(Press-News.org)
“[...] the biological mechanisms linking aging and osteoarthritis prevalence remain largely unknown.”
BUFFALO, NY- December 19, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 23, entitled, “Sirtuin 6 activation rescues the age-related decline in DNA damage repair in primary human chondrocytes.”
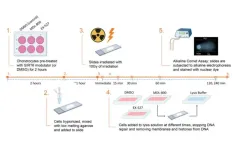
While advanced age is widely recognized as the greatest risk factor for osteoarthritis (OA), the biological mechanisms behind this connection remain unclear. Previous work has demonstrated that chondrocytes from older cadaveric donors have elevated levels of DNA damage as compared to chondrocytes from younger donors. In this new study, researchers Michaela E. Copp, Jacqueline Shine, Hannon L. Brown, Kirti R. Nimmala, Oliver B. Hansen, Susan Chubinskaya, John A. Collins, Richard F. Loeser, and Brian O. Diekman from University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, North Carolina State University, Rush University Medical Center, and Thomas Jefferson University aimed to determine whether a decline in DNA repair efficiency is one explanation for the accumulation of DNA damage with age, and to quantify the improvement in repair with activation of Sirtuin 6 (SIRT6).
“In this study, we use irradiation as an acute model of DNA damage to bring the level of damage to equivalent levels across chondrocytes from donors of various ages.”
After acute damage with irradiation, DNA repair was shown to be more efficient in chondrocytes from young (≤45 years old) as compared to middle-aged (50–65 years old) or older (>70 years old) cadaveric donors. Activation of SIRT6 with MDL-800 improved the repair efficiency, while inhibition with EX-527 reduced the rate of repair and increased the percentage of cells that retain high levels of damage.
In addition to affecting repair after acute damage, treating chondrocytes from older donors with MDL-800 for 48 hours significantly reduced the amount of baseline DNA damage. Chondrocytes isolated from the knees of mice between 4 months and 22 months of age revealed both an increase in DNA damage with aging, and a decrease in DNA damage following MDL-800 treatment. Lastly, treating murine cartilage explants with MDL-800 lowered the percentage of chondrocytes with high p16 promoter activity, which supports the concept that using SIRT6 activation to maintain low levels of DNA damage may prevent the initiation of senescence.
“In conclusion, the findings presented here support the hypothesis that the efficiency of DNA damage repair declines with age in chondrocytes and that SIRT6 activation improves repair both in response to an acute irradiation challenge and in the context of age-related damage accumulation. These results emphasize the critical role of SIRT6 in DNA repair and support further studies investigating the use of MDL-800 (or alternative SIRT6 activators) in mitigating senescence induction and ameliorating OA development.”
Read the full paper: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.205394
Corresponding Author: Brian O. Diekman
Corresponding Email: bdiekman@email.unc.edu
Keywords: SIRT6, MDL-800, cartilage, aging, comet assay
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article: https://aging.altmetric.com/details/email_updates?id=10.18632%2Faging.https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.205394
About Aging:
Launched in 2009, Aging publishes papers of general interest and biological significance in all fields of aging research and age-related diseases, including cancer—and now, with a special focus on COVID-19 vulnerability as an age-dependent syndrome. Topics in Aging go beyond traditional gerontology, including, but not limited to, cellular and molecular biology, human age-related diseases, pathology in model organisms, signal transduction pathways (e.g., p53, sirtuins, and PI-3K/AKT/mTOR, among others), and approaches to modulating these signaling pathways.
Please visit our website at www.Aging-US.com and connect with us:
SoundCloud
Facebook
X, formerly known as Twitter
Instagram
YouTube
LabTube
LinkedIn
Reddit
Pinterest
Click here to subscribe to Aging publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com.
Aging (Aging-US) Journal Office
6666 E. Quaker Str., Suite 1B
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957, option 1
###
END
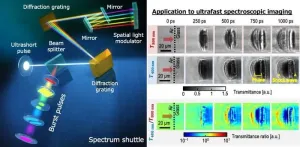
The generation and manipulation of high-repetition pulses hold great promise across various applications, including high-speed photography, laser processing, and acoustic wave generation. Gigahertz (GHz) burst pulses, with intervals ranging from ~0.01 to ~10 nanoseconds, are particularly valued for visualizing ultrafast phenomena and improving laser processing efficiency.
