The silent killer gets louder as high blood pressure risks trend upward
2023-12-12
(Press-News.org)
Research from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TDMU) warns that rates of urgent dialysis and death are on the rise over the last decade in people hospitalized for acute high blood pressure.
Tokyo, Japan – High blood pressure is called the silent killer because symptoms can remain hidden until a medical crisis strikes. You might think hypertension is no longer serious because blood pressure medication is widely available, but newly reported trends in people with dangerously high blood pressure might change your mind.
In a study recently published in Hypertension, researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TDMU) found that people admitted to the hospital over the last decade with spiking blood pressure—also known as acute hypertension—are increasingly likely to need urgent kidney dialysis or to die in the hospital.
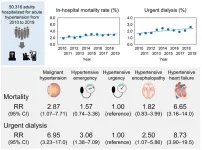
The researchers examined the medical records of more than 50,000 patients admitted to the hospital for acute hypertension between 2010 and 2019. Over the study’s 10 years, urgent dialysis rates rose significantly, from 1.52% to 2.6%.
“Of note, the rising trend in urgent dialysis was similar in patients who were younger, male, or overweight, and those with hypertensive heart failure. People with these traits are a high-risk group,” says the study’s lead author, Hisazumi Matsuki. “Unfortunately, the urgent dialysis procedure can cause complications like infection or bleeding, which in turn may increase the patient’s risk of dying.”
Mortality rates also increased over the 10 years from 1.83% to 2.88%, but not only because of the risks associated with urgent dialysis. “We saw a trend towards rising in-hospital mortality rates since 2010, particularly in patients who were elderly, male, and underweight, and in patients with hypertensive heart failure,” says senior author Shintaro Mandai.
However, mortality rates were lower in patients who were overweight. “We observed the obesity paradox, which is an unexpected decrease in mortality that sometimes accompanies an increased body mass index,” notes senior author Shinichi Uchida. “Underweight patients tend to have poor nutritional status and low physical activity and may have underlying conditions causing weight loss. Additionally, it can be difficult to find hidden heart congestion if the patient has no overt rise in blood pressure.”
Despite advances in hypertension treatment, the authors note that there has been no decrease in the number of acute hypertension cases. High blood pressure leads to serious organ damage by altering the structure of blood vessels, which run through every part of the body. People with hypertension need appropriate outpatient care and intensive blood pressure control, such as blood pressure medication, exercise, and healthy diets.
The research also highlights the importance of detecting hidden congestion early and providing underweight patients with nutritional support. Measures must be taken to avoid as many unplanned hospital admissions due to acute hypertension as possible.
###
The article, “National Trends in Mortality and Urgent Dialysis after Acute Hypertension in Japan from 2010 through 2019,” was published in Hypertension at DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.123.21880
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-12-12
Researchers have come one step closer to answering why, in some patients, a type of lymphoma changes from indolent to aggressive, and in particular they are closer to identifying which patients are at high risk of this change happening.
Part of the answer lies in the protein expression in the tumour, explains Associate Professor Maja Ludvigsen from the Department of Clinical Medicine at Aarhus University. Maja is one of the authors of a new study on the subject, which has just been published in the scientific journal Blood Advances.
Follicular ...
2023-12-12
INDIANAPOLIS – There have been few studies of LGBTQ+ older adults residing in nursing homes. A new article from faculty of Regenstrief Institute and Indiana University explores care of the growing number of LGBTQ+ older adults living in these facilities. The paper highlights the experiences and needs of this population, outlines best facility practices and presents valuable resources for culturally appropriate and inclusive care.
Social isolation, limited community supports, dementia, decreased functional abilities, economic ...
2023-12-12
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- By studying how spider silk responds to sound, researchers at Binghamton University, State University of New York have developed a patent for a brand-new microphone technology.
Using biomimicry as a model, Binghamton University Distinguished Professor of Engineering Ron Miles worked with then-doctoral student and current Assistant Professor of Mechanical Engineering Jian Zhou to patent a bio-inspired flow microphone — the very patent that has now been commercialized by the Canadian venture firm TandemLaunch and its spin-off company Soundskrit, which has also recently ...
2023-12-12
Anesthesiologist and global health expert Dr. Gunisha Kaur and her research team recently won a prestigious National Academy of Medicine (NAM) Catalyst Prize.
The Catalyst Awards are a branch of the Healthy Longevity Global Competition that seeks to expand the human healthspan—usually defined as how many healthy years a person lives—by rewarding cutting-edge ideas to improve the physical, mental, or social wellbeing and health of people as they age. Up to 20 awards are being given this year to United States-based innovators, out of 1,100 applications received from organizations focused on “science, medicine, ...
2023-12-12
Our reading skills, and understanding of a text, depend on several factors.
“These include decoding texts, learning the letters of the alphabet, and knowing the different words and how they sound. However, vocabulary is also important,” says Professor Hermundur Sigmundsson at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) Department of Psychology.
He is behind a special edition of Frontiers in Psychology together with Professors Heikki Lyytinen from the University of Jyväskylä and Elena L. Grigorenko from the University of Houston.
Most people can learn how ...
2023-12-12
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — When it comes to greenhouse gases, methane is one the biggest contributors. Not only is it massively abundant — it’s about 25 times more potent than carbon dioxide at trapping heat in the atmosphere.
That makes tracking methane emissions critically important, and nowhere more so than in the Arctic, which is now the fastest warming part of the globe. A new study conducted at Brown University helps shed light on the actual atmospheric methane emissions from Arctic ...
2023-12-12
Two-thirds of patients discontinued their medication, switched to a different medication class or intensified their treatment
Discontinuation was higher (50%) among GLP-1 RA drugs, which are linked to gastrointestinal side effects
Findings could have implications for patients taking GLP-1 RAs to treat obesity
First large U.S. study to show such high discontinuation rates
CHICAGO --- Most patients with Type 2 diabetes will end up needing to add a second-line medication after metformin — the go-to primary drug for glucose management — ...
2023-12-12
Waltham — December 7, 2023 —
At discharge from the hospital, Black Medicare beneficiaries are less likely to be referred for home health care (HHC), compared to white patients reports a survey study in Medical Care. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
The disparity in referral for HHC among Black Medicare patients appears greatest among those with low "readiness for discharge" scores, according to the new research, led by Olga Yakusheva, PhD, of University of Michigan School of Nursing and School of Public Health.
Does ...
2023-12-12
BOSTON, December 12, 2023 — NEJM Group, publisher of the New England Journal of Medicine, today announced the launch of its newest title, NEJM AI, a peer-reviewed, monthly journal dedicated to the latest research and application of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning in medicine. In addition to original research articles, the journal publishes reviews, policy perspectives and educational material for clinicians, scientists, health care leaders, policy makers, regulators, and executives with pharmaceutical, device-manufacturing and technology companies. Benchmark data sets and protocols are ...
2023-12-12
In addition to being one of the largest, most diverse metropolitan areas in the world with a population of 6.1 million, South Florida hosts more than 9.7 million acres of farmland with a revenue of more than $7 billion in recent years. However, climate change, extreme weather events, poor soils, pests and disease, and workforce shortages present unique challenges in this region.
To address a critical need to train a diverse workforce with new sets of tools and skills to confront these emerging challenges, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] The silent killer gets louder as high blood pressure risks trend upward





