(Press-News.org) CAMBRIDGE, MA -- With help from an artificial language network, MIT neuroscientists have discovered what kind of sentences are most likely to fire up the brain’s key language processing centers.
The new study reveals that sentences that are more complex, either because of unusual grammar or unexpected meaning, generate stronger responses in these language processing centers. Sentences that are very straightforward barely engage these regions, and nonsensical sequences of words don’t do much for them either.
For example, the researchers found this brain network was most active when reading unusual sentences such as “Buy sell signals remains a particular,” taken from a publicly available language dataset called C4. However, it went quiet when reading something very straightforward, such as “We were sitting on the couch.”
“The input has to be language-like enough to engage the system,” says Evelina Fedorenko, Associate Professor of Neuroscience at MIT and a member of MIT’s McGovern Institute for Brain Research. “And then within that space, if things are really easy to process, then you don’t have much of a response. But if things get difficult, or surprising, if there’s an unusual construction or an unusual set of words that you’re maybe not very familiar with, then the network has to work harder.”
Fedorenko is the senior author of the study, which appears today in Nature Human Behavior. MIT graduate student Greta Tuckute is the lead author of the paper.
Processing language
In this study, the researchers focused on language-processing regions found in the left hemisphere of the brain, which includes Broca’s area as well as other parts of the left frontal and temporal lobes of the brain.
“This language network is highly selective to language, but it’s been harder to actually figure out what is going on in these language regions,” Tuckute says. “We wanted to discover what kinds of sentences, what kinds of linguistic input, drive the left hemisphere language network.”
The researchers began by compiling a set of 1,000 sentences taken from a wide variety of sources — fiction, transcriptions of spoken words, web text, and scientific articles, among many others.
Five human participants read each of the sentences while the researchers measured their language network activity using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). The researchers then fed those same 1,000 sentences into a large language model — a model similar to ChatGPT, which learns to generate and understand language from predicting the next word in huge amounts of text — and measured the activation patterns of the model in response to each sentence.
Once they had all of those data, the researchers trained a mapping model, known as an “encoding model,” which relates the activation patterns seen in the human brain with those observed in the artificial language model. Once trained, the model could predict how the human language network would respond to any new sentence based on how the artificial language network responded to these 1,000 sentences.
The researchers then used the encoding model to identify 500 new sentences that would generate maximal activity in the human brain (the “drive” sentences), as well as sentences that would elicit minimal activity in the brain’s language network (the “suppress” sentences).
In a group of three new human participants, the researchers found these new sentences did indeed drive and suppress brain activity as predicted.
“This ‘closed-loop’ modulation of brain activity during language processing is novel,” Tuckute says. “Our study shows that the model we’re using (that maps between language-model activations and brain responses) is accurate enough to do this. This is the first demonstration of this approach in brain areas implicated in higher-level cognition, such as the language network.”
Linguistic complexity
To figure out what made certain sentences drive activity more than others, the researchers analyzed the sentences based on 11 different linguistic properties, including grammaticality, plausibility, emotional valence (positive or negative), and how easy it is to visualize the sentence content.
For each of those properties, the researchers asked participants from crowd-sourcing platforms to rate the sentences. They also used a computational technique to quantify each sentence’s “surprisal,” or how uncommon it is compared to other sentences.
This analysis revealed that sentences with higher surprisal generate higher responses in the brain. This is consistent with previous studies showing people have more difficulty processing sentences with higher surprisal, the researchers say.
Another linguistic property that correlated with the language network’s responses was linguistic complexity, which is measured by how much a sentence adheres to the rules of English grammar and how plausible it is, meaning how much sense the content makes, apart from the grammar.
Sentences at either end of the spectrum — either extremely simple, or so complex that they make no sense at all — evoked very little activation in the language network. The largest responses came from sentences that make some sense but require work to figure them out, such as “Jiffy Lube of — of therapies, yes,” which came from the Corpus of Contemporary American English dataset.
“We found that the sentences that elicit the highest brain response have a weird grammatical thing and/or a weird meaning,” Fedorenko says. “There’s something slightly unusual about these sentences.”
The researchers now plan to see if they can extend these findings in speakers of languages other than English. They also hope to explore what type of stimuli may activate language processing regions in the brain’s right hemisphere.