While methods for producing GHz burst pulses exist, challenges persist, such as low throughput of pulse energy, poor tunability of pulse intervals, and the complexity ...
An article published in the Chemical Engineering Journal describes a strategy to produce a material based on zinc oxide (ZnO) capable of degrading sertraline, an antidepressant that has been detected, like other drugs, in groundwater worldwide and is considered an emerging pollutant. This kind of substance has certain physicochemical properties that hinder removal by conventional wastewater treatment methods.
The research was supported by FAPESP and conducted in Brazil by scientists at the Center for Development of Functional Materials (CDMF), the Brazilian ...
The University of Stuttgart and Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) have announced an agreement to build two new supercomputers at the High-Performance Computing Center of the University of Stuttgart (HLRS).
In the first stage, a transitional supercomputer, called Hunter, will begin operation in 2025. This will be followed in 2027 with the installation of Herder, an exascale system that will provide a significant expansion of Germany’s high-performance computing (HPC) capabilities. Hunter and Herder will offer researchers ...
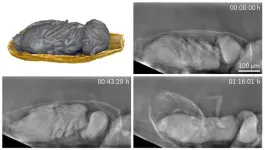
X-ray imaging visualizes hidden structures and processes in living cells and organisms. The radiation that consists of highly energy-rich electromagnetic waves, however, has an ionizing effect and may damage the genetic material. This limits the possible observation period. While conventional X-ray images of soft tissue are of low contrast, phase contrast methods produce far better image contrasts at a reduced radiation dose. With higher resolution, however, gentle imaging becomes increasingly difficult, as a higher dose is required. Moreover, ...
Recently, a research team led by Prof. Sun Zhong at Peking University reported an analog hardware solution for real-time compressed sensing recovery, which has been published as an article titled "In-memory analog solution of compressed sensing recovery in one step" in Science Advances. In this work, a design based on a resistive memory (also known as memristor) array for performing instantaneous matrix-matrix-vector multiplication (MMVM) is first introduced. Based on this module, then an analog matrix computing circuit that solves compressed sensing (CS) recovery in one step (within few microseconds) is disclosed.
CS ...
Tim Garrett has devoted his scientific career to characterizing snowflakes, the protean particles of ice that form in clouds and dramatically change as they fall to Earth.
Now the University of Utah atmospheric scientist is unlocking the mystery of how snowflakes move in response to air turbulence that accompanies snowfall using novel instrumentation developed on campus. And after analyzing more than half a million snowflakes, what his team has discovered has left him astonished.
Rather than something incomprehensibly complicated, predicting how snowflakes move proved to be surprisingly ...
Physician-researchers from Mass Eye and Ear, a member of Mass General Brigham, report the first pediatric case of bilateral vocal cord paralysis after COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) infection. The patient, an otherwise healthy 15-year-old female, came to the emergency department at Massachusetts General Hospital with symptoms of respiratory distress nine days after diagnosis with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Examination with an endoscope revealed bilateral vocal cord paralysis, which is an immobility of both vocal cords found in the larynx or voice box. The researchers concluded that this paralysis was likely a downstream ...
People living in different communities follow different social customs or norms. In some places, for instance, it might be standard practice to greet each person you see on the street, while in others that simply isn’t done. In some cases, such differences may even vary from one neighborhood to the next. Now researchers reporting in the journal iScience on December 19 have found similarly varied social traditions and styles among neighboring groups of vervet monkeys.
“We report the existence of behavioral traditions of social customs in vervet ...
Researchers at UNIL’s Department of Ecology and Evolution reveal the existence of social traditions in vervet monkeys. This work was published in iScience on December 19, 2023.
British tits have learned from each other how to pierce the lids of milk bottles left on doorsteps. On the island of Koshima, Japanese macaques started washing sweet potatoes to rid them of sand. The animal realm is full of examples of traditions linked to food, tool use or hunting techniques that have spread within specific communities. However, few traditions of social nature, i.e. how individuals interact with each other, have been described.
A ...
WASHINGTON, Dec. 19, 2023 – A winter wonderland calls to mind piles of fluffy, glistening snow. But to reach the ground, snowflakes are swept into the turbulent atmosphere, swirling through the air instead of plummeting directly to the ground.
The path of precipitation is complex but important to more than just skiers assessing the potential powder on their alpine vacation or school children hoping for a snow day. Determining snowflake fall speed is crucial for predicting weather patterns and measuring climate ...