(Press-News.org) UC Riverside scientists have discovered a stealth molecular weapon that plants use to attack the cells of invading gray mold.
If you’ve ever seen a fuzzy piece of fruit in your fridge, you’ve seen gray mold. It is an aggressive fungus that infects more than 1,400 different plant species: almost all fruits, vegetables, and many flowers. It is the second most damaging fungus for food crops in the world, causing billions in annual crop losses.
A new paper in the journal Cell Host & Microbe describes how plants send tiny, innocuous-seeming lipid “bubbles” filled with RNA across enemy lines, into the cells of the aggressive mold. Once inside, different types of RNA come out to suppress the infectious cells that sucked them in.
“Plants are not just sitting there doing nothing. They are trying to protect themselves from the mold, and now we have a better idea how they’re doing that,” said Hailing Jin, Microbiology & Plant Pathology Department professor at UCR and lead author of the new paper.
Previously, Jin’s team discovered that plants are using the bubbles, technically called extracellular vesicles, to send small RNA molecules able to silence genes that make the mold virulent. Now, the team has learned these bubbles can also contain messenger RNA, or mRNA, molecules that attack important cellular processes, including the functions of organelles in mold cells.
“These mRNAs can encode some proteins that end up in the mitochondria of the mold cells. Those are the powerhouses of any cells because they generate energy,” Jin explained. “Once inside, they mess up the structure and function of the fungal mitochondria, which inhibits the growth and virulence of the fungus.”
It isn’t entirely clear why the fungus accepts the lipid bubbles. Jin theorizes they might just be hungry. “The fungus likely takes up the vesicles because they just want nutrients. They don’t know those RNAs are hidden in the vesicles,” she said.
The strategy is an efficient one for the plants, because one mRNA molecule can have an outsized effect on the fungus. “The beauty of delivering mRNA, instead of other forms of molecular weapons, is that one RNA can be translated into many copies of proteins. This amplifies the effect of the mRNA weapon,” Jin said.
Mold also uses these same lipid bubbles to deliver small, damaging RNAs into the plants they are infecting to suppress host immunity, an ability developed as part of a co-evolutionary arms race. Because RNAs are easily degraded, the bubbles provide excellent protection for transporting vulnerable cargo, for both plants and fungi.
“During infections, there are always a lot of communications and molecule exchanges where plants and fungi try to fight against each other,” Jin said. “Previously people looked at proteins being exchanged. Now, modern technology has enabled us to discover another important group of players in this battle.”
Going forward, the scientists are hoping to use this discovery to create innovative, eco-friendly fungicides. “RNA-based fungicides would not leave toxic residue in the environment and would not affect humans or animals. RNA is present in most food, and it is easily digested,” Jin said.
“There is a never-ending battle to control pests and pathogens. If we can deliver mRNA that interferes with mold cellular functions, we may be able to help plants more effectively fight in this battle.”
END
Discovery: Plants use “trojan horse” to fight mold invasions
Plant RNA defense systems hidden in unassuming “bubbles”
2023-12-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Could an electric nudge to the head help your doctor operate a surgical robot?
2023-12-20
People who received gentle electric currents on the back of their heads learned to maneuver a robotic surgery tool in virtual reality and then in a real setting much more easily than people who didn’t receive those nudges, a new study shows.
The findings offer the first glimpse of how stimulating a specific part of the brain called the cerebellum could help health care professionals take what they learn in virtual reality to real operating rooms, a much-needed transition in a field that increasingly relies on digital simulation training, said author and Johns Hopkins University roboticist Jeremy ...
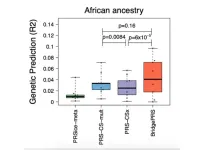
Mount Sinai researchers develop novel method to improve disease prediction across diverse ancestries
2023-12-20
A team of scientists from Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai has developed a groundbreaking statistical technique, “BridgePRS,” to enhance disease prediction in people of non-European ancestry, particularly those of African descent. This development represents a substantial step towards reducing health care inequities and a future of more personalized and precise medical interventions based on genetic information. Details of their work were published in Nature Genetics on Wednesday, December 20.
Current polygenic risk scores (PRS), essential tools for predicting disease risk encoded in our ...
How researchers are “CReATiNG” synthetic chromosomes faster and cheaper
2023-12-20
A groundbreaking new technique invented by researchers at the USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Science may revolutionize the field of synthetic biology. Known as CReATiNG (Cloning Reprogramming and Assembling Tiled Natural Genomic DNA), the method offers a simpler and more cost-effective approach to constructing synthetic chromosomes. It could significantly advance genetic engineering and enable a wide range of advances in medicine, biotechnology, biofuel production and even space exploration.
