(Press-News.org) CLEVELAND—Throughout our lives, changes in our DNA, called genetic mutations, occur in every healthy cell of the human body—mutations which have long been thought to be an important reason why our bodies age.
But it’s not known whether some people accumulate mutations at a faster or slower rate with age, and whether those differences might predict how long we live and the risk for aging-related diseases like cancer.
With a $3.5 million research project grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), Jonathan Shoag, a surgeon-scientist at the Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine and urologic oncologist at University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center's Urology Institute, and Gilad Evrony, a physician-scientist at New York University (NYU) Grossman School of Medicine and NYU Langone Hospital, seek to answer these critical questions.
Shoag and Evrony, together with a team of collaborators, will leverage new sequencing technologies in a large number of people to understand how mutations that arise throughout the lifespan may associate with the risk of aging-related diseases like cancer.
“Our study will help us understand healthy aging and define new predictors for aging-related diseases,” Shoag said. “This has the potential to allow us to try to prevent aging associated diseases sooner with clinical interventions.”
“Much remains unknown about how DNA mutations affect the fundamental process of aging, because only recently have the technologies become available to detect these changes in DNA,” Evrony said. “Studying aging-related mutations on a large scale will reveal how our genome dynamically changes throughout our lives.”
Shoag and Evrony are also part of the NIH Somatic Mosaicism across Human Tissues consortium, a multi-institutional effort designed to develop technologies to understand these mutations across the body.
###
Case Western Reserve University is one of the country's leading private research institutions. Located in Cleveland, we offer a unique combination of forward-thinking educational opportunities in an inspiring cultural setting. Our leading-edge faculty engage in teaching and research in a collaborative, hands-on environment. Our nationally recognized programs include arts and sciences, dental medicine, engineering, law, management, medicine, nursing and social work. About 6,200 undergraduate and 6,100 graduate students comprise our student body. Visit case.edu to see how Case Western Reserve thinks beyond the possible.
About University Hospitals / Cleveland, Ohio
Founded in 1866, University Hospitals serves the needs of patients through an integrated network of 21 hospitals (including five joint ventures), more than 50 health centers and outpatient facilities, and over 200 physician offices in 16 counties throughout northern Ohio. The system’s flagship quaternary care, academic medical center, University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center, is affiliated with Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, Northeast Ohio Medical University, Oxford University, the Technion Israel Institute of Technology and National Taiwan University College of Medicine. The main campus also includes the UH Rainbow Babies & Children's Hospital, ranked among the top children’s hospitals in the nation; UH MacDonald Women's Hospital, Ohio's only hospital for women; and UH Seidman Cancer Center, part of the NCI-designated Case Comprehensive Cancer Center. UH is home to some of the most prestigious clinical and research programs in the nation, with more than 3,000 active clinical trials and research studies underway. UH Cleveland Medical Center is perennially among the highest performers in national ranking surveys, including “America’s Best Hospitals” from U.S. News & World Report. UH is also home to 19 Clinical Care Delivery and Research Institutes. UH is one of the largest employers in Northeast Ohio with more than 30,000 employees. Follow UH on LinkedIn, Facebook and Twitter. For more information, visit UHhospitals.org.
END
Why do people age differently?
With $3.5M National Institutes of Health grant, research teams from Case Western Reserve University / University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center and NYU Grossman School of Medicine / NYU Langone Hospital hope to find out
2023-12-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Ali Khademhosseini named as 2023 National Academy of Inventors Fellow
2023-12-19
(LOS ANGELES) – December 18, 2023 - The National Academy of Inventors (NAI) has named Ali Khademhosseini, Ph.D., Director and CEO of the Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation (TIBI), as a 2023 National Academy of Inventors Fellow. This distinctive honor is the highest professional award that is exclusively bestowed upon inventors. The Academy has chosen to honor him for his achievements and contributions to the innovation ecosystem, which vastly influences science, society, and the global economy. Dr. Khademhosseini will be formally recognized at the NAI thirteenth annual meeting on June 18, 2024, where he will be presented with a medal by a senior official from the United States ...
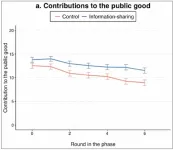
Information sharing and cooperation
2023-12-19
How is cooperation affected when people can receive secondhand information about what others are contributing? Ashley Harrell and Tom Wolff investigated this question through an online cooperation game. Participants were recruited from a large subject pool of university students and other adults, maintained by the Interdisciplinary Behavioral Research Center at Duke University. Over 200 participants were placed in groups of 6–10; however, each participant was only linked to some of the other participants. In the control condition, players could only see the contributions ...
How big events can disrupt public transit over an entire city
2023-12-19
COLUMBUS, Ohio – New technology has allowed scientists to see how a major sporting event can disrupt public transportation in an entire city for hours before and after the event.
Researchers conducted a case study in Columbus on days that The Ohio State University had home football games, attracting more than 100,000 fans to Ohio Stadium on the university’s campus.
Findings showed that bus service across the entire city was significantly less reliable for more than 7 hours on game days compared to other days, meaning that even bus riders who were not traveling near the university ...
Can AI think like a human?
2023-12-19
In a perspective, Athanassios S. Fokas considers a timely question: whether artificial intelligence (AI) can reach and then surpass the level of human thought. Typically, researchers have sought to measure the ability of computer models to accomplish complex goals, such as winning the game of Go or carrying on a conversation that seems human enough to fool an interlocutor. According to Fokas, this approach has a key methodological limitation. Any AI would have to be tested on every single conceivable human goal before anyone could claim that the program was thinking as well as a human. Alternative methodologies are therefore needed. In addition, the “complex goal” focus does not ...
