(Press-News.org) How can climate policy be made more just and fair? IIASA researchers have synthesized different dimensions of justice into a framework that can be used by climate scientists and policymakers, explaining how previous research has neglected many potential justice positions and how these can be implemented in policy contexts.
Dealing with climate change is not just about the environment – it is also about justice and fairness. This includes how we transition to cleaner ways of living, the different impacts on various groups of people, and who is responsible for what. Paying more attention to fairness and justice when making decisions will help policymakers to devise better climate policies that people can agree on.
Currently, people however don't always understand or talk about these concepts in the same way. While experts may think about justice and fairness when they plan ways to, for example, reduce carbon emissions, they often don't explain it clearly, instead using different words and measures, which can confuse both researchers and the public. This confusion makes it harder to share and understand the results.
In their new study published in Nature Climate Change, IIASA researchers propose a conceptual framework rooted in philosophical theory to address this gap in possibly the first systematic attempt to describe these different aspects or dimensions of justice for the climate domain in an interdisciplinary context. Their innovative framework synthesizes distributional, procedural, corrective, recognitional, and transitional justice that can be used by scientists and policymakers.
The framework aims to enhance interdisciplinary understanding of climate justice to prevent its mischaracterization and its misuse to justify delayed climate action. Recognizing that justice can either support or hinder decarbonization efforts, the researchers note that more research on justice-related issues is essential for the next cycle of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC).
“This framework aims to achieve three goals: improve clarity by using terminology from justice scholarship; promote awareness and consistency in examining justice concerns as part of a coherent whole; and enhance comparability across scenarios and modeling contexts, to facilitate discussions on these issues,” explains IIASA researcher Caroline Zimm, one of the study lead authors.
To implement this framework effectively, the authors propose the creation of a Justice Model Intercomparison Project (JUSTMIP) focused on mitigation scenarios.
“JUSTMIP would provide reporting templates for in-depth exploration of various research aspects, sectors, and model comparisons within the context of scenarios used by the next IPCC Assessment Report. This will raise awareness about the possibilities and limitations regarding justice considerations in these scenarios and enhance transparency,” notes IIASA Energy, Climate, and Environment Program Director, Keywan Riahi.
“It is important to note that our framework does not aim to evaluate what is just or unjust but rather provides a structured platform for identifying and discussing justice considerations. By bringing clarity and consistency to the discourse surrounding climate justice, this framework will empower both researchers and policymakers to navigate the intricate justice landscape and ensure that justice is a fundamental aspect of climate policy decisions,” concludes co-lead author Kian Mintz-Woo, a guest researcher at IIASA who is also associated with the Department of Philosophy and the Environmental Research Institute at University College Cork in Ireland.
This pioneering work is a significant step toward a more holistic and multidimensional understanding of justice in the context of climate change, offering a valuable tool to advance climate policy and research worldwide.
Reference
Zimm, C., Mintz-Woo, K., Brutschin, E., Hanger-Kopp, S., Hoffmann, R., Kikstra, J.S., Kuhn, M., Min, J., Muttarak, R., Pachauri, S., Patange, O., Riahi, K., Schinko, T. (2024). Justice considerations in climate research. Nature Climate Change DOI: 10.1038/s41558-023-01869-0
About IIASA:
The International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis (IIASA) is an international scientific institute that conducts research into the critical issues of global environmental, economic, technological, and social change that we face in the twenty-first century. Our findings provide valuable options to policymakers to shape the future of our changing world. IIASA is independent and funded by prestigious research funding agencies in Africa, the Americas, Asia, and Europe. www.iiasa.ac.at
END
Exploring dimensions of justice in climate science
2024-01-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
CHOP researchers develop algorithm to determine how cellular “neighborhoods” function in tissues
2024-01-08
Philadelphia, January 8, 2024 – Researchers from Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) have developed a new AI-powered algorithm to help understand how different cells organize themselves into particular tissues and communicate with one another. This new tool was tested on two types of cancer tissues to reveal how these “neighborhoods” of cells interact with one another to evade therapy, and more studies could reveal more information about the function of these cells in the tumor ...
Researchers engineer in vivo delivery system for prime editing, partially restoring vision in mice
2024-01-08
Prime editing, a versatile form of gene editing that can correct most known disease-causing genetic mutations, now has a new vehicle to deliver its machinery into cells in living animals.
A team of researchers at the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard has engineered virus-like particles to deliver prime editors to cells in mice at a high enough efficiency to rescue a genetic disorder. In the new work published today in Nature Biotechnology, the team adapted engineered virus-like particles (eVLPs) that they had previously designed to carry base editors — ...
