(Press-News.org) Frontline nurses who learned the Transcendental Meditation® (TM®) technique during the COVID-19 pandemic showed rapid and significant improvements in flourishing, PTSD, anxiety, and burnout over 3 months compared to controls, according to a study published today in the Journal of Nursing Administration.
The objective of this study was to evaluate the impact of Transcendental Meditation on nurses’ multidimensional well-being, conceptualized as the presence of flourishing and the absence of PTSD, anxiety, and burnout.
A total of 104 nurses in three Florida hospitals participated. Validated tools included the Secure Flourishing Index (SFI), PTSD Checklist for DSM-5 (PCL-5), General Anxiety Disorder-7 (GAD-7) and Maslach Burnout Inventory (MBI). Nurses also completed a Demographic Survey and a Meditation Frequency Questionnaire.
Clinical nurses who were randomized to the Transcendental Meditation group took the instruction with certified TM teachers, which included follow-up meetings over a 3-month period. Adherence to the study protocol was notably strong considering the disruption caused by the pandemic. The control group continued with “life as usual” and were offered the TM course at the conclusion of the study.
Study Results
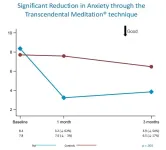
Based on the statistical analysis there was a 62% decrease in anxiety in the TM group from baseline to 1 month compared to 3% in the controls, and a 54% decrease in the TM group after 3 months compared to 17% in the controls.
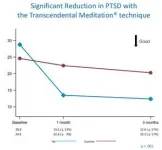
PTSD decreased 53% from baseline to 1 month in the TM group compared to 9% in the control group, and 57% in the TM group over 3 months compared to a 17% decrease in the controls.
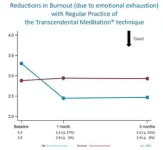
Burnout (due to emotional exhaustion) decreased by 27% from baseline to 1 month in the TM group compared to no change in the controls, and 24% in the TM group over the 3-month study period compared to no change in controls.
In the TM group, flourishing improved by 15% from baseline to 1 month compared to a decrease of 1% in the control group and increased 16% in the TM group compared to a 3% increase in controls from baseline to 3 months.
Authors’ Conclusion
According to lead author Jennifer Bonamer, PhD, RN, AHN-BC, NPD-BC, Nursing Professional Development Specialist at Sarasota Memorial Health Care System: "It has never been more crucial that we support the health of our nurses and other clinical staff. This study is important because it demonstrated that TM was substantially helpful, even during COVID, in reducing PTSD, anxiety and burnout experienced by nurses. Furthermore, it helped to improve nurses' experience of thriving (flourishing) beyond just surviving, even in the midst of today’s challenging healthcare environment."
The authors conclude this study demonstrates the effectiveness of nurses' practice of the TM technique to improve flourishing and reduce PTSD, anxiety, and burnout. TM provides nurses with a simple, effective, and evidence-based strategy for enhancing well-being, with the goal of retaining clinical nurses in practice.
About the Transcendental Meditation Technique
Transcendental Meditation is a simple, natural technique practiced 20 minutes twice each day while sitting comfortably with the eyes closed. It is easily learned, and is not a religion, philosophy, or lifestyle. It does not involve concentration, control of the mind, contemplation, or monitoring of thoughts or breathing. The practice allows the active thinking mind to settle down to a state of inner calm. For more information visit https://tm-nurses.org.
Study title: Clinical Nurse Well-Being Improved through Transcendental Meditation: A Multi-Method Randomized Controlled Trial
Authors: Jennifer I. Bonamer, PhD, RN, AHN-BC, NPD-BC; Mary Kutash, PhD, APRN; Susan Hartranft, PhD, APRN; Catherine Aquino-Russell, PhD, RN; Andrew Bugajski, PhD, RN; Ayesha Johnson, PhD.
Funding: Funding was provided by the David Lynch Foundation’s Heal the Healers Now campaign
DOI: DOI: 10.1097/NNA.0000000000001372
Publisher: The Journal of Nursing Administration is published by Wolters Kluwer.
END
New study shows Transcendental Meditation significantly reduced PTSD and anxiety in frontline nurses during COVID-19 pandemic by more than half over a 3-month period
2023-12-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New research identifies several warning signs that could predict intimate partner violence
2023-12-11
Intimate partner violence is widespread and can have severe physical and psychological health repercussions, but there is a shortage of research on reliable predictors of abuse before it occurs. New research, published in Social Psychological and Personality Science, identifies several warning signs that preceded and predicted intimate partner violence.
“Although future research is required to fully understand the associations between warning signs and abuse, these red flags could eventually be used ...
