(Press-News.org) Ozempic and other GLP1 agonists are associated with a reduced risk of developing cirrhosis and liver cancer in people with type 2 diabetes and chronic liver disease, according to a nationwide study from Karolinska Institutet in Sweden published in the journal Gut.
GLP1 agonists like Ozempic reduce blood sugar levels and are mainly used to treat type 2 diabetes. However, as the drug also reduces appetite, it is now increasingly used to treat obesity and has become a popular weight-loss drug.
Reduced risk of liver damage
Results from early clinical trials also suggest that GLP1 agonists may reduce the risk of liver damage. Therefore, researchers at Karolinska Institutet included all people in Sweden with chronic liver disease and type 2 diabetes in a register-based study. They then compared the risk of severe liver damage in those who were treated with GLP1 agonists and those who were not. The results show that those who took the drug for a long period of time had a lower risk of later developing more severe forms of liver disease such as cirrhosis and liver cancer.
According to the researchers, this suggests that GLP1 agonists could be an effective treatment to avoid severe liver disease in people with concurrent type 2 diabetes.
“Fatty liver disease is estimated to affect up to one in five people in Sweden, many of whom have type 2 diabetes, and about one in twenty develop severe liver disease,” says first author Axel Wester, assistant professor at the Department of Medicine, Huddinge, Karolinska Institutet. “Our findings are interesting because there are currently no approved drugs to reduce this risk.”
Many of the people in the study stopped taking GLP1 agonists, resulting in a lack of protective effect. However, those who continued taking their medication over a ten-year period were half as likely to develop severe liver disease.
Need to be confirmed
“The results need to be confirmed in clinical trials, but it will take many years for these studies to be completed,” says Axel Wester. “Therefore, we use existing registry data to try to say something about the effect of the drugs before that.”
A limitation of the method is that it is not possible to control for factors for which there is no data, such as blood tests to describe the severity of liver disease in more detail. However, the researchers have recently built a new database called HERALD where they have access to blood samples from patients in Region Stockholm.
“As a next step, we will investigate the effect of GLP1 agonists in this database,” says the study's last author Hannes Hagström, consultant in hepatology at the Karolinska University Hospital and adjunct professor at the Department of Medicine, Huddinge, Karolinska Institutet. “If we get similar results, it would further strengthen the hypothesis that GLP1 agonists can be used to reduce the risk of severe liver disease.”
The research was mainly funded by Region Stockholm (CIMED), the Swedish Research Council and the Swedish Cancer Society. Hannes Hagström’s research group has received funding from Astra Zeneca, EchoSens, Gilead, Intercept, MSD, Novo Nordisk and Pfizer, although no industry-supported funding was obtained for this specific study.
Publication: “Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and risk of major adverse liver outcomes in patients with chronic liver disease and type 2 diabetes”, Axel Wester, Ying Shang, Emilie Toresson Grip, Anthony A Matthews, Hannes Hagström. Gut, online 22 January 2024, doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2023-330962.
END
Popular diabetes drug may also reduce the risk of severe liver disease
2024-01-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
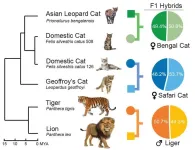
New publication describes findings on cat evolution, to aid in future disease studies
2024-01-23
DENVER/Jan. 23, 2024 – Morris Animal Foundation-funded researchers have delved into various cat species' entire DNA sequence (genome), uncovering novel perspectives on domestic and wild cat evolution. This new work highlights distinct genetic changes and will be a critical tool for researchers investigating feline diseases and characteristics.
This study, which led to the findings published in Nature Genetics, used cutting-edge genome sequencing and assembly technologies to generate a more comprehensive and complete cat genome assembly, providing fundamental information on the feline blueprint and aiding in advancements in feline medicine.
"This ...
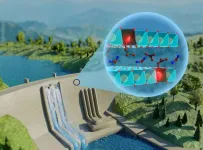
Liquid lithium on the walls of a fusion device helps the plasma within maintain a hot edge
2024-01-23
Emerging research suggests it may be easier to use fusion as a power source if liquid lithium is applied to the internal walls of the device housing the fusion plasma.
Plasma, the fourth state of matter, is a hot gas made of electrically charged particles. Scientists at the Department of Energy’s Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) are working on solutions to efficiently harness the power of fusion to offer a cleaner alternative to fossil fuels, often using devices called tokamaks, which confine plasma using magnetic fields.
“The purpose of these devices is to confine the energy,” said Dennis Boyle, a staff research physicist ...
