(Press-News.org) Environmental epidemiologists at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health, in collaboration with an interdisciplinary team of researchers at Oregon State University, Pacific Northwest National Labs, and Mt. Sinai School of Medicine, report on the findings of a new study of air pollution exposures collected using personal wristband monitors worn by pregnant individuals in New York City matched with data from a questionnaire. Factors predictive of exposures to air pollution include income, time spent outdoors, maternal age, country of birth, transportation type, and season.
The researchers examined an unprecedented number of 61 air pollution compounds known as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and compared them to 75 questionnaire variables, making the study the most comprehensive analysis of its kind. PAHs are created by combustion and can be found in sources like automotive exhaust and tobacco smoke; exposure to these compounds has been linked to various adverse health effects, including those related to fetal growth and neurodevelopment. The study’s findings appear online in the Journal of Exposure Science And Environmental Epidemiology(link is external and opens in a new window).
Participants, 177 of whom were included in the final analysis, wore silicone wristbands for 48 hours during the third trimester of pregnancy to measure exposure to PAHs. They completed a questionnaire during the third trimester of their pregnancy, answering questions related to demographic and employment information, as well as their potential exposure sources, such as cooking, smoking, and transportation.
Julie Herbstman, PhD, director of the Columbia Center for Children’s Environmental Health and senior author of the study, commented, “This study represents a significant advancement in our understanding of personal PAH exposure. By uncovering the variables that play a crucial role in exposure levels, we are better equipped to develop interventions aimed at reducing health risks.”
Previous studies have been restricted to a limited number of compounds or specific exposure scenarios (e.g. toll station workers or cooks). Compared to these studies, the new study demonstrated substantially improved predictability due to the use of a larger dataset, as well as the use of a regression tree analysis, which accounted for each PAH compound as well as combined exposure to all PAHs. This approach helps researchers to identify those variables that are most important and/or predictive of exposure to a compound in the context of all other variables.
Sarah McLarnan, MPH, a PhD candidate at Columbia Mailman and the study’s first author, adds, “This study underscored the utility of silicone wristbands in evaluating PAH exposures and associated health outcomes. By combining questionnaire data with a 48-hour wristband deployment, we were able to refine measurements of exposure sources in terms of time and space, enabling more accurate source characterization.”
The study uncovered complex interactions between demographics and behaviors that shape exposure to individual compounds in different ways. Insights it gleaned require further study to understand the pathways by which various factors are linked to PAH exposures. As one example, the researchers are interested to know how maternal age and income are associated with behaviors or residential characteristics that are protective from some exposure sources but were shown to have opposite effect for some of the individual compounds.
The authors note that the wristbands are unable to detect all exposures to PAHs, particularly exposures via food. And because the wristbands were worn only for 48 hours, the exposures might not fully reflect an individual’s average exposure over the course of pregnancy.
We all can reduce our exposure to PAHs by avoiding tobacco smoke and ensuring we have good indoor ventilation, especially when cooking; reduce our intake of smoked, grilled, and charbroiled foods; limit exposure to diesel fumes and wood smoke; use cedar shavings or blocks in place of mothballs for pest control; and wear gloves to avoid skin contact with soot or creosote-treated lumber, and wear a mask if cutting treated lumber.
Previous research by the Columbia Center for Children’s Environmental Health has linked prenatal exposure to PAHs with numerous adverse outcomes in the child, including asthma, obesity, and developmental delays.
Additional co-authors include Lehyla Calero, Darrell Holmes, Elizabeth A. Gibson, and Haleigh M. Cavalier from Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health; Lisa M. Bramer and Katrina M. Waters from Pacific Northwest National Laboratory; Holly M. Dixon and Kim A. Anderson from Oregon State University; Diana Rohlman and Laurel Kincl from Oregon State University; and Rachel L. Miller from Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
This research was supported by National Institute of Health grants UH3OD023290, 1R21ES024718, 4R33ES024718, P30ES030287, P42ES016465, T32 ES007322; TRANSFORM TL-1 Fellowship 5TL1TR001875-07. Anderson and Rohlman disclose a financial interest in MyExposome, Inc., which is marketing products related to the research being reported. The authors have no other relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
END
Wristband monitors provide detailed account of air pollution exposure
2024-01-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scaling up urban agriculture: Research team outlines roadmap
2024-01-10
URBANA, Ill. — Urban agriculture has the potential to decentralize food supplies, provide environmental benefits like wildlife habitat, and mitigate environmental footprints, but researchers have identified knowledge gaps regarding both the benefits and risks of urban agriculture and the social processes of growing more food in urban areas.
In a new paper published in Nature Food, an interdisciplinary group of experts, including a researcher from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, survey ...