###
The research was funded by an Amazon Fellowship from the Science Hub, an International Doctoral Fellowship from the American Association of University Women, the MIT-IBM Watson AI Lab, the National Institutes of Health, the McGovern Institute, the Simons Center for the Social Brain, and MIT’s Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences.
END
Complex, unfamiliar sentences make the brain’s language network work harder
A new study finds that language regions in the left hemisphere light up when reading uncommon sentences, while straightforward sentences elicit little response.
2024-01-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
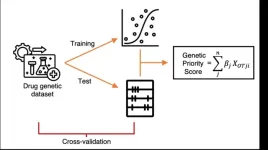
Novel genetic priority score unveiled to enhance target prioritization in drug development
2024-01-03
New York, NY [January 3, 2024]—Driven by the need for a better way to prioritize targets for drug development, the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai has led the development of a novel “genetic priority score” (GPS) that will integrate various types of human genetic data into a single easy-to-interpret score.
The findings were described in the January 3 online issue of Nature Genetics [DOI: 10.1038/s41588-023-01609-2].
Studies have shown that drugs have an increased likelihood of success in clinical trials when ...
Microbial awakening restructures high-latitude food webs as permafrost thaws
2024-01-03
Alaska is on the front lines of climate change, experiencing some of the fastest rates of warming of any place in the world. And when temperatures rise in the state’s interior—a vast high-latitude region spanning 113 million acres—permafrost there not only thaws, releasing significant amounts of its stored carbon back into the atmosphere where it further accelerates rising temperatures, but it decays. This decomposition has the potential to infuse above- and belowground food webs with carbon, which can affect ...
Bacteria load their syringes
2024-01-03
Disease-causing bacteria of the genus Salmonella or Yersinia can use tiny injection apparatuses to inject harmful proteins into host cells, much to the discomfort of the infected person. However, it is not only with a view to controlling disease that researchers are investigating the injection mechanism of these so-called type III secretion systems, also known as "injectisomes".
If the structure and function of the injectisome were fully understood, researchers would be able to hijack it to deliver specific drugs into cells, such as cancer cells. In fact, the structure of the injectisome has already been elucidated. ...
Greener and feasible production: Enzymatic methods for mono- and diacylglycerol synthesis in the food industry
2024-01-03
MAGs, predominantly in 1(3)-MAG form, and DAGs, with 1,3-DAGs as the more stable isomer, are crucial in food, cosmetic, and other industries. While MAGs are vital emulsifiers, comprising 75% of global production, DAGs are known as functional cooking oils that can reduce body fat and serum TAGs. However, their natural concentration in oils is low, prompting extensive research into their chemical and environmentally-friendly enzymatic production.
Recently, a review published in the Grain & Oil Science and Technology journal on 2 November 2023, has shed light on the advancements in enzymatic production methods with special efforts on practical and ...
Re-calibrating the sail plan for Native Hawaiians, Pacific Islanders in ocean sciences
2024-01-03
In Hawaiʻi and across much of Oceania, Pacific Islanders celebrate the connections between their islands and the ocean that surrounds them. “As descendants of the ocean, the dearth of Native Hawaiians and Pacific Islanders (NHPI) in ocean science seems inconsonant,” writes a team of authors that includes University of Hawai‘i (UH) at Mānoa faculty, students, and alumni in an article in a special issue of the journal Oceanography, “Building Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion in the Ocean Sciences. The authors ask, “Where are all our island people in the ...
Monetized evaluation of landscape resources of national parks based on the willingness to pay of multiple interest groups
2024-01-03
In China, national parks represent the country’s most unique natural landscapes. Scientific evaluation of landscape resources is significant for preserving the authenticity and integrity of national parks. Taking Qianjiangyuan National Park System Pilot Zone as an example, this research investigated the willingness of internal group (residents and administrative staff) and external group (tourists) to pay for a hypothetical market project based on the pilot zone via Contingent Valuation Method to acquire the monetized value of landscape resources in the national park, and applied Logistic Regression to analyze the influencing factors. The results show ...
How big data transforms the insurance sector
2024-01-03
In 2022, the insurance industry made a whopping USD 6 trillion globally—more than the entire economy of big countries like Japan and Germany. A new study, published in The Journal of Finance and Data Science, looked at how technology, especially big data, is shaking things up in insurance. Big data means using a lot of information to make better decisions.