AI in medical research: promise and challenges
2023-12-19
In an editorial, Monica M. Bertagnolli assesses the promise of artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML) to study and improve health. The editorial was written by Dr. Bertagnolli in her capacity as director of the National Cancer Institute. AI/ML offer powerful new tools to analyze highly complex datasets, and researchers across biomedicine are taking advantage. However, Dr. Bertagnolli argues that human judgment is still required. Humans must select and develop the right computational models and ensure that the data used to train ...
First comprehensive medical guideline on management of pouchitis released
2023-12-19
Bethesda, MD (Dec. 19, 2023) — The American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) has released the first comprehensive evidence-based guideline on the management of pouchitis, the most common complication people with ulcerative colitis experience following surgery to remove their colon.
Between 150,000 and 300,000 people with ulcerative colitis in the U.S. live with a surgically created internal reservoir or “pouch” created from their small intestine as an alternate way to store and pass ...
A neuromuscular model for drug development
2023-12-19
Scientists have so far identified around 800 different neuromuscular diseases. These conditions are caused by problems in the way muscle cells, motor neurons and peripheral cells interact. These disorders, including amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and spinal muscular atrophy, lead to muscle weakness, paralysis, and in some cases death.
“These diseases are highly complex, and the causes of the dysfunction can vary widely,” says Dr. Mina Gouti, head of the Stem Cell Modeling of Development and Disease Lab at the Max Delbrück Center. The problem might lie with the neurons, the muscle cells or the connections between the two. ...
Chilean researchers pledge for transformative change to tackle climate action
2023-12-19
Addressing climate change has become a central issue in Chile’s public policy. As part of that debate, Dr. Maisa Rojas, researcher in Atmospheric Physics, who currently serves as Chilean Minister for Environment and Marco Billi of the Centre for Climate and Resilience Research, Universidad de Chile, propose a new model of governance at the country level to facilitate the changes needed. The proposal – written before Dr. Rojas’ appointment to the Chilean government – is published in IOP Publishing’s journal Environmental Research Letters.
The model proposed places climate action ...
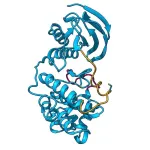
A new inactive form of p38a protein discovered
2023-12-19
p38a protein, which is associated with cancer and other diseases, adopts a previously unknown structure regulated by cellular redox conditions.
The finding may have implications when designing new drugs to block it.
The work developed by IRB Barcelona, in collaboration with the University of Barcelona and the company Nostrum Biodiscovery, has been published in the journal Nature Communications.
Barcelona, 19 December 2023 - p38a protein, a key enzyme in the regulation of various cellular functions, plays a crucial ...
Childhood trauma increases risk of chronic pain in adulthood, research to-date highlights
2023-12-19
Physical, sexual, or emotional abuse, or neglect, either alone or combined with other types of childhood trauma, increases the risk of chronic pain and related disability in adulthood, according to new research.
These new findings underscore the urgency of addressing adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) – potentially traumatic events that occur before 18 years of age – and taking steps to mitigate their long-term impact on people’s health.
The study ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Weill Cornell Medicine selected for Prostate Cancer Foundation Challenge Award
Largest high-precision 3D facial database built in China, enabling more lifelike digital humans
SwRI upgrades facilities to expand subsurface safety valve testing to new application
Iron deficiency blocks the growth of young pancreatic cells
Selective forest thinning in the eastern Cascades supports both snowpack and wildfire resilience
A sea of light: HETDEX astronomers reveal hidden structures in the young universe
Some young gamers may be at higher risk of mental health problems, but family and school support can help
Reduce rust by dumping your wok twice, and other kitchen tips
High-fat diet accelerates breast cancer tumor growth and invasion
Leveraging AI models, neuroscientists parse canary songs to better understand human speech
Ultraprocessed food consumption and behavioral outcomes in Canadian children
The ISSCR honors Dr. Kyle M. Loh with the 2026 Early Career Impact Award for Transformative Advances in Stem Cell Biology
The ISSCR honors Alexander Meissner with the 2026 ISSCR Momentum Award for exceptional work in developmental and stem cell epigenetics
The ISSCR honors stem cell COREdinates and CorEUstem with the 2026 ISSCR Public Service Award
Minimally invasive procedure effectively treats small kidney cancers
SwRI earns CMMC Level 2 cybersecurity certification
Doctors and nurses believe their own substance use affects patients
Life forms can planet hop on asteroid debris – and survive
Sylvia Hurtado voted AERA President-Elect; key members elected to AERA Council
Mount Sinai and King Saud University Medical City forge a three-year collaboration to advance precision medicine in familial inflammatory bowel disease
AI biases can influence people’s perception of history
Prenatal opioid exposure and well-being through adolescence
Big and small dogs both impact indoor air quality, just differently
Wearing a weighted vest to strengthen bones? Make sure you’re moving
Microbe survives the pressures of impact-induced ejection from Mars
Asteroid samples offer new insights into conditions when the solar system formed
Fecal transplants from older mice significantly improve ovarian function and fertility in younger mice
Delight for diastereomer production: A novel strategy for organic chemistry
Permafrost is key to carbon storage. That makes northern wildfires even more dangerous
Hairdressers could be a secret weapon in tackling climate change, new research finds
[Press-News.org] Why do people age differently?With $3.5M National Institutes of Health grant, research teams from Case Western Reserve University / University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center and NYU Grossman School of Medicine / NYU Langone Hospital hope to find out