(Press-News.org) A groundbreaking technology with immense potential in treating ischemic retinopathy in premature infants and diabetic patients has been developed by Professor Byoung Heon Kang and his research team in the Department of Biological Sciences at UNIST, in collaboration with Professor Dong Ho Park’s team at Kyungpook National University Hospital. Ischemic retinopathy, characterized by the breakdown of the blood-retinal barrier and abnormal blood vessel growth, often leads to vision impairment and loss. The researchers have identified the critical role of a mitochondrial chaperone called tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated protein 1 (TRAP1) in the pathogenesis of ischemic retinopathy.
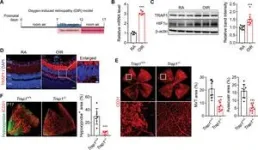
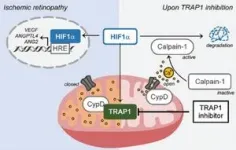
Through genetic Trap1 ablation or treatment with small molecule TRAP1 inhibitors, such as mitoquinone (MitoQ) and SB-U015, the research team successfully alleviated retinal pathologies in mouse models mimicking ischemic retinopathies. This therapeutic effect was attributed to the proteolytic degradation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF1α), a transcription factor implicated in the breakdown of the blood-retinal barrier and pathological neovascularization. The degradation of HIF1α was facilitated by the opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore and activation of the calcium-dependent protease calpain-1.
These findings open up new possibilities for innovative treatments against ischemic retinopathy, including retinopathy of prematurity and proliferative diabetic retinopathy. The technology focuses on targeting and regulating the aberrant activation of HIF1α and mitochondria under hypoxic conditions, providing a transformative approach to addressing the underlying causes of retinal diseases. Unlike conventional treatment methods, this technology can be easily administered using ophthalmic drugs, making it accessible to a wider range of patients.
“The excessive production of angiogenic factors in retinopathy is closely linked to mitochondrial properties,” explains Professor Kang. “By suppressing the expression of the TRAP1 protein, we can improve the condition of retinopathy.”
The therapeutic substance, currently being developed by Smartin Bio Inc., a startup company founded by Professor Byoung Heon Kang, is undergoing non-clinical trials. The findings of this research have been published in Advanced Science on January 12, 2024. This groundbreaking study was supported by the Mid-Career Research Program of the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) and the New Drug R&D Ecosystem Research Project of the Korea Drug Development Fund (KDDF).
The successful development of this technology holds great promise in revolutionizing the treatment landscape for ischemic retinopathy, offering both exceptional efficacy and convenient usability that surpasses the limitations of existing treatments. As further clinical trials and development progress, this breakthrough innovation brings hope for a brighter future for patients suffering from retinopathy.
Journal Reference
So-Yeon Kim, Nam Gu Yoon, Jin Young Im, et al., “Targeting the Mitochondrial Chaperone TRAP1 Alleviates Vascular Pathologies in Ischemic Retinopathy,” Adv. Sci., (2023).
END
Breakthrough technology offers promising treatment for ischemic retinopathy
2024-01-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Death rate higher than expected for patients with functional, nonepileptic seizures
2024-01-24
The death rate for patients with functional, nonepileptic seizures is higher than expected, with a rate comparable to epilepsy and severe mental illness, a Michigan Medicine-led study finds.
A team of researchers reviewed data from 700 patients who were diagnosed with functional seizures, also called psychogenic or nonepileptic seizures, between 2014 and mid-2023 and followed for a median of 15 months.
It is the largest study of its kind in the United States, matching international studies in Australia, Denmark, Sweden and the United Kingdom, all of which have nationalized health care systems.
Of the 700 patients with functional ...
National Science Foundation and The Kavli Foundation partner on call for research proposals in neurobiology and changing ecosystems
2024-01-24
The Kavli Foundation and the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) Directorate for Biological Sciences' Division for Integrative Organismal Systems have joined forces to launch a grant program in neurobiology and changing ecosystems. Research in this emerging field has great potential to reveal novel scientific insights that will accelerate understanding of basic biology in neural adaptation and resilience at the molecular, biophysical, cellular, and circuit levels.
“NSF’s partnership with The Kavli Foundation will enable the U.S. to advance research in this emerging and understudied field,” remarked Denise Dearing, Division ...