The study found that by using big data, insurance companies can understand risks better, offer fair prices and keep customers happier.
“What's surprising is how fast insurance companies are jumping on the big data bandwagon,” says first ...
Deep learning for phase recovery
2024-01-03
Light, as an electromagnetic field, has two essential components: amplitude and phase. However, optical detectors, usually relying on photon-to-electron conversion (such as charge-coupled device sensors and the human eye), cannot capture the phase of the light field because of their limited sampling frequency. Fortunately, as the light field propagates, the phase delay also causes changes in the amplitude distribution; therefore, we can record the amplitude of the propagated light field and then calculate the corresponding phase, called phase recovery. Some common phase ...
Chicken whisperers: humans crack the clucking code
2024-01-03
A University of Queensland-led study has found humans can tell if chickens are excited or displeased, just by the sound of their clucks.
Professor Joerg Henning from UQ’s School of Veterinary Science said researchers investigated whether humans could correctly identify the context of calls or clucking sounds made by domestic chickens, the most commonly farmed species in the world.
“In this study, we used recordings of chickens vocalising in all different scenarios from a previous experiment,” ...
Newly discovered genetic mutation protects against Parkinson’s disease and offers hope for new therapies
2024-01-03
A previously unidentified genetic mutation in a small protein provides significant protection against Parkinson’s disease and offers a new direction for exploring potential treatments, according to a new USC Leonard Davis School of Gerontology study.
The variant, located in a mitochondrial microprotein dubbed SHLP2, was found to be highly protective against Parkinson’s disease; individuals with this mutation are half as likely to develop the disease as those who do not carry it. The variant form of the protein is relatively rare and is found primarily in people of European descent.
The findings appear on January 3, 2024, in the journal Molecular Psychiatry.
First ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Call me invasive: New evidence confirms the status of the giant Asian mantis in Europe
Scientists discover a key mechanism regulating how oxytocin is released in the mouse brain
Public and patient involvement in research is a balancing act of power
Scientists discover “bacterial constipation,” a new disease caused by gut-drying bacteria
DGIST identifies “magic blueprint” for converting carbon dioxide into resources through atom-level catalyst design
COVID-19 vaccination during pregnancy may help prevent preeclampsia
Menopausal hormone therapy not linked to increased risk of death
Chronic shortage of family doctors in England, reveals BMJ analysis
Booster jabs reduce the risks of COVID-19 deaths, study finds
Screening increases survival rate for stage IV breast cancer by 60%
ACC announces inaugural fellow for the Thad and Gerry Waites Rural Cardiovascular Research Fellowship
University of Oklahoma researchers develop durable hybrid materials for faster radiation detection
Medicaid disenrollment spikes at age 19, study finds
Turning agricultural waste into advanced materials: Review highlights how torrefaction could power a sustainable carbon future
New study warns emerging pollutants in livestock and aquaculture waste may threaten ecosystems and public health
Integrated rice–aquatic farming systems may hold the key to smarter nitrogen use and lower agricultural emissions
Hope for global banana farming in genetic discovery
Mirror image pheromones help beetles swipe right
Prenatal lead exposure related to worse cognitive function in adults
Research alert: Understanding substance use across the full spectrum of sexual identity
Pekingese, Shih Tzu and Staffordshire Bull Terrier among twelve dog breeds at risk of serious breathing condition
Selected dog breeds with most breathing trouble identified in new study
Interplay of class and gender may influence social judgments differently between cultures
Pollen counts can be predicted by machine learning models using meteorological data with more than 80% accuracy even a week ahead, for both grass and birch tree pollen, which could be key in effective
Rewriting our understanding of early hominin dispersal to Eurasia
Rising simultaneous wildfire risk compromises international firefighting efforts
Honey bee "dance floors" can be accurately located with a new method, mapping where in the hive forager bees perform waggle dances to signal the location of pollen and nectar for their nestmates
Exercise and nutritional drinks can reduce the need for care in dementia
Michelson Medical Research Foundation awards $750,000 to rising immunology leaders
SfN announces Early Career Policy Ambassadors Class of 2026
[Press-News.org] Complex, unfamiliar sentences make the brain’s language network work harderA new study finds that language regions in the left hemisphere light up when reading uncommon sentences, while straightforward sentences elicit little response.