(Press-News.org) Our memories are rich in detail: we can vividly recall the color of our home, the layout of our kitchen, or the front of our favorite café. How the brain encodes this information has long puzzled neuroscientists.
In a new Dartmouth-led study, researchers identified a neural coding mechanism that allows the transfer of information back and forth between perceptual regions to memory areas of the brain. The results are published in Nature Neuroscience.
Prior to this work, the classic understanding of brain organization was that perceptual regions of the brain represent the world "as it is," with the brain’s visual cortex representing the external world based on how light falls on the retina, "retinotopically." In contrast, it was thought that the brain’s memory areas represent information in an abstract format, stripped of details about its physical nature. However, according to the co-authors, this explanation fails to take into account that as information is encoded or recalled, these regions may in fact, share a common code in the brain.
"We found that memory-related brain areas encode the world like a 'photographic negative' in space," says co-lead author Adam Steel, a postdoctoral researcher in the Department of Psychological and Brain Sciences and fellow in the Neukom Institute for Computational Science at Dartmouth. "And that ‘negative’ is part of the mechanics that move information in and out of memory, and between perceptual and memory systems."
In a series of experiments, participants were tested on perception and memory while their brain activity was recorded using a functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) scanner. The team identified an opposing push-pull like coding mechanism, which governs the interaction between perceptual and memory areas in the brain.
The results showed that when light hits the retina, visual areas of the brain respond by increasing their activity to represent the pattern of light. Memory areas of the brain also respond to visual stimulation, but, unlike visual areas, their neural activity decreases when processing the same visual pattern.
The co-authors report that the study has three unusual findings. The first is their discovery that a visual coding principle is preserved in memory systems.
The second is that this visual code is upside-down in memory systems. "When you see something in your visual field, neurons in the visual cortex are driving while those in the memory system are quieted," says senior author Caroline Robertson, an assistant professor of psychological and brain sciences at Dartmouth.
Third, this relationship flips during memory recall. "If you close your eyes and remember that visual stimuli in the same space, you'll flip the relationship: your memory system will be driving, suppressing the neurons in perceptual regions," says Robertson.
"Our results provide a clear example of how shared visual information is used by memory systems to bring recalled memories in and out of focus," says co-lead author Ed Silson, a lecturer of human cognitive neuroscience at the University of Edinburgh.
Moving forward, the team plans to explore how this push and pull dynamic between perception and memory may contribute to challenges in clinical conditions, including in Alzheimer’s.
Steel (adam.steel@dartmouth.edu) and Robertson (caroline.e.robertson@dartmouth.edu) are available for comment. Brenda Garcia '21 at Dartmouth also contributed to the study.
###
END
Researchers identify new coding mechanism that transfers information from perception to memory
2024-01-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A novel switch to turn genes on/off on cue, a promising step toward safer gene therapy
2024-01-02
Just like a doctor adjusts the dose of a medication to the patient’s needs, the expression of therapeutic genes, those modified in a person to treat or cure a disease via gene therapy, also needs to be maintained within a therapeutic window. Staying within the therapeutic window is important as too much of the protein could be toxic, and too little could result in a small or no therapeutic effect.
Although the principle of therapeutic window has been known for a long time, there has been no strategy to implement it safely, limiting the potential applications of gene therapy in the clinic. ...
Food insecurity among low-income adults dropped nearly 5% during pandemic-era SNAP expansion
2024-01-01
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 1 January 2024
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only ...
A tidy cell seems to keep aging at bay
2024-01-01
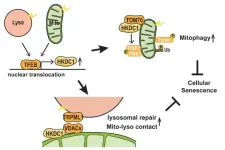
Osaka, Japan – Just as healthy organs are vital to our well-being, healthy organelles are vital to the proper functioning of the cell. These subcellular structures carry out specific jobs within the cell, for example, mitochondria power the cell and lysosomes keep the cell tidy.
Although damage to these two organelles has been linked to aging, cellular senescence, and many diseases, the regulation and maintenance of these organelles has remained poorly understood. Now, researchers at Osaka University have identified a protein, HKDC1, that plays a key role in maintaining these two organelles, thereby acting to prevent ...
