(Press-News.org) During the all-out invasion of Ukraine, Russia has deliberately chosen civilian targets, such as apartment buildings, presumably with the goal of deterring Ukrainian resistance. But does such terror deter or, in contrast, motivate resistance among ordinary Ukrainians? Henrikas Bartusevičius and colleagues conducted two-wave probability surveys in Ukraine in March and April 2022, with approximately 1,000 and 800 respondents in the first and second waves, respectively. Surveys were conducted online by a local survey agency, Info Sapiens. Respondents reported the frequency of military attacks (e.g., artillery shelling) on themselves, family, friends, and acquaintances. Respondents also indicated on a 7-point scale the likelihood of future engagement in four types of resistance: volunteering to care for the victims of war; helping resistance logistics; joining military combat in defense positions; and joining military combat in open battles. The surveys found that Ukrainians who had been more victimized by Russian violence were more willing to resist—especially to join military combat in defense positions. According to the authors, the Russian strategy of targeting civilians is not only costly and prohibited under international humanitarian law, it is unlikely to result in the desired erosion of Ukrainian resistance. According to the authors, terror against civilians is likely to strengthen Ukrainian resistance.
END
Civilian attacks and Ukrainian resistance
2023-12-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Drought and the rapid rise of skateboarding
2023-12-12
When a severe drought hit California in 1977, the state ordered citizens to drastically reduce domestic water usage. Water restrictions put in place occurred after a heady mix of prosperity and radical urban planning had resulted in the construction of more than 150,000 private swimming pools in California in the 1960s. The result was a ubiquitous new landscape feature: empty concrete pools. Ulf Büntgen and colleagues document how this novel geographic resource inspired surfers to develop professional vertical skateboarding in Los Angeles and environs. Other causal factors included the development of polyurethane ...
How a drought led to the rise of skateboarding in 1970s California
2023-12-12
Why did professional skateboarding arise in southern California in the 1970s? Was it a coincidence, or was it a perfect storm of multiple factors?
It’s fairly well-known that a drought in southern California in the mid-1970s led to a ban on filling backyard swimming pools, and these empty pools became playgrounds for freestyle skateboarders in the greater Los Angeles area. But a new cross-disciplinary study from the University of Cambridge shows that beyond the drought, it was the entanglement of environmental, economic and technological factors that led to the explosive rise of professional skateboarding culture in the 1970s.
The authors say that professional ...
A new brew: Evaluating the flavor of roasted, lab-grown coffee cells
2023-12-12
It may soon be time to wake up and smell the lab-grown coffee made from cultured plant cells. But it’s not clear whether drinks from this product replicate coffee beans’ complex flavors. Now, a study in ACS’ Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry found that some of the comforting aromas and tastes of a conventional cup of coffee could be reproduced by roasting and brewing coffee cell cultures.
Coffee is one of the most popular beverages worldwide. According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture, 23 billion pounds of beans are expected to be produced during the 2023–24 growing ...
Stability in physical and political science
2023-12-12
In a Perspective, a biophysical chemist, Kenneth J. Breslauer, and his brother, a political scientist, George W. Breslauer, explore the parallelisms between the concept of stability as it is used in their respective fields. The workings of a cell or molecule are generally understood to be reducible to physics, but social and political events are thought to be structured by human agency and a generous helping of chance. However, both molecular systems and socio-political organizations can be said to exhibit stability, instability, or so-called “metastability,” a state of precarious and kinetic stability. For example, a chemical system can be metastable when molecules ...
UTSA establishes new hub to improve management of digital assets
2023-12-12
UTSA has received a two-year, $300,000 grant from the National Science Foundation (NSF) to establish the National DigiFoundry (NDF), a consortium that has the potential to redefine the management of digital assets such as cryptocurrencies.
To develop the NDF, UTSA will create a new Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO), a national organization that promotes engagement and collaboration between the public and private sectors. At a time when digital assets, including cryptocurrencies, have surpassed a trillion dollars in market value, this collaboration is paramount, according to John Huggins, interim executive director of UTSA’s National ...
Daily singing workout keeps songbird males attractive
2023-12-12
Every year in the Christmas season it becomes clear again that some people are amazingly skilled singers, like Mariah Carey and George Michael. Their singing can stir strong emotions.
Singing involves probably the most complex, and mostly hidden, movements humans and animal can make. To become a good singer, you need to learn how to coordinate the movements of hundreds of muscles in your body with extreme precision. Therefore, you need a lot of talent, and practice.
We all know that athletes invest a lot of time exercising their limb ...
Scientists find new, better way to develop vaccines
2023-12-12
A new paper in Biology Methods & Protocols, published by Oxford University Press, indicates that researchers in Germany have developed a new system to display epitopes in mammal cells for immunization studies. They believe that this method can help scientists greatly in immunization efforts.
Promoting blood cells to produce antibodies against a specific viral protein is an important step in developing vaccines for human use. This can be challenging for researchers because whether the subjects develop antibodies depends on how scientists design ...
Creating a future, together, for rare-disease research
2023-12-12
Osaka, Japan – Patients with rare diseases have traditionally been the subjects of medical research. However, in recent years, their role has begun to shift from ‘research participants’ to ‘experts with a lived experience’, with some being involved in study planning, design and interpretation. Additionally they may soon be involved in helping pick the most important areas to prioritize for research.
In a study published last month in the journal Research Involvement and Engagement, researchers from Osaka University created an online space, referred to as the ‘Evidence-generating Commons’, for conversation, collaboration and ...
In a new light – new approach overcomes long-standing limitations in optics
2023-12-12
Osaka, Japan – When you look up at the sky and see clouds of wondrous shapes, or struggle to peer through dense, hazy fog, you’re seeing the results of ‘Mie scattering’, which is what happens with light interacts with particles of a certain size. There is a growing body of research that aims to manipulate this phenomenon and make possible an array of exciting technologies.
Now, in a study recently published in Nature Communications, a multi-institutional research team including Osaka University has overcome what were thought to be fundamental limitations of how to enhance the efficiency of Mie scattering.
Researchers in the field ...
Underwater architects: The ‘burrowing effect’ of foraminifera on marine environments
2023-12-12
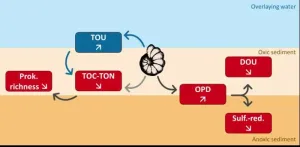
Dr. Dewi Langlet, a scientist at the Evolution, Cell Biology and Symbiosis Unit at the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology (OIST), studies foraminifera, single-cell organisms with shells made of calcium carbonate. He and his collaborators have shown for the first time that the burrowing of single-celled organisms in marine ecosystems affects oxygen distribution and bacterial diversity in sea sediments. Their findings have been published in the journal Biogeosciences.
Foraminifera are mostly marine organisms ...