(Press-News.org) New York, January 9, 2024 — A research paper published in Royal Society’s Biology Letters on January 10 has revealed that picrodontids —an extinct family of placental mammals that lived several million years after the extinction of the dinosaurs—are not primates as previously believed.
The paper—co-authored by Jordan Crowell, an Anthropology Ph.D. candidate at the CUNY Graduate Center; Stephen Chester, an Associate Professor of Anthropology at Brooklyn College and the Graduate Center; and John Wible, Curator of Mammals at the Carnegie Museum of Natural History— is significant in that it settled a paleontological debate that has been brewing for over 100 years while helping to paint a more clear picture of primate evolution.
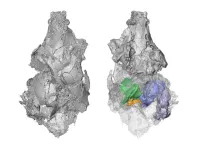
For the last 50 years, paleontologists have believed picrodontids, which were no larger than a mouse and likely ate foods such as fruit, nectar, and pollen, were primates, based on features of their teeth that they share with living primates. But by using modern CT scan technology to analyze the only known preserved picrodontid skull in Brooklyn College’s Mammalian Evolutionary Morphology Laboratory, Crowell, the lead author on the paper, worked with Chester, the paper’s senior author, and Wible to determine they are not closely related to primates at all.
“While picrodontids share features of their teeth with living primates, the bones of the skull, specifically the bone that surrounds the ear, are unlike that of any living primate or close fossil relatives of primates,” Crowell said. “This suggests picrodontids and primates independently evolved similarities of their teeth likely for similar diets. This study also highlights the importance of revisiting old specimens with updated techniques to examine them.”
Chester, who serves as Crowell’s Ph.D. adviser, has both a professional and personal interest in this research. It was Chester’s renowned colleague and “academic grandfather,” Professor Emeritus Frederick Szalay from CUNY’s Hunter College and the Graduate Center, who in 1968 first convincingly classified picrodontids as primates based on evidence from fossilized teeth. Szalay studied the teeth of the only known picrodontid skull, Zanycteris paleocenus, for his research—the same skull this team examined with the new technology that led to their discovery.
“The Zanycteris cranium was prepared and partially submerged in plaster around 1917, so researchers studying this important specimen at the American Museum of Natural History were not aware of how much cranial anatomy was hidden over the last 100 years” Chester said. “Micro-CT scanning has revolutionized the field of paleontology and allows researchers to discover so much more about previously studied fossils housed in natural history museum collections.”
The research was funded by grants Chester and Crowell secured through Brooklyn College from the National Science Foundation and The Leakey Foundation. Chester and Crowell are also currently working on several additional externally funded research projects focused on how primates and other mammals evolved following the extinction of the dinosaurs. They encourage undergraduates to contact them regarding funded research opportunities in the Mammalian Evolutionary Morphology Laboratory.
About the Graduate Center of The City University of New York
The CUNY Graduate Center is a leader in public graduate education devoted to enhancing the public good through pioneering research, serious learning, and reasoned debate. The Graduate Center offers ambitious students nearly 50 doctoral and master’s programs of the highest caliber, taught by top faculty from throughout CUNY — the nation’s largest urban public university. Through its nearly 40 centers, institutes, initiatives, and the Advanced Science Research Center, the Graduate Center influences public policy and discourse and shapes innovation. The Graduate Center’s extensive public programs make it a home for culture and conversation.
About Brooklyn College
Widely known for its offer of an excellent education at an affordable tuition and recognized nationally for its diverse student body, Brooklyn College has been an anchor institution within the borough of Brooklyn and greater New York City for more than 90 years. With approximately 15,000 students in more than 100 undergraduate and graduate degree programs in the arts, humanities, sciences, education, and business, the college is renowned for its rigorous academics, award-winning faculty, distinguished alumni, and community impact. Part of the City University of New York (CUNY), Brooklyn College offers a vibrant and supportive student experience on a beautifully landscaped 35-acre campus in the borough’s Midwood neighborhood.
###
END
Frontline healthcare workers in busy hospitals feel that they are “just rearranging the deckchairs on the Titanic” according to new research into the impact of under-resourced and high-pressure emergency hospital departments in the UK.
A study from the Royal College of Emergency Medicine and University of Bath, led by clinical psychologist Dr Jo Daniels in collaboration with colleagues at UWE Bristol and the University of Bristol, argues that hospitals need better leadership to help change cultures and support people’s basic needs.
