(Press-News.org) Cleveland Clinic researchers have successfully developed a therapeutic peptide that blocks aggressive cancer cells from multiplying rapidly. The results highlight a potential new strategy for developing targeted treatments for triple-negative breast cancer, which currently has no approved options.
Targeted drugs attack cancer cell functions directly, offering a more precise approach to complement broader treatments like chemotherapy. A research team led by Ofer Reizes, PhD, and Justin Lathia, PhD, designed a peptide therapeutic that disrupts the molecular processes behind aggressive cancer growth when delivered into cells.
The drug stopped cancer growth and induced tumor cell death, and only affected cancerous cells in preclinical work. The study was highlighted in the January issue of Molecular Cancer Therapeutics.
"It's devastating that we currently have such limited options to help people with triple-negative breast cancer," says Dr. Reizes, the Laura J. Fogarty Endowed Chair for Uterine Cancer Research. "We want our results to offer hope for these patients and their families and serve as a starting point to get more treatments into the development pipeline."
Peptides are short proteins made up of amino acids that are the "building blocks" of larger proteins. Natural and artificially synthesized proteins are commonly used to treat disease. Some peptides are used to supplement existing proteins in the body, like insulin in people with diabetes.
The peptide in development, based on a 2018 Cleveland Clinic discovery, serves as a proof-of-concept for this type of drug for triple-negative breast cancer.
Because triple-negative breast cancer cells lack certain receptors, drugs designed to treat other subtypes of breast cancer won't work. There are currently no targeted drugs approved for triple-negative breast cancer, which makes up 15% of breast cancer cases. To develop new drugs, investigators needed to identify new, effective targets.
A previous joint postdoctoral fellow with Dr. Reizes and Dr. Lathia's team found Cx26, a type of protein called a connexin, forms a molecular complex in triple-negative breast cancer cells that makes them more likely to recur or spread through the body. Investigators worked to find a way to disrupt that complex, which would limit the cancerous properties of the cells.
First authors Erin Mulkearns-Hubert, PhD, and Emily Esakov Rhoades, PhD, developed a peptide therapeutic, supported by a Department of Defense grant. The peptide's sequence is the same as the component of Cx26 necessary for the complex to form. The goal is to saturate the system with the peptide and interrupt the ability of the full-length proteins to bind, says Dr. Mulkearns-Hubert, a research associate in the Lathia lab.
"The peptide's design was actually relatively straightforward and worked beautifully, slowing tumor growth in preclinical models," she says. "Triple-negative breast cancer remains an incredibly difficult tumor type to treat, so developing and verifying strategies like this peptide's design is critical to moving forward."
Researchers observed that the drug prevented cancer stem cells in a dish from self-renewing, a characteristic of aggressive cancer cells that supports treatment resistance. The team is now working with Cleveland Clinic Innovations to develop the drug and explore potential for clinical trials.
END
New research highlights unprecedented targeted approach to treating triple-negative breast cancer
A peptide drug candidate based on a Cleveland Clinic discovery disrupted cancer growth and self-renewal
2024-01-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
ASBMB names Mona V. Miller as next executive officer
2024-01-17
The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology today named Mona V. Miller its next chief executive officer, effective April 1.
Miller is an experienced association leader with significant experience in strategic planning, advocacy and fundraising. Most recently, she was CEO of the American Society of Human Genetics. Before that she held multiple high-level positions at the Society for Neuroscience.
Miller said she was drawn to the ASBMB because “scientifically, biochemistry and molecular biology is at the forefront of knowledge that is transforming health and society.”
She said she looks forward to “focusing on the pivotal ...
Streamlining cognitive behavioral therapy for chronic insomnia
2024-01-17
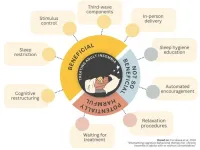
A combination of cognitive and behavioral strategies, ideally delivered in person by a therapist, maximizes the benefits of cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I), according to new research. CBT-I is a form of talk therapy, which can be delivered in person or through self-help guides. By analyzing 241 studies, involving over 30,000 adults, researchers identified the most beneficial components of CBT-I. These included: cognitive restructuring, third-wave components, sleep restriction, stimulus control and in-person delivery. Self-help with human encouragement could also be beneficial, while waiting for active treatment and enforcing ...
