(Press-News.org)
Overview
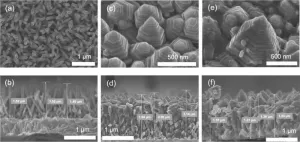
A research team consisting of members of the Egyptian Petroleum Research Institute and the Functional Materials Engineering Laboratory at the Toyohashi University of Technology, has developed a novel high-performance photoelectrode by constructing a zinc oxide nanopagoda array with a unique shape on a transparent electrode and applying silver nanoparticles to its surface. The zinc oxide nanopagoda is characterized by having many step structures, as it comprises stacks of differently sized hexagonal prisms. In addition, it exhibits very few crystal defects and excellent electron conductivity. By decorating its surface with silver nanoparticles, the zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode gains visible light absorption properties, enabling it to function under sunlight irradiation.
Details
Photoelectrochemical water splitting using sunlight is expected to be used as a technology to produce clean energy in the form of hydrogen. As key materials for this technology, photoelectrodes must have low overpotential against water splitting reactions, in addition to high solar absorption and charge transfer efficiencies. For practical applicability, this technology cannot use rare metals as primary materials, and the fabrication process must be industrialized; however, materials that satisfy these requirements have not yet been developed.
Accordingly, the research team solely focused on the zinc oxide nanopagoda array, as such arrays are inexpensive to produce, feature high electron conductivity, and are not vulnerable to raw material depletion. Initially, zinc oxide nanopagoda arrays were considered difficult to fabricate with good reproducibility. Led by Marwa Abouelela – a third-year doctoral student who is also the lead author of this paper - the team first optimized the synthesis process to ensure high reproducibility. When the photoelectrochemical properties of the obtained photoelectrode were evaluated, a relatively large photocurrent was observed to emerge under pseudo-sunlight irradiation. In addition to the high charge transfer efficiency associated with low defect density and high surface chemical reaction activity in many steps, an electromagnetic field analysis has revealed that the nanopagoda's unique nanostructure can efficiently capture ultraviolet rays contained in the incident light.
To ensure the effective utilization of visible light, which accounts for 55% of sunlight, the research team further improved the photoelectrochemical properties by decorating the zinc oxide nanopagoda surface with silver nanoparticles that exhibit localized surface plasmon resonance, increasing the photocurrent by approximately 1.5-fold. The action spectrum of the photocurrent value indicates that this improvement is primarily attributed to the hot electron transfer caused by visible light absorption by the localized surface plasmon resonance of silver nanoparticles. By optimizing the application of silver nanoparticles, it became possible to only improve the photoelectrochemical properties while preventing adverse effects on the properties of the nanopagoda itself.
Development background
Associate Professor Go Kawamura, one of the corresponding authors, stated the following: “Zinc oxide nanopagodas were considered for application only to electron gun emitters, utilizing their high charge transfer efficiency. However, because the structure has many steps, our initial idea was that it is highly active against surface chemical reactions and may be suitable for catalyzing photoelectrochemical reactions. Having succeeded in fabricating the nanopagoda, we aimed to improve the efficiency of sunlight utilization by applying silver nanoparticles that exhibit localized surface plasmon resonance, and evaluated the effect by electromagnetic field analysis; however, it was found that the zinc oxide nanopagoda captures incident light, especially ultraviolet rays, into its interior. Although this was completely unexpected, it was a fortunate discovery, as this property contributes to the improvement of photoelectrochemical properties.”
Future outlook
Currently, Marwa and students of the same laboratory are leading an investigation into the effect of precise structural control of zinc oxide nanopagodas, as well as surface decoration with other materials, on the photoelectrochemical properties of said pagodas. Because zinc oxide is prone to photocorrosion, it cannot withstand long-term sunlight irradiation by itself, leading us to focus on improving durability via surface decoration. Upon achieving both high photoelectrochemical properties and durability, we plan to carry out water splitting hydrogen production in a real environment (decomposition of river water or seawater by sunlight) and extract real problems.
Reference
Abouelela MM, Kawamura G, Tan WK, Amiruldin M, Maegawa K, Nishida J, Matsuda A (2024) Ag nanoparticles decorated ZnO nanopagodas for photoelectrochemical application. Electrochemistry Communications,158, 107645, 10.1016/j.elecom.2023.107645.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by JSPS Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research 21K18823, 21K18824, and 22K04737, the Casio Science Promotion Foundation, the ENEOS TonenGeneral Research/Development Encouragement & Scholarship Foundation, and the Ministry of Higher Education of the Arab Republic of Egypt PD-071.
