(Press-News.org)
Batteries that exploit quantum phenomena to gain, distribute and store power promise to surpass the abilities and usefulness of conventional chemical batteries in certain low-power applications. For the first time, researchers including those from the University of Tokyo take advantage of an unintuitive quantum process that disregards the conventional notion of causality to improve the performance of so-called quantum batteries, bringing this future technology a little closer to reality.
When you hear the word “quantum,” the physics governing the subatomic world, developments in quantum computers tend to steal the headlines, but there are other upcoming quantum technologies worth paying attention to. One such item is the quantum battery which, though initially puzzling in name, holds unexplored potential for sustainable energy solutions and possible integration into future electric vehicles. Nevertheless, these new devices are poised to find use in various portable and low-power applications, especially when opportunities to recharge are scarce.
At present, quantum batteries only exist as laboratory experiments, and researchers around the world are working on the different aspects that are hoped to one day combine into a fully functioning and practical application. Graduate student Yuanbo Chen and Associate Professor Yoshihiko Hasegawa from the Department of Information and Communication Engineering at the University of Tokyo are investigating the best way to charge a quantum battery, and this is where time comes into play. One of the advantages of quantum batteries is that they should be incredibly efficient, but that hinges on the way they are charged.
“Current batteries for low-power devices, such as smartphones or sensors, typically use chemicals such as lithium to store charge, whereas a quantum battery uses microscopic particles like arrays of atoms,” said Chen. “While chemical batteries are governed by classical laws of physics, microscopic particles are quantum in nature, so we have a chance to explore ways of using them that bend or even break our intuitive notions of what takes place at small scales. I’m particularly interested in the way quantum particles can work to violate one of our most fundamental experiences, that of time.”
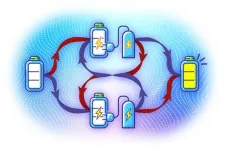
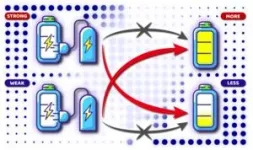
In collaboration with researcher Gaoyan Zhu and Professor Peng Xue from Beijing Computational Science Research Center, the team experimented with ways to charge a quantum battery using optical apparatuses such as lasers, lenses and mirrors, but the way they achieved it necessitated a quantum effect where events are not causally connected the way everyday things are. Earlier methods to charge a quantum battery involved a series of charging stages one after the other. However, here, the team instead used a novel quantum effect they call indefinite causal order, or ICO. In the classical realm, causality follows a clear path, meaning that if event A leads to event B, then the possibility of B causing A is excluded. However, at the quantum scale, ICO allows both directions of causality to exist in what’s known as a quantum superposition, where both can be simultaneously true.
“With ICO, we demonstrated that the way you charge a battery made up of quantum particles could drastically impact its performance,” said Chen. “We saw huge gains in both the energy stored in the system and the thermal efficiency. And somewhat counterintuitively, we discovered the surprising effect of an interaction that’s the inverse of what you might expect: A lower-power charger could provide higher energies with greater efficiency than a comparably higher-power charger using the same apparatus.”
The phenomenon of ICO the team explored could find uses beyond charging a new generation of low-power devices. The underlying principles, including the inverse interaction effect uncovered here, could improve the performance of other tasks involving thermodynamics or processes that involve the transfer of heat. One promising example is solar panels, where heat effects can reduce their efficiency, but ICO could be used to mitigate those and lead to gains in efficiency instead.
###
Journal article: Gaoyan Zhu, Yuanbo Chen, Yoshihiko Hasegawa, and Peng Xue. “Charging Quantum Batteries via Indefinite Causal Order: Theory and Experiment”, Physical Review Letters, DOI:
Funding:
This work has been supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 92265209 and 12025401). Y. H. acknowledges support by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number JP22H03659. Y.C. acknowledges support by JST SPRING, Grant Number JPMJSP2108.
Research contact:
Yoshihiko Hasegawa
Graduate School of Information Science and Technology,
The University of Tokyo, 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo, 113-0033, Japan
hasegawa@biom.t.u-tokyo.ac.jp
Hasegawa Laboratory
https://sites.google.com/view/hasegawalab/home
Graduate School of Information Science and Technology
https://www.i.u-tokyo.ac.jp/index_e.shtml
Press contact:
Mr. Rohan Mehra
Public Relations Group, The University of Tokyo,
7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo, 113-8656, Japan
press-releases.adm@gs.mail.u-tokyo.ac.jp
About The University of Tokyo
The University of Tokyo is Japan's leading university and one of the world's top research universities. The vast research output of some 6,000 researchers is published in the world's top journals across the arts and sciences. Our vibrant student body of around 15,000 undergraduate and 15,000 graduate students includes over 4,000 international students. Find out more at www.u-tokyo.ac.jp/en/ or follow us on Twitter at @UTokyo_News_en.