Just say no to that invitation
2023-12-11
It may feel unforgivably rude to reject an invitation – even one to an event you would much prefer not to attend – but people often overestimate the social consequences of saying no, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
“I was once invited to an event that I absolutely did not want to attend, but I attended anyways because I was nervous that the person who invited me would be upset if I did not – and that appears to be a common experience,” said lead author Julian Givi, PhD, an assistant professor at West Virginia University. “Our research shows, however, ...
Researchers compare mental illness, gun violence rates in U.S., Australia and U.K.
2023-12-11
Considerable attention has focused on mental illness as a major contributor to homicides in the United States. Serious mental illness affects more than 14 million Americans ages 18 and older and nearly 58 million people reported having a mental illness.
In 2021, 47,286 Americans died from gun violence – the highest ever – of which 46 percent were homicides and 54 percent were suicides involving firearms.
Researchers from Florida Atlantic University’s Schmidt College of Medicine and collaborators compared deaths from mental illness and gun violence in the U.S., Australia and the United Kingdom and their clinical ...
Science sheds light on shaking your holiday presents
2023-12-11
As holidays near, people are sneaking shakes of their presents to try to figure out what they’re getting. But present shakers might be a little less sly than they think. New research shows it’s incredibly easy for people watching others shake boxes to tell what they’re up to.
“There are few things more delightful than seeing a child’s eyes light up as they pick up a present and wonder what might be inside,” said author Chaz Firestone, a Johns Hopkins University assistant professor of psychological and brain sciences who investigates ...
Nanoparticle-delivered RNA reduces neuroinflammation in lab tests
2023-12-11
Some Covid-19 vaccines safely and effectively used lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) to deliver messenger RNA to cells. A new MIT study shows that different nanoparticles could be used for a potential Alzheimer’s disease (AD) therapy. In tests in multiple mouse models and with cultured human cells, a newly tailored LNP formulation effectively delivered small interfering RNA (siRNA) to the brain’s microglia immune cells to suppress expression of a protein linked to excessive inflammation in Alzheimer’s ...
New insight on electrochemical reactions – advancing the green transition
2023-12-11
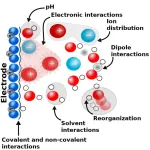
Electrochemical reactions are central to the green transitions. These reactions use the electric current and potential difference to carry out chemical reactions, which enables binding and realizing electric energy from chemical bonds. This chemistry is the basis for several applications, such as hydrogen technology, batteries, and various aspects of circular economy.
Developments and improvement in these technologies require detailed insight into the electrochemical reactions and different factors impacting them. Recent studies have shown that besides the electrode material also the used solvent, its acidity, and ...
New conductive, cotton-based fiber developed for smart textiles
2023-12-11
PULLMAN, Wash. – A single strand of fiber developed at Washington State University has the flexibility of cotton and the electric conductivity of a polymer, called polyaniline.
The newly developed material showed good potential for wearable e-textiles. The WSU researchers tested the fibers with a system that powered an LED light and another that sensed ammonia gas, detailing their findings in the journal Carbohydrate Polymers.
“We have one fiber in two sections: one section is the conventional cotton: flexible and strong enough for everyday use, and the other side is the conductive material,” said Hang Liu, WSU textile ...
New therapeutic target for rare type of childhood epilepsy
2023-12-11
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute, UCL and MSD have identified a potential treatment target for a genetic type of epilepsy.
Developmental and epileptic encephalopathies are rare types of epilepsy which start in early childhood. One of the most common types of genetic epilepsy, CDKL5 deficiency disorder (CDD), causes seizures and impaired development. Children are currently treated with generic antiepileptic drugs, as there aren’t yet any disease-targeting medications for this disorder.
CDD involves losing the function of a gene producing the CDKL5 enzyme, which phosphorylates proteins, meaning it adds an extra phosphate ...
Advanced MRI technology detects changes in the brain after COVID-19
2023-12-11
Researchers at Linköping University, Sweden, have examined the brains of 16 patients previously hospitalised for COVID-19 with persisting symptoms. They have found differences in brain tissue structure between patients with persisting symptoms after COVID-19 and healthy people. Their findings, published in the journal Brain Communications, can bring insights into the underlying mechanisms of persisting neurological problems after COVID-19.
Several previous studies of persisting problems after COVID have involved MRI brain scanning. Although researchers have found differences compared with healthy brains, these differences are not specific ...
New study reveals latest data on global burden of cardiovascular disease
2023-12-11
A world without cardiovascular disease (CVD) is possible, yet millions of lives are lost prematurely to heart disease each year, according to the new Global Burden of Disease (GBD) special report published today in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology. The report provides an update of health estimates for the global, regional and national burden and trends of CVD from 1990-2022 by analyzing the impact of cardiovascular conditions and risk factors across 21 global regions.
Research from this study reflects an urgent need ...