(Press-News.org) SAN DIEGO – Early results from a Phase I clinical trial of AT101, a new CAR T cell therapy that uses a distinct binding mechanism to target CD19, show a 100 percent complete response (CR) rate at the higher dose levels studied in the trial, according to researchers from the University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine and Penn Medicine’s Abramson Cancer Center. The findings were published today in Molecular Cancer and presented at the 65th American Society of Hematology (ASH) Annual Meeting and Exposition (Abstract 2096).
CAR T cell therapy has revolutionized treatment for many people with blood cancers who had run out of other treatment options. While some patients experience long-term responses to CAR T cell therapy, it doesn’t work–or the cancer eventually returns–for others. The CD19 CAR T cell therapies that are currently approved all target CD19 through the same epitope (FMC63). To try and make CD19 CAR T cell therapy more effective for more patients, Marco Ruella, MD, an assistant professor of Hematology-Oncology and Scientific Director of the Lymphoma Program, and his research team, along with the Korean company AbClon Inc, co-developed a CAR T product (AT101), using cells originating from the same patient, that targets CD19 through a different epitope, located closer to the cell membrane, via a novel antibody (h1218). In preclinical studies, the team previously demonstrated that h1218-CART19 had decreased T cell exhaustion and improved control compared to FMC63-CART19.
The Phase I first-in-human clinical trial (NCT05338931) was conducted in South Korea and enrolled 12 patients with relapsed or refractory B cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (NHL). The study was designed to increase the dose level of AT101 after safety was confirmed in the first six patients. After a median follow-up of 6.5 months, all six patients who received dose level 2 or higher experienced a complete response and their cancer has not relapsed.
“We’ve learned that the way you design your CAR really matters. Designing a different CAR might drastically change the way the T cells work, potentially allowing that CAR T cell product to work where other CAR T cell products have failed,” Ruella said. “We were not expecting such a drastic early difference in this study. The CART19 products that are already FDA-approved are very effective, and it’s not easy to do better. While there is not a randomized trial of this product yet, the initial results seem very promising, and we look forward to moving into the planned Phase II portion of the study.”
The drug was found to be safe, with manageable side effects, including cytokine-release syndrome in four patients and immune-cell-related neurotoxicity syndrome in three patients. One patient experienced grade 3 sepsis that resolved; the same patient later developed fatal neutropenic septic shock outside the dose-limiting toxicity time frame.
The Phase I study enrolled patients who had not previously received any other CAR19 therapy. In the Phase II expansion, the study will also include patients who have previously received CAR19 therapy.
Editor’s Note: The study was funded by AbClon Inc; Ruella is a paid consultant for the company and has a Sponsored Research Agreement with them.
Yunlin Zhang, MS, a research specialist in Ruella’s lab, will present the findings in a poster session on Saturday, Dec. 9, from 5:30 to 7:30 p.m. PT in the San Diego Convention Center Halls G-H.
###
Penn Medicine is one of the world’s leading academic medical centers, dedicated to the related missions of medical education, biomedical research, excellence in patient care, and community service. The organization consists of the University of Pennsylvania Health System and Penn’s Raymond and Ruth Perelman School of Medicine, founded in 1765 as the nation’s first medical school.
The Perelman School of Medicine is consistently among the nation's top recipients of funding from the National Institutes of Health, with $550 million awarded in the 2022 fiscal year. Home to a proud history of “firsts” in medicine, Penn Medicine teams have pioneered discoveries and innovations that have shaped modern medicine, including recent breakthroughs such as CAR T cell therapy for cancer and the mRNA technology used in COVID-19 vaccines.
The University of Pennsylvania Health System’s patient care facilities stretch from the Susquehanna River in Pennsylvania to the New Jersey shore. These include the Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, Penn Presbyterian Medical Center, Chester County Hospital, Lancaster General Health, Penn Medicine Princeton Health, and Pennsylvania Hospital—the nation’s first hospital, founded in 1751. Additional facilities and enterprises include Good Shepherd Penn Partners, Penn Medicine at Home, Lancaster Behavioral Health Hospital, and Princeton House Behavioral Health, among others.
Penn Medicine is an $11.1 billion enterprise powered by more than 49,000 talented faculty and staff.
END
Older patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph+) acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) who were not good candidates for the standard treatment of intensive chemotherapy had a median overall survival (OS) of 6.5 years on an alternate regimen of dasatinib and blinatumomab.
