(Press-News.org)
One of the things that makes developing effective treatments for Parkinson’s disease so challenging is its complexity. While some forms are caused by genetics, others have environmental factors, and patients can show a wide range of symptoms of varying severity. Diagnosis of Parkinson’s is also currently made very late, after the disease may have been in the brain for a decade or more.
In a paper published in The Lancet Neurology, a group of scientists argue that this complexity demands a new way of classifying the disease for research purposes, one based not on clinical diagnosis but biology. The authors have called their biological model “SynNeurGe”.
The “Syn” stands for alpha-synuclein, a protein that in most Parkinson’s patients causes abnormal deposits called Lewy bodies. Abnormalities in synuclein identify and probably cause degenerative changes in the brain that can impact movement, thinking, behaviour and mood.
“Neur” stands for neurodegeneration. This is the breakdown of the function of neurons in the brain. In doctor’s offices, specific neurons in the dopamine system are the way that Parkinson’s is diagnosed. In the SynNeurGe model, however, neurodegeneration in all areas of the brain are included in the classification.
The “Ge” stands for genetics. The role of genetics in Parkinson’s is complex. Mutations in many different genes have been found to predispose someone to the disease. The likelihood of developing Parkinson’s disease depends on the gene involved, the specific mutation within the gene and environmental exposures.
The authors argue that for research purposes, patients should be classified by the presence or absence of these three factors. This would allow the identification of Parkinson’s patients before symptoms appear, and aid the development of treatments tailored to patients’ unique biology. Right now, patients are diagnosed based on symptoms and signs, even though the disease may have been present in their brain for many years . By shifting classification criteria, researchers can identify disease earlier (even before people may experience symptoms), and target specific patient groups that have more in common with each other biologically, giving drug development a higher chance of success.
“Although this is still for research purposes, this is a major shift in thinking,” says Dr. Ron Postuma, a clinician-scientist at The Neuro (Montreal Neurological Institute-Hospital) of McGill University and one of the study’s authors. “If you think of it, it’s quite unusual that we’ve had to wait until Parkinson’s patients have important symptoms before we could make a diagnosis. We don’t wait for someone to feel pain from cancer before we diagnose it.Instead, we detect and diagnose it, hopefully before someone is aware of any symptoms. This research classification is a critical step towards bringing our thinking about Parkinson’s into the 21st century.”
“A biological classification of Parkinson’s disease: the SynNeurGe research diagnostic criteria” was published by Günter U. Höglinger et al. in The Lancet Neurology on Jan. 22, 2024, senior author Dr. Anthony Lang, the Lily Safra Chair in Movement Disorders at UHN’s Krembil Brain Institute, and the Jack Clark Chair for Parkinson's Disease Research and a Professor in the Department of Medicine, at the University of Toronto.
END
A new large, national study of collegiate student-athletes in the United States dispels a long-held belief about concussions, finding that women and men recover from sport-related head injuries within the same time frame.
Women and men’s recovery patterns ...
Waymark, the Medicaid provider enablement company, today published a peer-reviewed study in Nature’s Scientific Reports comparing the performance of Waymark SignalTM, the company’s proprietary machine learning technology, to conventional Medicaid risk models. The study found that Waymark Signal was 90 percent accurate in predicting avoidable emergency room (ER) and hospital utilization for patients receiving Medicaid — stronger performance than leading Medicaid risk models in the field.
Waymark ...
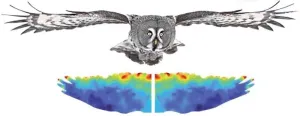
Owls are fascinating creatures that can fly silently through some of the quietest places. Their wings make no noise while flying, enabling them to accurately locate their prey using their exceptional hearing ability while remaining undetected. This unique ability depends on many factors and has long been a hot research subject.
Studies have found associations between the ability to fly silently and the presence of micro-fringes in owl wings. These trailing-edge (TE) fringes play a crucial role in suppressing the noise produced by wing ...
Web 3.0 is an internet paradigm that is based around blockchain technology, an advanced database mechanism. Compared to Web 2.0, the current internet paradigm, Web 3.0 provides some added advantages, such as transparency and decentralized control structures. This is because Web 3.0 is designed to work over trustless and permissionless networks. Unfortunately, owing to certain technical difficulties, the implementation of Web 3.0 media streaming requires modifications to the service architecture of existing media streaming services. These difficulties include the degradation ...
Aviation has grown considerably in recent decades and accounts for approximately 2 percent of global carbon dioxide emissions and some 4 percent of all climate change impacts annually. While aviation is an important contributor to climate change and other environmental problems, electrification is one option for reducing these environmental impacts. The first electric aircraft are already in operation today and are mainly small planes used for pilot training and short flights in the immediate area. This is the type of plane that was studied in the life cycle assessment.
“In the short-term future, battery-powered electric aircraft will probably mostly be used for shorter ...
While exposure to a single substance like DDT has been shown to create inherited disease susceptibility, a recent study in animals found exposure to multiple different toxicants across generations can amplify those health problems.
In the study, published in the journal Environmental Epigenetics, an initial generation of pregnant rats was exposed to a common fungicide, then their progeny to jet fuel and the following generation to DDT. When those rats were then bred out to a fifth unexposed generation, the incidence of obesity as well as kidney and prostate diseases in those animals were compounded, ...
Research Highlights:
Positive, warm relationships between caregiver and child were associated with higher odds of attaining ideal heart health at multiple points across a 20-year span of adulthood.
Meanwhile, experiencing childhood adversity such as abuse was associated with a lower chance of reaching optimal cardiovascular health in adulthood.
Lower annual income as an adult — $35,000 or less — may confound the health effects of childhood adversity.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET Tuesday, Jan. 23, 2024
DALLAS, Jan. 23, 2024 — Throughout adulthood, ...
The fastest growing type of offset on the global carbon market subsidizes the distribution of efficient cookstoves in developing countries to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, but a new study finds that the credits overestimate the stoves’ carbon savings by a factor of 10.
The overestimation undermines efforts to counteract carbon emissions to slow climate change, since companies use these offsets to meet climate targets and to sell products labeled as “carbon neutral” instead of making real reductions in greenhouse gas emissions. It also undermines ...
Scientists at the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC) in Madrid have found that one of the most potent genetic risk factors for Alzheimer disease, apolipoprotein E4 (APOE4), is also associated with an increased risk of developing subclinical atherosclerosis in middle age. The study also demonstrates protection against subclinical atherosclerosis in people carrying the variant APOE2, which protects against Alzheimer disease.
The study, coordinated by Dr. Marta Cortés Canteli and CNIC General Director Dr. Valentín Fuster, sheds light on the role of APOE in the development of cardiovascular diseases ...
The ‘ten electron’ rule provides guidance for the design of single-atom alloy catalysts for targeted chemical reactions.
A collaborative team across four universities have discovered a very simple rule to design single-atom alloy catalysts for chemical reactions. The ‘ten electron rule’ helps scientists identify promising catalysts for their experiments very rapidly. Instead of extensive trial and error experiments of computationally demanding computer simulations, catalysts’ composition can be proposed simply looking at the periodic table.
Single-atom alloys are a class of catalysts made of two metals: a few atoms of reactive metal, ...