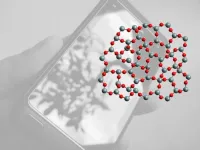
Novel material facilitates measurement of concrete deterioration in buildings and other structures
2024-01-23
Concrete is an essential material in the construction industry, where it is fundamental to the foundations and structures of dwellings and office buildings, as well as roads, dams and bridges, among many other infrastructure projects. However, the service life of concrete is limited, and it must be monitored in order to guarantee the safety of these structures. To facilitate fast, low-cost, in-situ analysis that dispenses with the need to take samples to a laboratory, researchers at the University of São Paulo’s Physics Institute (IF-USP) in Brazil, in collaboration with colleagues at the University of Leuven in Belgium, have developed a luminescent material that reveals the presence ...
Gene expression atlas captures where ovulation can go awry
2024-01-23
ITHACA, N.Y. -- An interdisciplinary collaboration used a cutting-edge form of RNA tagging to map the gene expression that occurs during follicle maturation and ovulation in mice.
The resulting atlas reveals a slew of previously unknown cellular and molecular interactions that drive ovulation, which is crucial for female fertility. The findings could prove pivotal for developing therapeutic treatments for infertility.
The research, published Jan. 22 in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, was ...
MU study shows blood pressure drug can reduce anxiety for people with autism
2024-01-23
A new study at the University of Missouri’s Thompson Center for Autism and Neurodevelopment found that propranolol, a medication that treats high blood pressure, can also help lower anxiety for kids and young adults with autism spectrum disorder (ASD).
Given that some individuals with ASD tend to struggle with anxiety at a far greater rate than their neurotypical peers, the new finding can significantly help such individuals with ASD. David Beversdorf, a clinician at the Thompson Center, led the study, which involved 69 patients over a three-year span. Compared to a placebo group, the participants who received propranolol showed ...
Analysis of US Census survey data reveals uptick in anxiety and depression among women in states with trigger laws post-Dobbs abortion decision
2024-01-23
An analysis of national survey data conducted by researchers at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health found a small but statistically significant increase in self-reported anxiety and depression symptoms among respondents in states that banned abortion after the U.S. Supreme Court’s reversal of Roe v. Wade in June 2022 compared to respondents in states that did not enact bans.
The Dobbs decision, handed down on June 24, 2022, overturned the 1973 Roe v. Wade decision that made abortion a constitutionally protected right and returned the question of abortion regulation to individual states. The Dobbs decision ...
JMIR Publications prepares to celebrate 25 years of publishing digital health research
2024-01-23
(Toronto, January, 23, 2024) 2024 will mark the 25th anniversary for JMIR Publications, the leading open access digital health research publisher. Founded in 1999 by Gunther Eysenbach, MD, MPH, FACMI, chief executive officer and executive editor, JMIR Publications has grown to now include 35 journals that have published over 52,000 papers that have garnered over 500,000 citations and millions of views from users around the world.
JMIR Publications functions as a hub for digital health research. With its reputation for high-quality ...
Rutgers health researchers develop software to predict diseases
2024-01-23
IntelliGenes, a first of its kind software created at Rutgers Health, combines artificial intelligence (AI) and machine-learning approaches to measure the significance of specific genomic biomarkers to help predict diseases in individuals, according to its developers.
A study published in Bioinformatics explains how IntelliGenes can be utilized by a wide range of users to analyze multigenomic and clinical data.
Zeeshan Ahmed, lead author of the study and a faculty member at Rutgers Institute for Health, Health Care Policy and Aging Research (IFH), said there currently are no AI or machine-learning ...
Innovative tech shows promise to boost rubber production in US
2024-01-23
COLUMBUS, Ohio – With disease and high demand posing threats to the world’s primary natural rubber supply in Southeast Asia, scientists are working to ramp up the U.S. rubber market by advancing methods to extract latex from two sustainable North American plant sources: a dandelion species and a desert shrub.
Researchers reported their methods to improve efficiency and increase latex yield in two recent publications, building upon decades of research led by Katrina Cornish, professor of horticulture and crop science and food, agricultural and biological engineering at The Ohio State University.
Cornish and colleagues ...
Corning uses neutrons to reveal ‘atomic rings’ help predict glass performance
2024-01-23
Glass is being used in a wider range of high-performance applications, including those for consumers and industry, military and aerospace electronics, coatings and optics. Because of the extreme precision demanded for use in products such as mobile phones and jet aircraft, glass substrates must not change their shape during the manufacturing process.
Corning Incorporated, a manufacturer of innovative glass, ceramics and related materials, invests a tremendous amount of resources into studying the stability of different types of glass. Recently, Corning researchers found that understanding the stability ...