CReATiNG works by cloning and reassembling natural DNA segments from yeast, allowing scientists to create synthetic chromosomes that can replace their native counterparts in cells. ...
IOP Publishing expands open access in Asia Pacific region with its first Read and Publish agreement in Taiwan
2023-12-20
IOP Publishing (IOPP) has secured its first ‘Read and Publish’ transformative agreement in Taiwan, demonstrating its dedication to expanding open access (OA) to research in the Asia-Pacific (APAC) region and at scale globally.
The three-year transformative agreement with the Physics Research Promotion Centre, which is part of the National Science and Technology Council (NSTC), will enable 20 Taiwanese universities to offer their researchers unlimited OA publishing at no cost to them. The agreement will also allow authors to retain copyright ...
Mediterranean diet ‘a straightforward approach’ among many nutritional options for improving the chance of success in IVF
2023-12-20
Adjuvant therapies to help infertile women conceive by IVF - especially those whose treatments have been unsuccessful in the past - are now a common feature both before and during the treatment cycle. Now, a new analysis of the evidence for many nutritional supplements and diets thought to improve outcome in IVF has concluded that adopting a Mediterranean diet during treatment would offer a single ‘straightforward approach’ with good evidence of benefit in contrast to that of a Western diet.
Evidence from studies of nine commonly used nutritional supplements was found to be inconsistent and not always of good quality. The analysis, by Professor Roger ...
Could gamma brain stimulation help combat Alzheimer’s disease?
2023-12-20
A review in the Journal of Internal Medicine explores the potential of non-invasive interventions such as light, sound, and magnets to stimulate gamma brain waves for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Such strategies may be beneficial because Alzheimer’s disease is characterized by reduced fast brain oscillations in the gamma range (30–100 Hz).
The authors note that recent studies reveal that it is feasible and safe to induce 40 Hz brain activity in patients with Alzheimer’s disease through a range of methods. Also, preliminary evidence suggests that such treatment can yield beneficial ...
How does the inability to burp affect daily life?
2023-12-20
The inability to burp—called retrograde cricopharyngeus dysfunction (R-CPD)—is caused by failure of the throat’s cricopharyngeal muscle to relax to allow the outward passage of gas. An interview-based study in Neurogastroenterology & Motility that included 199 adults affected by the condition reveals the impact of R-CPD on quality of life.
Most participants reported abdominal bloating, socially awkward gurgling noises, excessive flatulence, and difficulty vomiting. Only half discussed their symptoms with their primary care clinician, and 90% felt they did not receive ...
Does losing a parent during childhood contribute to separation anxiety and anxious attachment in women?
2023-12-20
Women who lost a parent early in life may be more likely to experience separation anxiety with romantic partners during adulthood, according to a study published in Stress and Health. In addition to feeling distressed when separated from their partners, these women may also experience anxious attachment, or worry that significant others will not be available at times of need.
The study included 60 women who lost one or both parents in their youth and 60 who had living parents. Based on participants’ answers to questionnaires, women who lost a parent reported higher levels of anxious attachment and adult separation anxiety ...
Do steroid creams affect bone health?
2023-12-20
New research indicates that higher doses of topical corticosteroids, which are commonly used to treat inflammatory skin conditions, are linked with elevated risks of osteoporosis and bone fractures associated with osteoporosis. The findings are published in the Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology and are based on information from the Taiwan National Health Insurance Research Database.
Investigators selected 129,682 osteoporosis cases and 34,999 major osteoporotic fracture (MOF) cases and matched them with 518,728 and 139,996 controls (without osteoporosis or MOF) ...
360-degree head-up display view could warn drivers of road obstacles in real time
2023-12-20
Researchers have developed an augmented reality head-up display that could improve road safety by displaying potential hazards as high-resolution three-dimensional holograms directly in a driver’s field of vision in real time.
Current head-up display systems are limited to two-dimensional projections onto the windscreen of a vehicle, but researchers from the Universities of Cambridge, Oxford and University College London (UCL) developed a system using 3D laser scanner and LiDAR data to create a fully 3D representation of London streets.
The system ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Discovery: Plants use “trojan horse” to fight mold invasionsPlant RNA defense systems hidden in unassuming “bubbles”