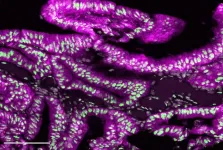
(Press-News.org) For the first time ever, an international team of researchers has created a complete cell atlas of a whole mammalian brain. This atlas serves as a map for the mouse brain, describing the type, location, and molecular information of more than 32 million cells and providing information on connectivity between these cells. The mouse is the most commonly used vertebrate experimental model in neuroscience research, and this cellular map paves the way for a greater understanding of the human brain—arguably the most powerful computer in the world. The cell atlas also lays the foundation for the development of a new generation of precision therapeutics for people with mental and neurological disorders of the brain.
The findings were funded by the National Institutes of Health’s Brain Research Through Advancing Innovative Neurotechnologies® Initiative, or The BRAIN Initiative®, and appear in a collection of 10 papers published in Nature.
“The mouse atlas has brought the intricate network of mammalian brain cells into unprecedented focus, giving researchers the details needed to understand human brain function and diseases,” said Joshua A. Gordon, M.D., Ph.D., Director of the National Institute of Mental Health, part of the National Institutes of Health.
The cell atlas describes the types of cells in each region of the mouse brain and their organization within those regions. In addition to this structural information, the cell atlas provides an incredibly detailed catalog of the cell’s transcriptome—the complete set of gene readouts in a cell, which contains instructions for making proteins and other cellular products. The transcriptomic information included in the atlas is hierarchically organized, detailing cell classes, subclasses, and thousands of individual cell clusters within the brain.
The atlas also characterizes the cell epigenome—chemical modifications to a cell’s DNA and chromosomes that alter the way the cell’s genetic information is expressed—detailing thousands of epigenomic cell types and millions of candidate genetic regulation elements for different brain cell types.
Together, the structural, transcriptomic, and epigenetic information included in this atlas provide an unprecedented map of cellular organization and diversity across the mouse brain. The atlas also provides an accounting of the neurotransmitters and neuropeptides used by different cells and the relationship among cell types within the brain. This information can be used as a detailed blueprint for how chemical signals are initiated and transmitted in different parts of the brain. Those electrical signals are the basis for how brain circuits operate and how the brain functions overall.
“This product is a testament to the power of this unprecedented, cross-cutting collaboration and paves our path for more precision brain treatments,” said John Ngai, Ph.D., Director of the NIH BRAIN Initiative.”
Of the 10 studies included in this collection, seven are funded through the NIH BRAIN Initiative Cell Census Network (BICCN), and two are funded through the larger NIH BRAIN Initiative. The core aim of the BICCN, a groundbreaking, cross-collaborative effort to understand the brain’s cellular makeup, is to develop a comprehensive inventory of the cells in the brain—where they are, how they develop, how they work together, and how they regulate their activity—to better understand how brain disorders develop, progress, and are best treated.
“By leveraging the unique nature of its multi-disciplinary and international collaboration, the BICCN was able to accomplish what no other team of scientists has been able to before,” said Dr. Ngai. “Now we are ready to take the next big step—completing the cell maps of the human brain and the nonhuman primate brain.”
The BRAIN Initiative Cell Atlas Network (BICAN) is the next stage in the NIH BRAIN Initiative’s effort to understand the cell and cellular functions of the mammalian brain. BICAN is a transformative project that, together with two other large-scale projects—the BRAIN Initiative Connectivity Across Scales and the Armamentarium for Precision Brain Cell Access—aim to revolutionize neuroscience research by illuminating foundational principles governing the circuit basis of behavior and informing new approaches to treating human brain disorders.
Reference: Yao, Z., van Velthoven, C. T. J., Kunst, M., Zhang, M., McMillen, D., Lee, C., Jung, W., Goldy, J., Abdelhak, A., Aitken, M., Baker, K., Baker, P., Barkan, E., Bertagnolli, D., Bhandiwad, A., Bielstein, C., Bishwakarma, P., Campos, J., Carey, D., … Zeng, H. (2023). A high-resolution transcriptomic and spatial atlas of cell types in the whole mouse brain. Nature. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-06812-z
END
Scientists unveil complete cell map of a whole mammalian brain
NIH-funded atlas characterizes over 32 million cells across the mouse brain
2023-12-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Cholesterol-lowering therapy may hinder aggressive type of colorectal tumor
2023-12-13
Hard-to-detect colorectal pre-cancerous lesions known as serrated polyps, and the aggressive tumors that develop from them, depend heavily on the ramped-up production of cholesterol, according to a preclinical study from researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine. The finding points to the possibility of using cholesterol-lowering drugs to prevent or treat such tumors.
In the study, published Oct. 13 in Nature Communications, the researchers analyzed mice that develop serrated polyps and tumors, detailing the chain of molecular events in these tissues that leads to increased cholesterol production.
They ...
Inequity in U.S. wildfire emergency response
2023-12-13
WASHINGTON, DC, 2023 – Recent U.S. wildfire events -- including the 2023 Maui wildfire in Hawaii, the 2022 Hermit’s Peak/Calf Canyon fire in New Mexico, and the 2020 Cameron Peak Fire in Colorado -- are tragic examples of how disadvantaged communities can suffer most during and after a wildfire. While all three fires had a devastating impact on an entire community, they disproportionately affected low-income populations who were left without adequate insurance or the financial means to rebuild their homes.