END
Do you celebrate your birthday in the same month as your mum? If so, you are not alone. The phenomenon occurs more commonly than expected – a new study of millions of families has revealed.
Siblings also tend to share month of birth with each other, as do children and fathers, the analysis of 12 years’ worth of data shows, whilst parents are also born in the same month as one another more often than would be predicted.
Previous research has found that women’s season of ...
Bat numbers declined as Britain’s trees were felled for shipbuilding in the early colonial period, new research shows.
The study, by the University of Exeter and the Bat Conservation Trust (BCT), found Britain’s Western barbastelle bat populations have dropped by 99% over several hundred years.
Animals’ DNA can be analysed to discover a “signature” of the past, including periods when populations declined, leading to more inbreeding and less genetic diversity.
Scientists used this method to discover the historic decline ...
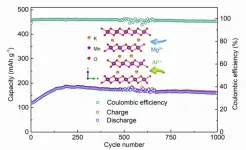
Due to the merits of low cost, low installation requirements, and high-level safety, aqueous rechargeable batteries (ARBs) offer an ideal option for dealing with future energy-demand pressure. Traditional aqueous batteries are mostly concentrated on mono-valent metal-ion, such as Li+, Na+, and K+. Compared to mono-valent carriers, multivalent cations have the capability to transfer more than one electron, and thereby to potentially provide better energy storage. To date, aqueous multivalent ion batteries based on Zn2+ have received a lot of attention. However, the investigations on aqueous ...
Research led by Professor John McGrath from the University of Queensland found that the concentration of the C4 protein, an important part of the immune system, was not associated with risk of mental disorders.
However, the research also showed that a higher concentration of the C3 protein reduces the risk of schizophrenia in women, and studies based on the genetic correlates of C4 found strong links with several autoimmune disorders.
Professor John McGrath from UQ’s Queensland Brain Institute said his colleagues at Aarhus University in Denmark looked at ...
A clinical trial reported in 2021 and conducted by a team of researchers from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis and the International Centre for Diarrhoeal Disease Research in Dhaka, Bangladesh, showed that a newly designed therapeutic food aimed at repairing malnourished children’s underdeveloped gut microbiomes was superior to a widely used standard therapeutic food.
Now, another study from the same research team at Washington University School of Medicine has identified key, naturally occurring biochemical components of this new therapeutic food and the important bacterial strains that process these ...
NEW ORLEANS, La. – Ochsner Health announces plans for The Gayle and Tom Benson Ochsner Children’s Hospital, made possible through a transformational gift from Mrs. Gayle Benson.
“We are proud to unveil much-anticipated plans for a new home for Louisiana’s No. 1 ranked children’s hospital,” said Pete November, CEO, Ochsner Health. “Ochsner is deeply grateful for Mrs. Benson and her unparalleled act of generosity, which will significantly impact the lives of countless families throughout Louisiana and the Gulf South. This facility will enable us to care for more children, retain and attract top pediatric physicians ...
The genetic alphabet contains just four letters, referring to the four nucleotides, the biochemical building blocks that comprise all DNA. Scientists have long wondered whether it’s possible to add more letters to this alphabet by creating brand-new nucleotides in the lab, but the utility of this innovation depends on whether or not cells can actually recognize and use artificial nucleotides to make proteins.
Now, researchers at Skaggs School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences at the University of California San Diego have ...
A decades-long decline in smoking prevalence in England has nearly ground to a halt since the start of the pandemic, according to a new study led by UCL researchers.
The study, funded by Cancer Research UK and published in the journal BMC Medicine, looked at survey responses from 101,960 adults between June 2017 and August 2022.
Before the Covid-19 pandemic, from June 2017 to February 2020, smoking prevalence fell by 5.2% a year, but this rate of decline slowed to 0.3% during the pandemic (from April 2020 to August 2022), the study ...
Fossil fuels are at the heart of most human activities, contributing to the increase in greenhouse gas emissions and the ever-rising atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) levels. CO2 levels are projected to increase exponentially in future, resulting in severe environmental and ecological impacts. A beacon of hope amidst this chaos are eco-friendly alternatives to fossil fuels.
Green energy sources can be developed using advanced biotechnological techniques. One such intervention is the use of biorefineries or microbial cell factories, that convert biomass (organic matter like plants and solid waste) into energy and valuable by-products. The first (1G) ...
The personal yet global struggle with mental health may be more visible now than ever before. Yet many people still find it difficult to access the support they need. In Japan, suicide is sadly the leading cause of death for young people. Researchers, including from the University of Tokyo, have carried out a six-year study to better understand the myriad of factors which can impact adolescent mental health. After surveying 2,344 adolescents and their caregivers, and using computer-based deep learning to process the results, they were able to identify five categories which the young people could be grouped into. Nearly 40% of those involved were ...