(Press-News.org)
“TAR cloning is used to genetically engineer synthetic viruses with novel properties that may be used for the development of new vaccines.”
BUFFALO, NY- January 8, 2024 – A new review paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on December 22, 2023, entitled, “Transformation-associated recombination (TAR) cloning and its applications for gene function; genome architecture and evolution; biotechnology and biomedicine.”
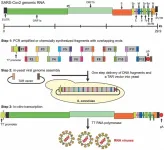
Transformation-associated recombination (TAR) cloning represents a unique tool to selectively and efficiently recover a given chromosomal segment up to several hundred kb in length from complex genomes (such as animals and plants) and simple genomes (such as bacteria and viruses). The technique exploits a high level of homologous recombination in the yeast Sacharomyces cerevisiae.
“TAR cloning has become a valuable procedure for the selective and efficient isolation and manipulation of large DNA molecules. [...] The ability to isolate individual gene alleles will help to clarify whether a particular allele is associated with predisposition to different diseases, including cancer.”
In this new review, researchers Natalay Kouprina and Vladimir Larionov from the National Cancer Institute's Developmental Therapeutics Branch summarized multiple applications of the pioneering TAR cloning technique, developed previously for complex genomes, for functional, evolutionary, and structural studies, and extended the modified TAR versions to isolate biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs) from microbes, which are the major source of pharmacological agents and industrial compounds, and to engineer synthetic viruses with novel properties to design a new generation of vaccines. TAR cloning was adapted as a reliable method for the assembly of synthetic microbe genomes for fundamental research.
“In this review, we also discuss how the TAR cloning in combination with HAC (human artificial chromosome)- and CRISPR-based technologies may contribute to the future.”
Read the full paper: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.28546
Correspondence to: Natalay Kouprina
Email: kouprinn@mail.nih.gov
Keywords: transformation-associated recombination, TAR, microbes, biomedicine, biotechnology
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article: https://oncotarget.altmetric.com/details/email_updates?id=10.18632%2Foncotarget.28546
About Oncotarget: Oncotarget (a primarily oncology-focused, peer-reviewed, open access journal) aims to maximize research impact through insightful peer-review; eliminate borders between specialties by linking different fields of oncology, cancer research and biomedical sciences; and foster application of basic and clinical science.
To learn more about Oncotarget, visit Oncotarget.com and connect with us on social media:
X, formerly known as Twitter
Facebook
YouTube
Instagram
LinkedIn
Pinterest
LabTube
Soundcloud
Click here to subscribe to Oncotarget publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact: media@impactjournals.com.
Oncotarget Journal Office
6666 East Quaker Str., Suite 1A
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957 (option 2)
###
END
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Mobile phones pack a lot of information into pocket-sized devices, which is why users may want to slow down the next time they’re scrolling through social media or checking email on a mobile app. People process information more efficiently but tend to be less vigilant about misinformation on their mobile phones compared to personal computers (PCs), according to a team led by Penn State researchers. This is especially true for users who have developed a routine or habit of using their ...
AMHERST, Mass. – In a first-of-its-kind research breakthrough, a team of scientists at the University of Massachusetts Amherst has analyzed and described what they call the “mosquito effect,” which sheds light on how certain pathogens, such as cancerous tumor cells, can outwit the body’s immune system.
Just as mosquitoes ingest their host’s blood, the immune system’s T cells incorporate cytoplasmic material from tumors into their own cytoplasm. While it has long been known that many kinds of cells can transfer cellular material from one to another, the transfer of the cytoplasm has never been observed in T cells. Subsequent single-cell RNA (scRNA) ...
Researchers have developed a new soft robot design that engages in three simultaneous behaviors: rolling forward, spinning like a record,and following a path that orbits around a central point. The device, which operates without human or computer control, holds promise for developing soft robotic devices that can be used to navigate and map unknown environments.
The new soft robots are called twisted ringbots. They are made of ribbon-like liquid crystal elastomers that are twisted – like a rotini ...
In recent years, there has been rising concern that tiny particles known as microplastics are showing up basically everywhere on Earth, from polar ice to soil, drinking water and food. Formed when plastics break down into progressively smaller bits, these particles are being consumed by humans and other creatures, with unknown potential health and ecosystem effects. One big focus of research: bottled water, which has been shown to contain tens of thousands of identifiable fragments in each container.
Now, using newly refined technology, researchers have entered a whole ...
The body’s immune response to Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) may play a role in causing damage in people with multiple sclerosis, according to a new study led by UTHealth Houston.
EBV infection has long been associated with multiple sclerosis, but how the infection might contribute to multiple sclerosis has not been clear. More than 95% of people have been infected with this very common virus; however, it typically remains in its latent stage and doesn’t cause any issues. In some cases, though, the T-cells specific for the EBV infection may cause ...
EMBARGO: THIS CONTENT IS UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL 3 P.M. U.S. EASTERN STANDARD TIME ON JANUARY 8. INTERESTED MEDIA MAY RECIVE A PREVIEW COPY OF THE JOURNAL ARTICLE IN ADVANCE OF THAT DATE OR CONDUCT INTERVIEWS, BUT THE INFORMATION MAY NOT BE PUBLISHED, BROADCAST, OR POSTED ONLINE UNTIL AFTER THE RELEASE WINDOW.
A global study organized and led by Colorado State University scientists shows that the effects of extreme drought – which is expected to increase in frequency with climate change – has been greatly underestimated for grasslands and shrublands.
The findings – published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences – quantify the impact of extreme ...
Researchers at McMaster University have discovered a molecular “barcode” system used by disease-causing bacteria to distinguish between beneficial and toxic molecules.
Published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), the new study shows that many bacteria can figuratively scan genetic codes to learn which proteins to keep and which proteins to expel into the environment.
According to researchers, those proteins that are expelled are often toxic to human cells, making the ...
Well-managed migration can enable migrants to boost sustainable development, research shows.
Sustainable development means enhancing wellbeing in ways that equitably meet needs of present and future generations.
Migration is often viewed as a threat to this – and to stability and security – while the benefits for migrants and host nations and regions are overlooked.
The new research – a set of studies published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences – shows new policies are needed for managing migration to maximise sustainability, and to minimise involuntary displacement due to conflict or disasters.
The ...
Novel Test Holds Promise for Detecting Parkinson’s Disease Early
Investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital and the Wyss Institute are working together to develop a new approach to detect and quantify minute amounts of a biomarker of Parkinson’s disease and related disorders at early stages
The platform has the potential to create early applicable molecular diagnostics, improve clinical trials, and facilitate drug screening
(Boston) — In the development of Parkinson’s ...
When imagining corals, the picture that comes to mind is usually a stationary one: a garden of rock-like structures covering sections of the ocean floor. Reef conservation efforts typically focus on preserving established coral and protecting them from known stressors such as pollution, overfishing and runoff from coastline populations.
However, new research near Miloliʻi in the southwestern part of Hawai’i Island shows that identifying and protecting marine ecosystems, both down-current and up-current of coral reefs, specifically areas where coral larvae are more likely to survive and thrive, is crucial to future coral conservation and restoration efforts—especially ...