To study inequities in U.S. wildfire management, ...
When parents drink during Super Bowl, kids get harsh discipline
2023-12-13
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Parents who drank alcohol while watching the Super Bowl were more likely than those who abstained to use aggressive discipline on their children during the game, a new study shows.
Most of the parents in the study – more than 90% - were mothers, which is significant, said Bridget Freisthler, lead author of the study and professor of social work at The Ohio State University.
“The links between alcohol use, aggression and watching violent sports have been studied almost exclusively among ...
Reported drug use among adolescents continued to hold below pre-pandemic levels in 2023
2023-12-13
The percentage of adolescents reporting they used any illicit substances in 2023 continued to hold steady below the pre-pandemic levels reported in 2020, with 10.9% of eighth graders, 19.8% of 10th graders, and 31.2% of 12th graders reporting any illicit drug use in the past year, according to the latest results from the Monitoring the Future survey. Reported use for almost all substances decreased dramatically between 2020 and 2021, after the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic and related changes like school closures and social distancing. In 2022, most reported substance use among adolescents ...
Study: digital leisure reading does little to improve reading comprehension for students
2023-12-13
Washington, December 13, 2023—For years, research showed that print reading, whether for leisure or school, improved developing readers’ ability to comprehend text. However, the explosive use of digital reading devices, constant access to these devices, and new types of reading materials have introduced new reading habits. Now, a new comprehensive review of research on digital leisure reading habits finds a virtually nonexistent relationship between digital reading and improvement in reading comprehension among students.
The study was published in Review of Educational Research, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Educational ...
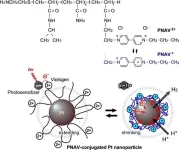
Towards next-generation nanocatalysts to revolutionize active electron transfer
2023-12-13
Ishikawa, Japan -- Various molecular systems have been developed by researchers for photoinduced (i.e., light-driven) electron transfer, including supramolecules, hybrid materials, and organic polymeric systems. While these systems fulfill the distance criterion required by the electron donor and acceptor for efficient electron transfer, they frequently fall short in accommodating molecular motion, especially in fluid environments. Is there a viable approach to design a system that facilitates electron transfer without succumbing to these limitations?
This issue has been specifically addressed in a recent study. ...
Helping more people get to safety in a wildfire
2023-12-13
WASHINGTON, DC, Dec. 13, 2023 – Wildfires pose an increasing threat to communities at the wildland-urban interface (WUI) – where dry, flammable vegetation borders back yards, often in remote locations. Despite the well-known danger, many communities at highest risk do not have a strong wildfire evacuation plan in place. (One of these was the town of Lahaina on Maui, where wind-driven wildfires killed nearly 100 people in August 2023.)
Researchers from UCLA’s John Garrick Institute for the Risk Sciences have built a new web-based software platform that allows emergency planners to design custom-made evacuation plans for their communities ...
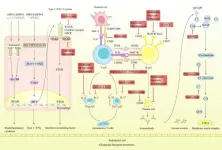
Review in Chinese Medical Journal highlights the challenges and recent advances in targeted therapies for lupus nephritis
2023-12-13
Patients with lupus nephritis (LN), a severe complication of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), often undergo progressive kidney damage, with approximately 20% of these patients advancing to end-stage renal disease. The current therapeutic landscape for LN, dominated by glucocorticoids and immunosuppressants, is limited by suboptimal response rates, the risk of disease flare-ups and adverse effects, accentuating the necessity for safer and more effective treatment modalities. In the latest issue of the Chinese Medical Journal (CMJ) published online on December 15, 2023, a review authored by Dr. Wei Chen from the Department of Nephrology of the First Affiliated ...
Parker Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy (PICI) welcomes Weill Cornell Medicine to cancer research consortium
2023-12-13
San Francisco and New York — Dec. 13, 2023 — The Parker Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy (PICI), the largest concentration of immuno-oncology (IO) expertise in the world, announced it has added Weill Cornell Medicine to its network of preeminent academic and medical research institutions at the forefront of the fight against cancer. Under the agreement, Weill Cornell Medicine, with new PICI Network researchers, will establish a PICI immuno-oncology research center in New York City.
Since its inception, PICI has distributed $260 million to member researchers to support ...
Saving endangered species: New AI method counts manatee clusters in real time
2023-12-13
Manatees are endangered species volatile to the environment. Because of their voracious appetites, they often spend up to eight hours a day grazing for food within shallow waters, making them vulnerable to environmental changes and other risks.
Accurately counting manatee aggregations within a region is not only biologically meaningful in observing their habit, but also crucial for designing safety rules for boaters and divers as well as scheduling nursing, intervention, and other plans. Nevertheless, counting manatees ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Increased risk of bullying in open-plan offices
Frequent scrolling affects perceptions of the work environment
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
[Press-News.org] Scientists unveil complete cell map of a whole mammalian brainNIH-funded atlas characterizes over 32 million cells across the mouse brain