(Press-News.org) Polar bears are icons of the Arctic, elusive and vulnerable. Detailed monitoring of their populations is crucial for their conservation — but because polar bears are so difficult to find, we are missing critical data about population size and how well connected those populations are. Scientists have now developed a new tool to help: DNA analysis using skin cells shed in the bears’ footprints in the snow.
“It is particularly challenging, expensive, and time-consuming to find polar bears in the Arctic, let alone count them and understand how they are coping with climate change,” said Dr Melanie Lancaster of the World Wide Fund for Nature Global Arctic Programme, senior author of the study in Frontiers in Conservation Science.
Every contact leaves a trace
The scientists were inspired by forensic techniques which can be applied to tiny, degraded DNA samples. With these techniques, it isn’t necessary to physically capture bears, which can be stressful and dangerous for both bears and humans, and is a source of concern to some local Indigenous communities. Instead, scientists can look at sources of DNA shed in passing — environmental DNA.
“Many Inuit express concern about invasive research methods,” said Elisabeth Kruger of the World Wildlife Fund, an author of the article. “People are concerned about the welfare of the individual polar bear and the health and safety of people who may harvest the bear later. This is one of the reasons we are so excited about new methods like this - the person collecting the sample never needs to even see or be seen by the polar bear.”
A common form of environmental DNA is deposited when animals defecate. However, the DNA quality is not always good enough for the individual-level analysis needed for conservation. Additionally, for territorial animals like the two other species the scientists tested — lynxes and snow leopards — sampling feces could affect the animals’ behavior. So the researchers turned to skin cells in snowy footprints.
“The tracks usually contain fresh cells, and the DNA is intact because of the cold ‘storage’ temperature. DNA that has passed the gut is much more degraded and therefore more challenging to work on,” said Dr Micaela Hellström of MIX Research Sweden AB, lead author.
Walking in their footsteps
The scientists collected snow from individual tracks made by Alaskan polar bears and Swedish Eurasian lynxes in the wild and in captivity. They also collected snow from tracks made by a captive snow leopard. Additional materials like hair, saliva, and mucus were sampled, confirming that the tracks provided accurate genotypes.
24 wild polar bear tracks and 44 wild lynx tracks were sampled. The researchers melted and filtered the snow to collect environmental DNA, then carried out microsatellite analysis. Although the concentrations of DNA retrieved from tracks sampled in the wild were very low, it was possible to retrieve nuclear DNA from 87.5% of wild polar bear tracks and 59.1% of wild lynx tracks. 13 of the wild polar bear samples could be genotyped, identifying 12 different individuals.
11% of the lynx tracks could be genotyped, but when the scientists only looked at the tracks sampled by trained personnel, this rose substantially. They were able to retrieve nuclear DNA from 76% of samples collected by trained personnel, and to genotype 24% of those sampled.
A paws-off approach
This technique has huge potential to inform conservation of these animals, to better understand their populations and behavior, and to manage conflict with humans through accurate identification of animals. Although non-invasive sampling has a lower success rate, ease of collection means that it can significantly expand sample sizes.
“We hope this method will be taken up by the polar bear research community, with the involvement of hunters, volunteers, and Indigenous communities, as a new way to collect information on polar bears,” said Lancaster. “We also hope the method will be expanded to other animals living in snowy environments — we have shown it works for lynx and snow leopards as a start.”
END
Following in polar bears' footprints: DNA from snow tracks could help monitor threatened animals
Scientists have found a way of capturing DNA from snow tracks — a promising non-invasive method of monitoring elusive animals like polar bears
2023-12-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
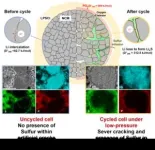
Investigation of degradation mechanism for all-solid-state batteries takes another step toward commercialization
2023-12-04
Often referred to as the ‘dream batteries’, all-solid-state batteries are the next generation of batteries that many battery manufacturers are competing to bring to market. Unlike lithium-ion batteries, which use a liquid electrolyte, all components, including the electrolyte, anode, and cathode, are solid, reducing the risk of explosion, and are in high demand in markets ranging from automobiles to energy storage systems (ESS). However, devices that maintain the high pressure (tens of MPa) required for stable operation of all-solid-state batteries have problems that reduce the battery performance, such as energy density and capacity, ...
Decoding flavonoid metabolism: a closer look at plant-based diets
2023-12-04
In a world where plant-based lifestyles are on the rise, the power of foods such as broccoli, celery, and tofu, which are rich in flavonoids, is becoming clearer. Flavonoids are phenolic compounds produced by plants that are essential for plant development and defense and have long been said to have therapeutic and preventive effects against cancer and heart disease. However, the exact process of how our bodies metabolize flavonoids remains unclear.