Facial recognition app for dogs developed to help in fight against rabies
2024-01-24
A new mobile phone-based facial recognition application for dogs has the potential to significantly improve rabies vaccination efforts in endemic areas like Africa and Asia, according to a study on the research published in the journal Scientific Reports.
Led by researchers at Washington State University, a team used the app to test its effectiveness at a rabies vaccination clinic in rural Tanzania where they microchipped, vaccinated and registered dogs. The technology proved remarkably accurate during a subsequent visit to surrounding villages once poor images and improperly recorded ...
New study unveils how plants control the production of reactive oxygen species
2024-01-24
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are highly reactive molecules containing oxygen. These compounds, which are normal byproducts of biological processes in all living organisms such as aerobic respiration as well as photosynthesis, are highly toxic. In most cases, ROS damage cellular machinery and can trigger a harmful stress response if their levels are not kept in tight check; this is why antioxidants are an important part of our diet.
However, over the past few decades, scientists have discovered that ROS are often intentionally ...
Rice study unlocks breakthrough for breast cancer bone metastases
2024-01-24
HOUSTON – (Jan. 24, 2023) – Rice University researchers in the lab of chemist Han Xiao have identified a promising new immunological pathway to treat stubborn bone tumors, one of most prevalent forms of metastases in breast cancer patients.
“More than 70% of people with metastatic breast cancer will see the cancer cells move to bone, which can lead to skeletal-related events like bone pain, fractures, and hypercalcemia,” said Yixian Wang, a Rice graduate student in the Han lab who is a lead author on a study published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. ...
The fountain of youth is … a T cell?
2024-01-24
The fountain of youth has eluded explorers for ages. It turns out the magic anti-aging elixir might have been inside us all along.
Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Assistant Professor Corina Amor Vegas and colleagues have discovered that T cells can be reprogrammed to fight aging, so to speak. Given the right set of genetic modifications, these white blood cells can attack another group of cells known as senescent cells. These cells are thought to be responsible for many of the diseases we grapple with later in life.
Senescent cells are those that stop replicating. As we age, they build up in our bodies, ...
Infants born to COVID-infected mothers have triple the risk of developing respiratory distress
2024-01-24
New UCLA-led research finds that infants born full term to mothers who were infected with COVID-19 during pregnancy had three times the risk of having respiratory distress compared with unexposed infants, even though they themselves were not infected with the virus. The risk was significantly lower when the mothers infected during pregnancy were previously vaccinated.
The researchers found that in-utero exposure to SARS-CoV-2 sparked an “inflammatory cascade” in the infants, increasing the risk of a breathing disorder that most often ...
More than half of US adults don’t know heart disease is leading cause of death, despite 100-year reign
2024-01-24
Highlights:
More than half (51%) of respondents in a 2023 Harris Poll survey conducted on behalf of the American Heart Association did not identify heart disease as the leading cause of death in the U.S.
According to the 2024 Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics: A Report of U.S. and Global Data From the American Heart Association, heart disease has been the leading cause of death in the U.S. for 100 years.
Heart disease along with stroke, which is the fifth leading cause of death, claimed more lives ...
Ultrafast excitations in correlated systems
2024-01-24
An international team of researchers from the European XFEL together with colleagues from the Max Born Institute in Berlin, Universities of Berlin and Hamburg, The University of Tokyo, the Japanese National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), the Dutch Radboud University, Imperial College London, and Hamburg Center for Ultrafast Imaging, have presented new ideas for ultrafast multi-dimensional spectroscopy of strongly correlated solids. This work has now been published in Nature Photonics.
"Strongly correlated solids are complex and fascinating quantum systems in which new electronic states often ...
Chemotherapy becomes more efficient when senescent cells are eliminated by immunotherapy
2024-01-24
Barcelona, 24 January 2024 – Cancer treatments, including chemotherapy, in addition to killing a large number of tumour cells, also result in the generation of senescent tumour cells (also called “zombi cells”). While senescent cells do not reproduce, they do, unfortunately, generate a favourable environment for the expansion of tumour cells that may have escaped the effects of the chemotherapy and eventually result in tumour regrowth.
An international team of researchers led by Dr. Manuel Serrano at IRB Barcelona have described how cancer cells that have become senescent after ...