are also present during wakefulness in people with epilepsy and may protect against increased brain excitability associated with the condition, finds a new study led by researchers at UCL.
The research, published in Nature Communications and involving the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) UCLH Biomedical Research Centre, examined electroencephalogram (EEG) scans from electrodes in the brains of 25 patients with focal epilepsy (a type of epilepsy characterised by seizures arising from a specific part of the brain), while they carried out an associative memory task.
The electrodes ...
Loss of auditory nerve fibers uncovered in individuals with tinnitus
2023-11-30
A new study from Mass Eye and Ear investigators shows that individuals who report tinnitus, which present as a ringing in the ears in more than one out of ten adults worldwide, are experiencing auditory nerve loss that is not picked up by conventional hearing tests. This work is part of a P50 grant awarded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to Mass Eye and Ear researchers within the Eaton-Peabody Laboratories (EPL) for their work on cochlear synaptopathy, which is commonly referred to as “hidden hearing loss.” The results from this study provide a better understanding on the origins of tinnitus and are published ...
Li Chan announced as winner of the 2024 European Journal of Endocrinology (EJE) Award
2023-11-30
The European Society of Endocrinology (ESE) is delighted to announce that the 2024 European Journal of Endocrinology (EJE) Award has been awarded to Professor Li Chan.
Li Chan is Professor of Molecular Endocrinology and Metabolism at the Centre for Endocrinology, William Harvey Research Institute, at the Queen Mary University of London.
The European Journal of Endocrinology Award is presented to a candidate who has significantly contributed to the advancement of knowledge in the field of endocrinology through publication.
Professor Chan has been undertaking world class research in the biology ...
Large language model shows promise in helping clinicians identify postpartum hemorrhage
2023-11-30
Postpartum hemorrhage is the leading cause of maternal mortality and morbidity worldwide and a common pregnancy complication. This serious medical condition is understudied and not universally defined or well represented in health records. A new study by investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, used the large language model Flan-T5 to extract medical concepts from electronic health records in order to better define and identify the populations impacted by postpartum hemorrhage.
The study found the model to be 95 percent accurate in identifying patients with the condition, and resulted ...
Protected droplets a new transport route for medicines
2023-11-30
Microgels form a thin protective shell around a droplet until the temperature rises above 32 degrees. Then the microgels shrink and the droplet dissolves in the surrounding liquid. A study by researchers from the University of Gothenburg now reveals the underlying mechanism behind this process. The discovery could revolutionise methods of targeting medicines to specific locations within the body.
Emulsions consist of numerous droplets that are present in a liquid without dissolving and mixing with the liquid. For example, milk consists of fat droplets stabilised by milk proteins that are dispersed in water. In many applications ...
Rice husk and recycled newspaper may be the eco-friendly insulation material of the future
2023-11-30
The building sector is the second largest sector in plastic consumption and is responsible for more than a third of energy related greenhouse gas emissions worldwide. Manufacturing processes of construction materials pollute air, land, and water. Accordingly, construction materials made from agro-industrial waste become increasingly attractive due to their lower environmental impact.
To contribute to a new generation of materials made from what is often considered waste, researchers in Panama have now developed a rice husk-based insulation material and evaluated its thermal and mechanical ...
Tufts University launches first undergrad degree in cellular agriculture
2023-11-30
In his Value Creation project in Cell Ag class, Tufts senior Adham Ali faced an intriguing assignment: work with a group of peers to design a product that uses cellular agriculture (or cell ag, for short) to make life easier for consumers.
Majoring in biochemistry, Ali took the class as part of his minor in cell ag—a minor he registered for only this semester, because it’s brand-new at Tufts.
It’s also the world’s first and only undergraduate degree in the field.
Usually used as part of a nascent—and rapidly growing—field that cultivates lab-grown meat from cells in bioreactors, the processes of cellular agriculture can ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
[Press-News.org] A novel targeted molecular therapy for drug-resistant biliary tract cancerResearchers from Japan uncover the effects and mechanism of a microRNA that suppresses the progression of gemcitabine-resistant biliary tract cancers