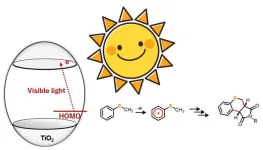
Chemical synthesis using titanium dioxide: An eco-friendly and innovative approach
2024-01-01
Heterocyclic compounds are organic molecules with a ring structure comprising at least two or more elements. In most cases, these rings are composed of carbon atoms along with one or more other elements such as nitrogen, oxygen, or sulfur. They are highly sought-after as raw materials in the chemical and pharmaceutical industry, owing to their versatility and excellent physiological activities. While several methods are available for synthesizing these compounds, most of them involve high temperature and pressure conditions, or the use of precious ...
Want to quit smoking in 2024? Cytisine can help … if you live in the right country
2024-01-01
A new study published in Addiction has found that cytisine, a low-cost, generic stop-smoking aid that has been used in eastern Europe since the 1960s, increases the chances of successful smoking cessation by more than two-fold compared with placebo and may be more effective than nicotine replacement therapy. It has a benign safety profile, with no evidence of serious safety concerns. Sounds perfect for your New Year resolution, doesn’t it? But there’s a catch: Cytisine is not licensed or marketed in most countries outside of central and eastern Europe, ...
Sodium’s high-pressure transformation can tell us about the interiors of stars, planets
2023-12-29
Travel deep enough below Earth’s surface or inside the center of the Sun, and matter changes on an atomic level.
The mounting pressure within stars and planets can cause metals to become nonconducting insulators. Sodium has been shown to transform from a shiny, gray-colored metal into a transparent, glass-like insulator when squeezed hard enough.
Now, a University at Buffalo-led study has revealed the chemical bonding behind this particular high-pressure phenomenon.
While it’s been theorized that high pressure essentially squeezes sodium’s electrons out into the spaces between atoms, researchers’ quantum chemical ...
Endocrine Society applauds Ohio governor veto of state ban on gender-affirming care for minors
2023-12-29
WASHINGTON—The Endocrine Society, the world’s oldest and largest professional medical society devoted to the study and treatment of hormone-related conditions, applauds Governor Mike Dewine’s veto of a proposed Ohio law that would have banned gender-affirming care for minors. The bill he vetoed contradicts mainstream medical practice and scientific evidence and would have taken medical decision-making out of the hands of families and their physicians and instead relied upon government officials.
More ...
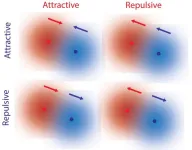
Molecules exhibit non-reciprocal interactions without external forces, new study finds
2023-12-29
Researchers from the University of Maine and Penn State discovered that molecules experience non-reciprocal interactions without external forces.
Fundamental forces such as gravity and electromagnetism are reciprocal, where two objects are attracted to each other or are repelled by each other. In our everyday experience, however, interactions don’t seem to follow this reciprocal law. For example, a predator is attracted to prey, but the prey tends to flee from the predator. Such non-reciprocal interactions are essential for complex behavior associated with living organisms. ...
MSK research highlights, December 29, 2023
2023-12-29
New research from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK) developed CAR T cells that target two acute myeloid leukemia-specific antigens; shed new light on a genetic element called LINE-1, opening the door to new treatments; identified a key regulator of blood stem cell fate; and found an immunotherapy technique using antibodies that target CD47 shows promise in mice.
CAR T Cells that target two antigens treat AML with minimal toxicity
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) has so far resisted treatment with chimeric ...
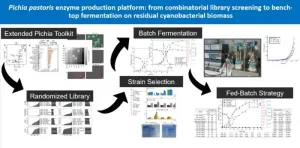
Novel solution for Pichia pastoris enzyme production platform
2023-12-29
The demand for industrial enzymes is continually rising, driven by the growing need to shift towards more sustainable industrial processes. Our research outlines a novel approach in enzyme production, harnessing the untapped potential of cyanobacterial biomass within the P. pastoris platform. Group Leader, Dr. Schieder, highlights the nature of the study, stating, "Our work reveals the potential of cyanobacterial biorefineries to support enzyme production."
This achievement stems from an extensive multi-field approach. We characterized and expanded a combinatorial library, streamlining P. pastoris engineering for enhanced efficiency. ...