(Press-News.org) New biomarkers with improved diagnostic performance for early detection of lupus nephritis have been discovered in the University of Houston lab of Chandra Mohan, a pioneer in lupus research. Early identification of renal involvement in lupus and prompt treatment are essential in reducing the pain, suffering and eventual mortality it causes.
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), commonly called lupus, is an autoimmune disease that occurs when the body attacks its own tissues and organs. Inflammation from the disease can impact many different parts of the body including joints, skin, kidneys, blood cells, brain and heart. Lupus nephritis is one of the most frequent and severe clinical manifestations of SLE, and the leading cause of death.
As reported by Mohan, Hugh Roy and Lillie Cranz Cullen Endowed Professor of Biomedical Engineering, in the Journal of Autoimmunity, “These studies add at least six novel urine biomarkers of active renal lupus validated across two ethnically diverse patient cohorts.”
“We and others have reported several urine proteins that can serve as harbingers of renal involvement in lupus. Here, we report on a novel technique based on the use of antibodies and DNA amplification that can detect even low concentrations of proteins. This technique is called Proximity Extension Assay (PEA),” said Mohan.
By applying PEA proteomics (the study of protein interactions, function, composition and structures) to urine samples, Mohan and team identified several proteins that were significantly elevated in the urine of lupus patients with active renal disease.
The study offered independent validation of several previously reported urine biomarkers for active renal lupus, including proteins such as ALCAM, CD163, MCP1, SELL, ICAM1, VCAM1, NGAL and TWEAK. The researchers also identified additional urine protein biomarkers not previously reported, including ICAM-2, FABP4, FASLG, IGFBP-2, SELE, and TNFSF13B/BAFF.
Examining the renal expression of these molecules suggests that both immune cells and non-immune cells in the kidneys may be releasing these biomarker proteins into the urine.
"These studies have expanded the repertoire of urinary proteins that can be used to monitor renal status in a patient with lupus,” said Mohan, whose team includes lead author, post-doctoral fellow, Yaxi Li; Dr. Ramesh Saxena, UT Southwestern, Dallas; Dr. Chi Chiu Mok, Tuen Mun Hospital, Hong Kong; and Claudia Pedroza and Kyung Hyun Lee, UTHealth Houston.
END
New biomarkers for active lupus nephritis discovered
Antibodies and DNA used to find the biological markers of disease
2024-01-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New research examines how assumptions affect motion capture technology
2024-01-22
Motion capture technology has applications in a wide range of fields, including entertainment, medicine, and sports, to name a few. But what if the measurements these systems were based on were rooted in social practices and biased assumptions, leading to errors that become ingrained over time?
This question is at the heart of new research co-authored by Mona Sloane, an assistant professor of data science and media studies at the University of Virginia.
Sloane and her co-authors — Abigal Jacobs, an assistant ...
Scientists identify mutations that cause inherited kidney disease
2024-01-22
Genetic changes or mutations can cause hereditary kidney disease, which can eventually lead to dialysis or the need for kidney transplantation. Identifying the cause of inherited kidney disease is the first step in identifying a treatment.
With that goal in mind, researchers at Wake Forest University School of Medicine and the First Faculty of Medicine of Charles University in Prague, Czech Republic, have discovered a new genetic cause of inherited kidney disease.
The findings were recently published in Kidney International.
According to Anthony J. Bleyer, M.D., ...
How the brain responds to reward is linked to socioeconomic background
2024-01-22
MIT neuroscientists have found that the brain’s sensitivity to rewarding experiences — a critical factor in motivation and attention — can be shaped by socioeconomic conditions.
In a study of 12 to 14-year-olds whose socioeconomic status (SES) varied widely, the researchers found that children from lower SES backgrounds showed less sensitivity to reward than those from more affluent backgrounds.
Using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), the research team measured brain activity as the children played a guessing game in which they earned extra money for each correct ...