An international team of researchers led by visiting researcher Tsutomu Shimada and Professor Shigeo ...
New rule for emergency departments to safely reduce use of CTs after falls in older patients
2023-12-04
How do emergency department staff determine whether older adults who have fallen need imaging? A new decision rule will help emergency department physicians determine which older adults need imaging for head injuries, describes new research in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.230634.
With aging populations, emergency departments are managing an increasing number of older adults who fall; falling on level ground, like in one's house, is a common cause of a brain bleed. Computed tomography (CT) of the head is commonly used to assess patients who have fallen, but sending every patient who has fallen ...
Primary care lessons for Canada from OECD countries
2023-12-04
To improve primary care, Canada can learn from Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) countries with high rates of patients attached to primary care clinicians, write authors in an analysis in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.221824.
It is well known in Canada that there is a crisis in primary care, with about 17% of people reporting that they were without a regular primary care clinician before the COVID-19 pandemic. ...
Ohio State survey finds Americans struggle to maintain healthy habits during the holiday season
2023-12-04
EMBARGOED UNTIL MONDAY, DECEMBER 4, 2023 AT 12:01 a.m. EST
The holiday season is a time for joy and celebration but many Americans admit the endless flurry of activities make it difficult to eat healthy, exercise and get adequate rest, according to a new survey from The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center.
Two-thirds of those surveyed said they overindulge in food, nearly 45% said they take a break from exercise and more than half report feeling tired and have less time for themselves. Plus, a third admit they drink more alcohol during the holidays.
“Holiday travel, activities with friends and ...
Needle-free ultrasound vaccine delivery #Acoustics23
2023-12-04
SYDNEY, Dec. 4, 2023 – An estimated quarter of adults and two-thirds of children have strong fears around needles, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Yet, public health depends on people being willing to receive vaccines, which are often administered by a jab.
Darcy Dunn-Lawless, a doctoral student at the University of Oxford’s Institute of Biomedical Engineering, is investigating the potential of a painless, needle-free vaccine delivery by ultrasound. He will share the recent advancements in this promising technique as part of Acoustics 2023 Sydney, running ...
Being overweight hampers body’s immune response to SARS-CoV-2
2023-12-03
University of Queensland-led research shows being overweight can impair the body’s antibody response to SARS-CoV-2 infection but not to the protection offered by vaccination.
Research lead, School of Chemistry and Molecular Biosciences PhD candidate Marcus Tong, said the finding built on the team’s existing research on how COVID-19 affects people who are overweight.
“We’ve previously shown that being overweight – not just being obese – increases the severity of SARS-CoV-2,” Mr Tong said.
“But this ...
Translation inhibition in CRISPR-Cas antiviral defense system
2023-12-02
The recent publication in Science by Mogila, Tamulaitiene et al. represents a continuation of the successful scientific research conducted by Gintautas Tamulaitis’ group. In this study, the Vilnius University researchers using bioinformatic analysis, biochemical, and structural studies characterized a novel family of effector proteins, named Cami1. They showed that when a virus attacks a bacterium, CRISPR-Cas10 signaling molecules activate Cami1 - a ribosome-dependent ribonuclease. “Activated Cami1 cleaves mRNAs that are involved in protein synthesis, thereby inhibiting cell growth. This allows the bacterium to save resources and prevents production ...
Vitamin D supplements do not prevent bone fractures in children
2023-12-02
A major clinical trial led by Queen Mary University of London and the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health has found that vitamin D supplements do not increase bone strength or prevent bone fractures in children with vitamin D deficiency. The findings challenge widely held perceptions relating to the effects of vitamin D on bone health.
Around one-third of children have at least one fracture before the age of 18. This is a major global health issue, as childhood fractures can lead to life years of disability and/or poor quality of life. The potential for vitamin D supplements to improve bone strength has attracted growing interest in recent years, based ...
Aging societies more vulnerable to collapse
2023-12-01
Societies and political structures, like the humans they serve, appear to become more fragile as they age, according to an analysis of hundreds of pre-modern societies. A new study, which holds implications for the modern world, provides the first quantitative support for the theory that the resilience of political states decreases over time.
Triggers of societal collapse have been well studied and vary from conquest and coups to earthquakes and droughts. This new study shows that pre-modern states faced a steeply increasing risk of collapse within the first two centuries after they ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
[Press-News.org] Following in polar bears' footprints: DNA from snow tracks could help monitor threatened animalsScientists have found a way of capturing DNA from snow tracks — a promising non-invasive method of monitoring elusive animals like polar bears