Photostimulation: non-invasive and effective therapeutic approach for Alzheimer’s disease
2024-01-09
(Press-News.org)
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is an age-related neurodegenerative disorder. β-amyloid (Aβ) deposition in the brain is a crucial contributor to the pathogenesis of AD, mitigating excessive cerebral Aβ burden has been considered as a possible therapeutic strategy for AD. Meningeal lymphatic vessels (MLVs) are recently discovered structures responsible for exchanging soluble components between the cerebrospinal fluid and interstitial fluid, and have been proved to be a potential pathway of Aβ drainage.
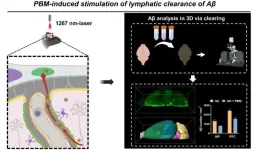
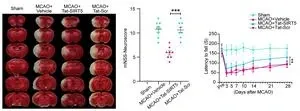
Researchers at Huazhong University of Science and Technology (HUST), China, collaborated with researchers at Saratov State University, Russia, demonstrate that 1267-nm photobiomodulation (PBM) significantly alleviates Aβ deposition and cognitive decline in 5xFAD mice, and is safe as it does not induce a significant increase in cortical temperature. With the combination of 3D tissue optical clearing imaging and automatic brain region segmentation, they show that PBM can reduce Aβ plaques in the prefrontal cortex and the hippocampus, but to varying degrees in different subregions. PBM-mediated stimulation of Aβ elimination from the brain via the MLVs system may be a key mechanism in its therapeutic effects for AD in mice. The work entitled “Photostimulation of lymphatic clearance of β-amyloid from mouse brain: a new strategy for the therapy of Alzheimer’s disease” was published on Frontiers of Optoelectronics (published on Dec. 14, 2023).
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-01-09
Love is blind, the saying goes, and thanks to a world-first Australian study, we are now a step closer to understanding why.
It is well known that romantic love changes the brain, releasing the so-called love hormone oxytocin, responsible for the euphoria we feel when falling in love.
Now, researchers from the ANU, University of Canberra and University of South Australia have measured how a part of the brain is responsible for putting our loved one on a pedestal in that first flush of romance.
In the world’s first study investigating the link between the human brain’s behavioural activation ...
2024-01-09
Ammonia is a necessary feedstock to produce nitrogen-based fertilizers, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and polymers. To date, about 80% of global ammonia is used to produce nitrogen-based fertilizers which relates to 50% of global food production. The global production of ammonia is about 180 million metric tons per year through the carbon-intensive and highly energy-consuming Haber-Bosch process. The high energy consumption, high carbon intensity, and high capital investment of the Haber-Bosch process make the development of environmentally sustainable and affordable routes for ammonia synthesis under ambient conditions more urgent. The electrochemical ammonia ...
2024-01-09
Measuring airborne grass allergen levels instead of pollen counts will be more beneficial for hay fever sufferers as new research shows grass allergen levels are more consistently associated with hay fever symptoms than grass pollen counts.
The research, published today in The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology and led by King’s College London and Imperial College London, shows for the first time that measuring airborne allergen levels will help people with hay fever better control their symptoms.
1 in 4 adults in the UK suffer from hay fever from late-March to September. Symptoms include a runny or blocked ...
2024-01-09
Women with autoimmune disease are more likely to suffer from depression during pregnancy and after childbirth; conversely, women with a history of perinatal depression are at higher risk of developing autoimmune disease, a new study from Karolinska Institutet published in the journal Molecular Psychiatry reports.
In autoimmune disease, the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own healthy tissue. Some of the most common autoimmune diseases are gluten intolerance (coeliac disease), autoimmune thyroiditis, rheumatoid ...
2024-01-09
A study of seriously ill patients from academic medical centers across the country has found that nearly a quarter had a delayed or missed diagnosis.
All the patients had either been transferred to the intensive care unit (ICU) after being admitted or died in the hospital. The researchers concluded that three-quarters of these diagnostic errors contributed to temporary or permanent harm, and that diagnostic errors played a role in about one in 15 of the deaths.
The most common errors identified in the study involved delayed rather than missed diagnoses, for example because a specialist was consulted too late or an alternate diagnosis was not considered ...
2024-01-09
LA JOLLA, CA— Ethanol—the compound found in alcoholic beverages—interferes with the normal functioning of a long list of biological molecules, but how each of these interactions contributes to the behavioral effects of alcohol is not fully understood. A guiding, but elusive, goal of researchers is to identify the protein (or proteins) to which ethanol binds that makes some people vulnerable to excessive drinking. Solving this question would point the way to effective therapies for alcohol use disorder, ...
2024-01-09
As climate change fuels sea level rise, younger people will migrate inland, leaving aging coastal populations — and a host of consequences — in their wake, a study by Florida State University researchers finds.
While destination cities will work to sustainably accommodate swelling populations, aging coastal communities will confront stark new challenges, including an outflow of vital human infrastructure such as health care workers, said Associate Professor of Sociology Matt Hauer, lead author of the study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of ...
2024-01-09
Following an extensive national search, Diane M. Simeone, MD, has been appointed director of Moores Cancer Center at UC San Diego Health, effective April 1, 2024.
Simeone brings robust institutional, national and international leadership experience to both oncologic patient care and scientific research, with a focus on establishing novel models of interdisciplinary collaboration. She is an internationally recognized surgeon-expert in the biology and multidisciplinary treatment of pancreatic neoplasms, with an active clinical practice in pancreatic surgery.
Simeone currently serves as the Laura and Isaac Perlmutter ...
2024-01-08
How do you deploy an environmental sensor to collect climate change readings over a prolonged period on an uninhabited island without failing? How do you power a seismic detector to operate for months in an underwater cave?
In environments that are difficult to reach because of the hazards or hardships for humans, a device behaving like a native plant could be the answer. This is the approach taken by Suyi Li, associate professor in mechanical engineering at Virginia Tech, and Clemson professor and collaborator Ian Walker. Their work is being advanced ...
2024-01-08
Almost a quarter of patients who were admitted to the ICU or died in 29 hospitals in the United States experienced a diagnostic error
Efforts and initiatives are underway across the country to address and prevent the causes of diagnostic errors
A new study from researchers from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, in collaboration with researchers at the University of California San Francisco, has shed light on the rate and impact of diagnostic errors in hospital settings. In an analysis of electronic health records from 29 hospitals across the country of 2,428 patients who ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Photostimulation: non-invasive and effective therapeutic approach for Alzheimer’s disease