In addition to reflections ...
The acidity of Antarctica’s coastal waters could double by the end of the century, threatening whales, penguins and hundreds of other species that inhabit the Southern Ocean, according to new research from the Univeristy of Colorado Boulder.
Scientists projected that by 2100, the upper 650 feet (200 meters) of the ocean—where much marine life resides—could see more than a 100% increase in acidity compared with 1990s levels. The paper, appeared Jan. 4 in the journal Nature Communications.
“The findings are critical for our understanding ...
HOUSTON (Jan 9, 2024)— A breakthrough study led by Dr. Mehdi Razavi at The Texas Heart Institute (THI), in collaboration with a biomedical engineering team of The University of Texas at Austin (UT Austin) Cockrell School of Engineering led by Dr. Elizabeth Cosgriff-Hernandez, sets the foundation of a ground-breaking treatment regimen for treating ventricular arrhythmia. Their study published in Nature Communications demonstrates the design and feasibility of a new hydrogel-based pacing modality.
The urgent need for an effective therapeutic ...
JUPITER, Fla. — Like the Greek mythological beast with a snake’s tail and two ferocious heads, a potential Parkinson’s medicine created in the lab of chemist Matthew Disney, Ph.D., is also a type of chimera bearing two heads. One seeks out a key piece of Parkinson’s-causing RNA, while the other goads the cell to chop it to pieces for recycling.
The research is described in the Jan. 9 issue of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, or PNAS.
Parkinson’s is a frustrating and all too common disease. Slowly, people with Parkinson’s lose brain cells and other neurons needed to make the neurotransmitter dopamine. This progressive ...
In the fascinating world of plant biology, an innovative study recently featured on the cover of The Plant Journal has been turning heads. The research delves into the intricate defense mechanisms of tomatoes against the notorious bacterial pathogen, Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato (Pst). It's a classic tale of nature's arms race: as pathogens evolve to outsmart plant defenses, plants counter with more sophisticated immune responses.
The study is based on research conducted by scientists in Dr. Greg Martin’s lab ...
Astronomers using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope have found a brown dwarf (an object more massive than Jupiter but smaller than a star) with infrared emission from methane, likely due to energy in its upper atmosphere. This is an unexpected discovery because the brown dwarf, W1935, is cold and lacks a host star; therefore, there is no obvious source for the upper atmosphere energy. The team speculates that the methane emission may be due to processes generating aurorae.
These findings are being presented at the 243rd meeting of the American Astronomical Society in New Orleans.
To help explain the mystery of the infrared ...
Beer pong. Quarters. Flip cup. The drinking games college students play can seem like an alcohol-laced version of intramural sports.
When college-aged drinkers imbibe too heavily, the risk for physically harming a romantic partner rises considerably.
What if there was a way for heavy drinkers to monitor their alcoholic intake and blood-alcohol levels in real time, before an intimate situation cascades into physical violence?
Or, as Virginia Tech researcher and assistant professor of psychology Meagan Brem put it: “If we can identify ...
Led by researchers from Université de Montréal's Trottier Institute for Research on Exoplanets (iREx), a team of astronomers has harnessed the power of the revolutionary James Webb Space Webb Telescope (JWST) to study the "hot Saturn" exoplanet HAT-P-18 b.
Their findings, published last month in the journal Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, paint a complete picture of the HAT-P-18 b's atmosphere while exploring the great challenge of distinguishing its atmospheric signals from the activity of its star.
HAT-P-18 b is located over 500 light-years away ...
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), a common infection in children and senior adults, can also infect nerve cells and trigger inflammation leading to nerve damage, according to a new Tulane University study.
RSV can cause mild symptoms such as coughing, sneezing and fever or lead to more severe conditions such as pneumonia or bronchiolitis. But since the disease was first discovered in 1956, it has been thought to only infect the respiratory tract.
This study, published in The Journal of Infectious Diseases, is the first to prove that RSV can penetrate nerve cells and may provide the ...
https://www.ninds.nih.gov/news-events/press-releases/common-marker-neurological-diseases-may-play-role-healthy-brainsResearchers have discovered that a protein called phosphorylated α-synuclein, which is associated with several neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s disease and Lewy body dementia, is also involved in the normal processes of how neurons communicate with each other in a healthy brain. The research, published in Neuron, was funded in part by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS), a part of the National Institutes of Health.
Phosphorylation is a process where a phosphate ...