These long-term results from the S1318 clinical trial will be presented at the 65th American Society of Hematology (ASH) Annual Meeting and Exposition in San Diego on December 9 (abstract 1499).
Anjali S. Advani, MD, a SWOG investigator at Cleveland Clinic Cancer Institute, led the study, with ...
Mindfulness-Oriented Recovery Enhancement (MORE) — a behavioral intervention that integrates training in mindfulness, emotion regulation strategies and savoring of natural rewards — could hold the key to mitigating relapse in women undergoing medically assisted opioid use disorder treatment, a Rutgers study found.
The pilot study published in the journal Explore, is the first to evaluate the potential neural changes that underlie women’s emotion regulation and craving after an eight-week MORE intervention.
Previous studies have shown that women report higher opioid craving and show a greater inability to ...
Imagine if scientists developed a customizable cancer vaccine that was available — and affordable — for everyone. What if a patient scheduled for surgery also had the option of taking a pill whose composition includes nanorobotics capable of performing the procedure?
These and other medical scenarios may seem far-fetched and better suited to a science fiction thriller. However, the Advanced Research Projects Agency for Health (ARPA-H) is seeking to take such ideas from the drawing board to ...
Almost US$7 trillion per year in government subsidies and private investment - around 7 per cent of global GDP - has a direct negative impact on nature.
Nature-based solutions remain dramatically underfunded. Current public and private finance flows are only US$200 billion per year. To meet climate, biodiversity, and restoration targets, this needs to triple by 2030 and quadruple by 2050.
Realignment of public and private nature-negative finance flows is urgently needed
Dubai, 9 December 2022 – Close to $7 trillion is invested globally each year in activities that have a direct negative impact on nature from both public and private sector sources - equivalent to ...
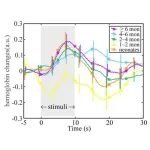
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have measured how oxygenated hemoglobin levels in the blood change in infants’ brains in response to touch. Using spectroscopy methods with external sensors placed on the scalp of sleeping infants, they found that the time at which levels peak doesn’t change with infant age, but the amount by which it varies over time does. Insights like this shed light on how the physiology of infants develop.
The first phase of a newborn’s life is a dazzling array of rapid developmental ...
Which charities will be most effective in ensuring your donation is put to good use? For the first time in the Netherlands, researchers applied scientific methods to pinpoint which charities achieve the most with the donations they receive. The University of Amsterdam and Stichting Doneer Effectief (Donate Effectively Foundation) unveiled the list on Friday, 8 December, during a sold out evening in Rotterdam. ‘We are talking about the Champions League of good causes,’ says professor of Philanthropy & Sustainable Investment Paul Smeets of the University of Amsterdam. The ranking ...
The shimmering green, red and purple curtains of the northern and southern lights — the auroras — may be the best-known phenomena lighting up the nighttime sky, but the most mysterious are the mauve and white streaks called Steve and their frequent companion, a glowing green "picket fence."
First recognized in 2018 as distinct from the common auroras, Steve — a tongue-in-cheek reference to the benign name given a scary hedge in a 2006 children's movie — and its associated picket fence were nevertheless thought to be caused by the same physical processes. But scientists were left scratching their heads about how these glowing emissions ...
The High Energy Physics Advisory Panel (HEPAP) to the High Energy Physics program of the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy and the National Science Foundation’s Division of Physics has released a new Particle Physics Project Prioritization Panel (P5) report, which outlines particle physicists’ recommendations for research priorities in a field whose projects — such as building new accelerator facilities — can take years or decades, contributions from thousands of scientists, and billions of dollars.
The 2023 P5 report represents the major activity in the field of particle physics that ...
CHAPEL HILL, NC — Eating food and absorbing its nutrients is an everyday occurrence, but this normal activity can look different for someone who suffers from inflammatory bowel disease. IBD, which includes Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, can cause chronic inflammation of the digestive tract – which for many reasons can lead to malnutrition. This malnourished state is associated with an increased risk of morbidity and mortality, and new findings show that many patients in IBD clinic screen positive for malnutrition, leading to the critical need for same-day ...
The following news release on the 2023 Particle Physics Project Prioritization Panel (P5) report is based on one issued today by the American Physical Society (APS) with added content specific to the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory. For more information about Brookhaven Lab’s research in particle physics, contact: Karen McNulty Walsh, kmcnulty@bnl.gov, (631) 344-8350. For APS media inquiries, contact Anna Torres, torres@aps.org, (301) 209-3605.
WASHINGTON, ...