END
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Oregon State University researchers have discovered vitamin B1 produced by microbes in rivers, findings that may offer hope for vitamin-deficient salmon populations.
Findings were published in Applied and Environmental Microbiology.
The authors say the study in California’s Central Valley represents a novel piece of an important physiological puzzle involving Chinook salmon, a keystone species that holds significant cultural, ecological and economic importance in the Pacific Northwest and Alaska.
Christopher ...
Overview
A research team from the Institute for Research on Next-generation Semiconductor and Sensing Science (IRES²) at the Toyohashi University of Technology, National Institute of Technology, Ibaraki College, and TechnoPro R&D Company has successfully demonstrated low-invasive neural recording technology for the brain tissue of diabetic mice. This was achieved using a small needle-electrode with a diameter of 4 µm. Recording neuronal activity within the diabetic brain tissue is particularly challenging due to various complications, including the development of cerebrovascular disease. Because of the significant advantage of the miniaturized needle-electrode compared to conventional ...
Medical technology innovations achieved by integrating science and medicine have improved the quality of life for patients. Especially noteworthy is the emergence of electronic devices implanted in the body, such as in the heart or brain, which enable real-time measurement and regulation of physiological signals, presenting new solutions for challenging conditions like Parkinson's disease. However, technical constraints have hindered the semi-permanent use of electronic devices after their implantation.
A collaborative research team led by Professor Sung-Min Park from the Departments of Convergence IT Engineering, Mechanical Engineering, and ...
LOS ANGELES — Hearing loss affects approximately 40 million American adults, yet only one in 10 people who need hearing aids use them, research shows.
Those who don’t use hearing aids but should may want to make wearing them one of their New Year’s resolutions, according to a new study from Keck Medicine of USC published today in The Lancet Healthy Longevity.
“We found that adults with hearing loss who regularly used hearing aids had a 24% lower risk of mortality than those who never wore them,” ...
Australian researchers have successfully trialled a novel experiment to address offensive and rude comments in operating theatres by placing ‘eye’ signage in surgical rooms.
The eye images, attached to the walls of an Adelaide orthopaedic hospital’s operating theatre without any explanation, had the desired effect in markedly reducing poor behaviour among surgical teams.
Lead researcher University of South Australia Professor Cheri Ostroff attributed the result to a perception of being “watched”, even though the eyes were not real.
The three-month experiment ...
The avocado has soared to unprecedented heights of popularity, gracing the plates of toast enthusiasts and health-conscious individuals worldwide. But what are the overlooked consequences of our latest food obsession?
“The avocado has come to represent so much more than just a fruit. It’s wrapped up with ideas of generational conflict, environmental chaos and social injustice. Over the last century, through careful marketing, it has evolved into a commodity crop with a huge social media following.” says Honor May Eldridge, a food policy expert who works to promote sustainable agriculture around the ...
CLEVELAND, Ohio – Jonathan Stamler, MD, has been named a Fellow of the National Academy of Inventors (NAI). Dr. Stamler is the co-founder and president of Harrington Discovery Institute at University Hospitals (UH), and the Robert S. and Sylvia K. Reitman Family Foundation Distinguished Professor of Cardiovascular Innovation at the Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine.
Election as an Academy Fellow is the highest professional distinction awarded solely to inventors and the 2023 Class of Fellows ...
Suzanne Lenhart, Chancellor’s Professor in the Department of Mathematics, will join a storied list of honored speakers to deliver the Josiah Willard Gibbs Lecture at the world’s largest annual math gathering, the American Mathematics Society (AMS) Joint Mathematics Meetings (JMM2024), taking place January 3–6, 2024, in San Francisco.
JMM2024 brings researchers from 20 national and international partner associations to share the latest developments in mathematical thought and application.
Lenhart is the ...
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. – The blood-brain barrier blocks the entry of antibodies into the brain. This limits the potential use of antibody therapeutics to treat brain diseases, such as brain tumors.
Elsewhere in the body, more than 100 United States Food and Drug Administration-approved therapeutic antibodies are used by medical teams to treat cancers and autoimmune, infectious and metabolic diseases. Finding ways to transport therapeutic antibodies across the blood-brain barrier — from the peripheral blood stream into the central nervous system — could create effective treatments that act in the brain.
In a study published in the journal Frontiers in Cell and Developmental ...
Today, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) announced the issuance of a Request for Proposals (RFPs) for the competitive selection of a management and operating contractor for Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (FNAL).
FNAL is a single-purpose laboratory that leads the nation in the construction and operation of world-leading accelerator and detector facilities and in the development of the underlying technology for particle physics research. Its mission is centered on delivering breakthrough science and technology ...