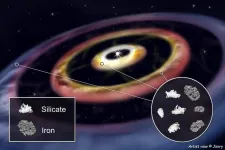
Three iron rings in a planet-forming disk
2024-01-08
The origin of Earth and the Solar System inspires scientists and the public alike. By studying the present state of our home planet and other objects in the Solar System, researchers have developed a detailed picture of the conditions when they evolved from a disk made of dust and gas surrounding the infant sun some 4.5 billion years ago.
Three rings hinting at two planets
With the breathtaking progress made in star and planet formation research aiming at far-away celestial objects, we can now investigate the conditions in environments around young stars and compare them to the ones derived for the early Solar System. Using the European Southern Observatory’s (ESO) Very Large ...
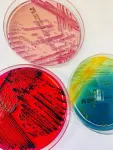
More than thirty new species of bacteria discovered in patient samples
2024-01-08
Unknown germs are a common occurrence in hospitals. Researchers at the University of Basel have spent many years collecting and analyzing them. They have identified many new species of bacteria, some of which are significant for clinical practice.
Bacterial infections can be treated more efficiently if the cause of the disease is known. In most cases, all it takes to identify a pathogen is an analysis in a medical laboratory. Sometimes, however, the standard methods are insufficient – for example, if the species of bacteria has not yet been classified or ...
Where do patients choose to undergo breast cancer surgery, and do these choices drive health care inequality?
2024-01-08
Including patients as partners for making decisions about their medical treatments is an important aspect of patient-centered care. A new study from England examined choices that patients with breast cancer make when considering where to have surgery for their condition and assessed how policies that offer such choices might affect inequalities in the health care system. The findings are published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
For the study, investigators analyzed data from the National Health Service (NHS), the publicly ...
Some mosquitoes like it hot
2024-01-08
Certain populations of mosquitoes are more heat tolerant and better equipped to survive heat waves than others, according to new research from Washington University in St. Louis.
This is bad news in a world where vector-borne diseases are an increasingly global health concern. Most models that scientists use to estimate vector-borne disease risk currently assume that mosquito heat tolerances do not vary. As a result, these models may underestimate mosquitoes’ ability to spread diseases in a warming world.
Researchers led by Katie M. Westby, a senior scientist at Tyson Research Center, Washington ...
Out-of-pocket cost increase could put HIV prevention medications out of reach
2024-01-08
PHILADELPHIA – Increasing patients’ out of pocket costs for HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP), medications, which have been shown to dramatically reduce the risk of HIV infection, could lead to a significant reduction in PrEP use and a rise in HIV infection rates, according to a new study co-led by researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania and Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
The study, published today in Health Affairs, was designed, in part, to explore the impact that out-of-pocket cost increases could have, depending on the outcome of an ongoing court case challenging certain ...
Survey finds majority of Americans think bariatric surgery is a shortcut to losing pounds, should only be a last resort
2024-01-08
Orlando, Fla - More than two in five U.S. adults suffer from obesity, an epidemic that continues to trend upward. While bariatric surgery is an extremely effective treatment option, a new national survey by Orlando Health reveals common stigmas that may deter those who qualify for surgery from pursuing the treatment they need.
“Treatment plans for obesity are tailored to each individual patient based on things like body mass index and existing medical conditions and may include medication, lifestyle changes, counseling and bariatric surgery,” said Andre Teixeira, MD, medical ...
First ever scientific study on First World War crater reveals new details on its history
2024-01-08
The spectacular explosion of the mine at Hawthorn Ridge – a fortified German front-line position in the First World War – marked the beginning of the Battle of the Somme, and remains one of the best-known pieces of film from the whole conflict.
More than 60ft below the surface, British miners had dug a gallery for more than 900 metres from their lines and packed it with 40,000 lbs of explosives. It was one of 19 mines placed beneath German front positions that were detonated on 1st July, 1916 to mark the start of the offensive.
But the detonation of the ...
Blood flow changes in the eyes could influence visual symptoms of migraines
2024-01-06
A recent study found changes in blood flow in the retina could explain why some migraine patients experience visual symptoms. The findings could represent a long-sought observable marker for migraines that doctors can use to aid in the clinical treatment of the condition.
While patients with migraines often experience symptoms such as pain around the eye, sensitivity to light, blind spots and visual blurring, the mechanisms behind those symptoms have not been well understood. UCLA Health researchers used a non-invasive imaging technique, known as optical coherence tomography angiography, or OCTA, ...