Black people face strokes at higher rates, younger ages than white people
2024-01-10
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, JANUARY 10, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – Black people consistently had a higher rate of stroke than white people over a recent 22-year period, according to a study published in the January 10, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The study also found that the average age of Black people experiencing stroke was nearly 10 years younger than that of white people, another inequity that grew over time.
“We found that the rate of stroke is decreasing over time in both Black and white people—a very encouraging trend for U.S. prevention efforts,” said study ...
ASBMB announces 2024 class of fellows
2024-01-10
The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology today announced its 2024 class of fellows. The honorific program recognizes scientists who have made outstanding contributions to the field through their research, teaching, mentoring or other forms of service.
Edward Eisenstein, an associate professor of bioengineering at the University of Maryland and ASBMB Membership Committee chair, and Judith Bond, an adjunct professor of biochemistry and biophysics at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and ...
Researchers step closer to mimicking nature’s mastery of chemistry
2024-01-10
In nature, organic molecules are either left- or right-handed, but synthesizing molecules with a specific “handedness” in a lab is hard to do. Make a drug or enzyme with the wrong “handedness,” and it just won’t work. Now chemists at the University of California, Davis, are getting closer to mimicking nature’s chemical efficiency through computational modeling and physical experimentation.
In a study appearing Jan. 10 in Nature, Professor Dean Tantillo, graduate students William DeSnoo and Croix Laconsay, and colleagues at the Max Planck ...
Dark web fentanyl-selling operations have grown rapidly, offer steep discounts
2024-01-10
Overdose deaths in North America have skyrocketed, primarily because of the spread of illegally manufactured fentanyl. In a new study, researchers analyzed an early and prominent fentanyl-selling operation on the dark web. The organization sustained a significant growth rate, which allowed it to offer consumers steep discounts. In light of these findings, the authors conclude that it might be challenging to constrain supply by shuttering individual organizations since remaining organizations could grow rapidly to fill unmet demand.
The study was conducted by researchers at Carnegie ...
Can drinking alkaline water help prevent kidney stones? Not likely, study finds
2024-01-10
Waltham — January 10, 2024 — Bottled water marketed as "alkaline water" is unlikely to be an effective alternative for prevention of recurrent urinary stones, reports a study in the January issue of The Journal of Urology®, an Official Journal of the American Urological Association (AUA). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"While alkaline water products have a higher pH than regular water, they have a negligible alkali content – ...
Tactile lithophane development makes hard scientific data available to students with blindness
2024-01-10
WACO, Texas (Jan. 10, 2024) – A first-of-its-kind tactile learning device developed by Baylor University chemistry professors to make science accessible to students with blindness or low vision (BLV) has opened the possibility of the transfer of any scientific data or images for sighted students into functional, thorough formats for students with blindness. The study was published today in the journal Science Advances.
The latest research from Bryan F. Shaw, Ph.D., professor of chemistry and biochemistry at Baylor, focused on the development of a codex using lithophane – an ancient art form – to convert images from scientific textbooks into tactile ...
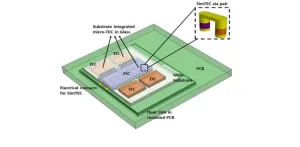
Glass packaging with a mix of thermoelectric in the vias
2024-01-10
Photonics offers various advantages, including enablement of high-speed and low-loss communication by leveraging light properties in optical data communication, biomedical applications, automotive technology, and artificial intelligence domains. These advantages are realized through complex photonic circuits, comprising diverse photonic elements that are integrated on a photonic chip. Electronic chips are then added to supplement the photonic chips for certain functions, such as light source operation, modulation, and amplification. The close integration of electronic and photonic chips on a substrate is a critical aspect of photonic packaging.
Photonic packaging plays a vital role in ...
Genetics may influence the body’s response to low oxygen, Pitt study finds
2024-01-10
PITTSBURGH, Jan. 10, 2024 – University of Pittsburgh Schools of Medicine researchers uncovered a fundamental mechanism that controls the body’s response to limited oxygen and regulates blood vessel disease of the lung.
By combing through genomes of more than 20,000 individuals in the U.S., France, England and Japan and combining the results with molecular studies in the lab, the team discovered a shared genetic trait that could predict a higher risk of small lung vessel disease called pulmonary hypertension and its more severe ...
mRNA technology could be possible treatment for rare diseases
2024-01-10
By exploiting the technology used in Covid-19 vaccines, a team led by UCL, King’s College London and Moderna scientists has created an effective therapy for a rare disease, in a study in mice, demonstrating the technology’s potential therapeutic use in people.
The research, published in Science Translational Medicine, found that messenger RNA (mRNA) could be used to correct a rare liver genetic disease known as argininosuccinic aciduria in a mouse model of the disease.
Argininosuccinic aciduria is an inherited metabolic disorder that affects how the body ...