New reagent improves the process of making sulfur-containing compounds that may be used in medicines
2024-01-22
During the past decade, there has been significant development of new sulfur containing compounds that are used in various industries, including pharmaceuticals and agricultural products. Sulfoximines, sulfonimidoyl fluorides and sulfonimidamides are types of sulfur-containing chemical compounds that have wide-ranging potential as therapeutic drugs. However, the synthesis process for these compounds is complex and has several limitations. In a new article published in Nature Chemistry, Moffitt Cancer Center researchers describe their ...
New candidate for universal memory is fast, low-power, stable and long-lasting
2024-01-22
We are tasking our computers with processing ever-increasing amounts of data to speed up drug discovery, improve weather and climate predictions, train artificial intelligence, and much more. To keep up with this demand, we need faster, more energy-efficient computer memory than ever before.
Researchers at Stanford have demonstrated that a new material may make phase-change memory—which relies on switching between high and low resistance states to create the ones and zeroes of computer data—an improved option for future AI and data-centric systems. ...
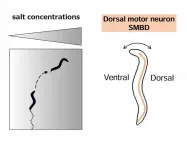
Follow the salt: connecting salt concentrations and motion in roundworms
2024-01-22
Joint research led by Ayaka Matsumoto and Yuichi Iino of the University of Tokyo demonstrated that temporal decrease in salt concentration leads to the activation of the neck motor neuron of roundworms only in a specific phase of its activity. The activation adjusts the roundworm's trajectory toward higher salt concentrations. The finding pinpoints the neural mechanism by which roundworms integrate sensory and motor information, a first step toward understanding the neural mechanisms of navigation in more complex animals. The findings were published in the journal Proceedings ...
Planetary Commons: Fostering global cooperation to safeguard critical Earth system functions
2024-01-22
“Stability and wealth of nations and our civilisation depends on the stability of critical Earth system functions that operate beyond national borders. At the same time, human activities push harder and harder on the planetary boundaries of these pivotal systems. From the Amazon rainforest to the Greenland ice masses, there are rising risks of triggering irreversible and unmanageable shifts in Earth system functioning. As these shifts affect people across the globe, we argue that tipping elements should be ...
Manipulated hafnia paves the way for next-gen memory devices
2024-01-22
EMBARGOED: NOT FOR RELEASE UNTIL 3:00 P.M. U.S. EASTERN TIME ON JANUARY 22, 2024
Scientists and engineers have been pushing for the past decade to leverage an elusive ferroelectric material called hafnium oxide, or hafnia, to usher in the next generation of computing memory. A team of researchers including the University of Rochester’s Sobhit Singh published a Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences study outlining progress toward making bulk ferroelectric and antiferroelectric hafnia available for use in a variety of applications.
In a specific crystal phase, hafnia exhibits ferroelectric properties—that is, electric polarization that can be changed in one direction ...
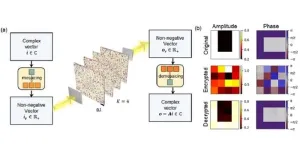
Optical computing boost with diffractive network advance
2024-01-22
State-of-the-art neural networks heavily rely on linear operations, such as matrix-vector multiplications and convolutions. While dedicated processors like GPUs and TPUs exist for these operations, they have limitations in terms of power consumption and bandwidth. Optics is better suited for such operations because of its inherent parallelism, large bandwidth, and computation speed.
Diffractive deep neural networks (D2NN), also known as diffractive networks, constitute an emerging optical computing architecture. ...
Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine (WFIRM) to lead $40 Million initiative for AFIRM Consortium
2024-01-22
Winston Salem, NC – January 22, 2024 - The Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine, part of Wake Forest University School of Medicine, has been selected to lead the Armed Forces Institute of Regenerative Medicine (AFIRM) Consortium. The project - a $40 million, five year-long award from the Defense Health Agency (DHA) - will focus on taking regenerative medicine solutions for battlefield injuries to the next level, and ultimately to the general public.
Regenerative medicine is a science that takes advantage of the body's natural abilities to restore or replace damaged tissue and organs. WFIRM has managed two prior AFIRM consortia since ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
[Press-News.org] New biomarkers for active lupus nephritis discoveredAntibodies and DNA used to find the biological markers of disease