(Press-News.org) Binghamton University, State University of New York Distinguished Professor and Nobel Laureate M. Stanley Whittingham has been chosen as the joint winner of the $3 million 2023 VinFuture Grand Prize in recognition of his contributions to the invention of lithium-ion batteries. The prize recognized how the combination of solar energy and lithium battery storage is overcoming climate change and was recently presented by the Prime Minister of Vietnam.
“I am truly honored to be chosen for this prestigious honor,” said Whittingham. “VinFuture’s efforts to recognize green and sustainable energy is a noble cause, and one I am extremely proud to have played a role in.”
In his 30-plus-year career, Whittingham has been a pioneer in the development of lithium-ion batteries, for which he won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 2019. He holds the original patent on the use of intercalation chemistry in high-power density, highly reversible lithium batteries.
Whittingham was honored during a ceremony in Hanoi, Vietnam and broadcast live worldwide. The four winning works surpassed nearly 1,400 impressive nominations from 90 countries and territories. According to organizers, these breakthroughs have a profound impact on the present and future of humanity in crucial fields such as green and sustainable energy, climate change response, sustainable agriculture, food security, and healthcare – impacting the lives of billions of people worldwide.
The VinFuture Prize, established in 2020 by the VinFuture Foundation in Vietnam, honors exceptional inventors and researchers from academic institutions, research centers, and the industrial sector worldwide. It is dedicated to celebrating groundbreaking scientific research and technological innovations that bring significant and positive changes to the everyday lives of many people.
END
Binghamton University professor and Nobel Laureate Stanley Whittingham wins 2023 VinFuture Grand Prize
2024-01-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Deciphering molecular mysteries: new insights into metabolites that control aging and disease
2024-01-02
ITHACA, NY: In a significant advancement in the field of biochemistry, scientists at the Boyce Thompson Institute (BTI) and Cornell University have uncovered new insights into a family of metabolites, acylspermidines, that could change how we understand aging and fight diseases.
The study, recently published in Nature Chemical Biology, presents an unexpected connection between spermidine, a long-known compound present in all living cells, and sirtuins, an enzyme family that regulates many life-essential functions.
Sirtuins ...
Women’s and girls’ sports: more popular than you may think
2024-01-02
COLUMBUS, Ohio – The number of Americans who watch or follow girls’ and women’s sports goes well beyond those who view TV coverage of women’s athletic events, a new study suggests.
In fact, just over half of American adults spent some time watching or following female sports in the past year, the results showed.
U.S. adults spend about one hour a week consuming female sports content, which may seem higher than expected, according to the researchers. Still, it is only a small fraction of Americans’ overall sports consumption.
The study was ...
Calcium channel blockers key to reversing myotonic dystrophy muscle weakness, study finds
2024-01-02
New research has identified the specific biological mechanism behind the muscle dysfunction found in myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1) and further shows that calcium channel blockers can reverse these symptoms in animal models of the disease. The researchers believe this class of drugs, widely used to treat a number of cardiovascular diseases, hold promise as a future treatment for DM1.
“The main finding of our study is that combined calcium and chloride channelopathy is highly deleterious and plays a central role in the function impairment of muscle found in the disease,” said John Lueck, Ph.D., an assistant professor at the University of Rochester Medical Center (URMC) in the Departments ...
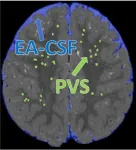
Enlarged spaces in infant brains linked to higher risk of autism, sleep problems
2024-01-02
Throughout the day and night, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) pulses through small fluid-filled channels surrounding blood vessels in the brain, called perivascular spaces, to flush out neuroinflammation and other neurological waste. A disruption to this vital process can lead to neurological dysfunction, cognitive decline, or developmental delays.
For the first time, researchers Dea Garic, PhD, and Mark Shen, PhD, both at the UNC School of Medicine’s Department of Psychiatry, discovered that infants with abnormally enlarged perivascular spaces have a 2.2 times greater chance of developing autism ...
Growth hormone influences regulation of anxiety via a specific group of neurons
2024-01-02
Growth hormone (GH) acts on many tissues throughout the body, helping build bones and muscles, among other functions. It is also a powerful anxiolytic. A study conducted by researchers at the University of São Paulo (USP) in Brazil has produced a deeper understanding of the role of GH in mitigating anxiety and, for the first time, identified the population of neurons responsible for modulating the influence of GH on the development of neuropsychiatric disorders involving anxiety, depression and post-traumatic stress. An article on the study is published in the Journal of Neuroscience.
In ...
Influencers’ vulnerabilities: a double-edged sword
2024-01-02
ITHACA, N.Y. – New Cornell University-led research finds that social media platforms and the metrics that reward content creators for revealing their innermost selves to fans open creators up to identity-based harassment.
“Creators share deeply personal – often vulnerable – elements of their lives with followers and the wider public,” said Brooke Erin Duffy, associate professor of communication. “Such disclosures are a key way that influencers build intimacy with audiences and form communities. There’s a pervasive sense that internet users clamor for less polished, less idealized, ...
Designing the ‘perfect’ meal to feed long-term space travelers
2024-01-02
Imagine blasting off on a multiyear voyage to Mars, fueled by a diet of bland, prepackaged meals. As space agencies plan for longer missions, they’re grappling with the challenge of how to best feed people. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Food Science & Technology have designed the optimal “space meal”: a tasty vegetarian salad. They chose fresh ingredients that meet male astronauts’ specialized nutritional needs and can be grown in space.
Astronauts in space burn ...
Perceived time has an actual effect on physical healing
2024-01-02
Perceived time has a significant impact on the actual time it takes to heal physical wounds, according to new research by Harvard psychologists Peter Aungle and Ellen Langer.
Their study, published late last month in Nature Scientific Reports, challenges conventional beliefs about psychological influences on physical health. The findings suggest a broader range of psychological influences than is currently appreciated.
To complete their study, the authors used a standardized procedure to mildly wound volunteer subjects. Perceived time was then manipulated in the lab, with each study participant completing three ...
Use of cryopreserved oocytes in patients with poor ovarian response
2024-01-02
About The Study: This study of 67,000 freezing cycles among 47,000 patients reveals a distinct pattern in the utilization of cryopreserved oocytes among patients undergoing planned oocyte cryopreservation in the U.S. Despite the increase in number of patients pursuing oocyte cryopreservation, there is a notably low rate of return to utilize previously vitrified oocytes; notably, patients with poor ovarian response are more likely to return, although the time to return is similar to those with normal ovarian response.
Authors: Yuval Fouks, M.D., M.P.H., of Boston IVF-The Eugin Group in Waltham, Massachusetts, is the corresponding ...
Problem-solving skills training for parents of children with chronic health conditions
2024-01-02
About The Study: The findings of this systematic review and meta-analysis of 23 randomized clinical trials including 3,100 parents suggest that problem-solving skills training for parents of children with chronic health conditions may improve the psychosocial well-being of the parents, their children, and their families. Further high-quality randomized clinical trials with longer follow-up times and that explore physical and clinical outcomes are encouraged to generate adequate evidence.
Authors: Yuanhui Luo, Ph.D., of Central South University in Changsha, Hunan, China, is the corresponding ...