Prenatal opioid exposure and immune-related conditions in children
2024-01-17
About The Study: Prenatal opioid exposure was associated with an increased risk of infection, eczema and dermatitis, and asthma, but not allergies and anaphylaxis or autoimmune conditions in this study of 401,000 neonates. These findings highlight the importance of further study of opioid-induced immune changes during pregnancy, the potential impact on long-term health in exposed children, and the mechanisms of opioid-induced immune dysregulation.
Authors: Erin Kelty, Ph.D., of the University of Western Australia in Crawley, Western Australia, ...
Comparative effectiveness of psychotherapy vs antidepressants for depression in heart failure
2024-01-17
About The Study: In this comparative effectiveness trial of behavioral activation psychotherapy (BA) and antidepressant medication management (MEDS) in 416 patients with heart failure experiencing depression, both treatments significantly reduced depressive symptoms by nearly 50% with no statistically significant differences between treatments. BA recipients experienced better physical health-related quality of life, fewer emergency department visits, and fewer days hospitalized. The study findings suggest that patients with heart failure could be given the choice between BA or MEDS to ameliorate depression.
Authors: Waguih ...
Origin of intense light in supermassive black holes and tidal disruption events revealed
2024-01-17
A new study by Hebrew University is a significant breakthrough in understanding Tidal Disruption Events (TDEs) involving supermassive black holes. The new simulations, for the first time ever, accurately replicate the entire sequence of a TDE from stellar disruption to the peak luminosity of the resulting flare. This study has unveiled a previously unknown type of shockwave within TDEs, settling a longstanding debate about the energy source of the brightest phases in these events. It confirms that shock dissipation powers the brightest weeks ...
Astronomers detect oldest black hole ever observed
2024-01-17
Researchers have discovered the oldest black hole ever observed, dating from the dawn of the universe, and found that it is ‘eating’ its host galaxy to death.
The international team, led by the University of Cambridge, used the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) to detect the black hole, which dates from 400 million years after the big bang, more than 13 billion years ago. The results, which lead author Professor Roberto Maiolino says are “a giant leap forward”, are reported ...
Columbia chemists create the first 2D heavy fermion
2024-01-17
Researchers at Columbia University have successfully synthesized the first 2D heavy fermion material. They introduce the new material, a layered intermetallic crystal composed of cerium, silicon, and iodine (CeSiI), in a research article published today in Nature.
Heavy fermion compounds are a class of materials with electrons that are up to 1000x heavier than usual. In these materials, electrons get tangled up with magnetic spins that slow them down and increase their effective mass. Such interactions are ...
Therapy versus medication: comparing treatments for depression in heart disease
2024-01-17
New research by investigators from the Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Neurosciences at Cedars-Sinai shows that behavioral activation therapy is as effective as antidepressant medications in treating symptoms of depression in patients with heart failure.
Heart failure affects nearly 6 million adults in the United States, and approximately 50% of heart failure patients experience symptoms of depression along with their condition. Past studies show patients with heart failure and depression have lower cardiac function, more emergency department ...
Active membranes: The future of fresh water is bright
2024-01-17
The growth of Los Angeles as a startup hub is highlighted by a robust and diverse entrepreneurial ecosystem within UCLA. The Magnify Incubator at CNSI is no exception to showcasing the range of early-stage businesses.
One such company within the Magnify incubator, Active Membranes, is innovating the future of fresh water through membrane desalination. As freshwater is becoming increasingly scarce around the globe, resources such as seawater and industrial wastewater are costly to procure and operate. The company’s patented technology is electrically conducting ...
What’s stopping US climate policies from working effectively
2024-01-17
In an effort to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and curb global warming, the U.S. has enacted several ambitious federal laws, such as the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) passed in 2022 and the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA) of 2021.
These provide significant investments in clean energy projects and encourage technological innovations. Some analyses suggest they could reduce greenhouse gas emissions by more than 40% below 2005 levels by 2030.
However, in a paper published Jan. 16 in the journal Nature Climate Change, researchers at the University ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
Microbial clues uncover how wild songbirds respond to stress
Researchers develop AI tools for early detection of intimate partner violence
Researchers develop AI tool to predict patients at risk of intimate partner violence
New research outlines pathway to achieve high well-being and a safe climate without economic growth
How an alga makes the most of dim light
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
[Press-News.org] New research highlights unprecedented targeted approach to treating triple-negative breast cancerA peptide drug candidate based on a Cleveland Clinic discovery disrupted cancer growth and self-renewal