(Press-News.org) Cryptocurrency is usually “mined” through the blockchain by asking a computer to perform a complicated mathematical problem in exchange for tokens of cryptocurrency. But in research appearing in the journal Chem on January 24, a team of chemists have repurposed this process, asking computers to instead generate the largest network ever created of chemical reactions which may have given rise to prebiotic molecules on early Earth.
This work indicates that at least some primitive forms of metabolism might have emerged without the involvement of enzymes, and it shows the potential to use blockchain to solve problems outside the financial sector that would otherwise require the use of expensive, hard to access supercomputers.
“At this point we can say we exhaustively looked for every possible combination of chemical reactivity that scientists believe to had been operative on primitive Earth,” says senior author Bartosz A. Grzybowski (http://grzybowski-group.net/default.asp) of the Korea Institute for Basic Science and the Polish Academy of Sciences.
To generate this network, the researchers chose a set of starting molecules likely present on early Earth, including water, methane, and ammonia, and set rules about which reactions could occur between different types of molecules. They then translated this information into a language understandable by computers and used the blockchain to calculate which reactions would occur over multiple expansions of a giant reaction network.
“The computer takes the primordial molecules and the accepted prebiotic chemistries. We coded it into the machine, and then we released it onto the world,” says Grzybowski.
Grzybowski’s team worked with chemists and computer-specialists at Allchemy, a company that uses AI for chemical synthesis planning, to generate the network using Golem, a platform that orchestrates portions of the calculations over hundreds of computers across the world, which receive cryptocurrency in exchange for computing time.
The resulting network, termed NOEL for the Network of Early Life, started off with over 11 billion reactions, which the team narrowed down to 4.9 billion plausible reactions. NOEL contains parts of well-known metabolic pathways like glycolysis, close mimics of the Krebs cycle, which organisms use to generate energy, and syntheses of 128 simple biotic molecules like sugars and amino acids.
Curiously, of the 4.9 billion reactions generated, only hundreds of reaction cycles could be called “self-replicating,” which means that the molecules produce additional copies of themselves. Self-replication has been postulated to be central to the emergence of life, but the vast majority of its known manifestations require complex macromolecules like enzymes.
“Our results mean that with only small molecules present, self-amplification is a rare event. I don’t think that this type of self-replication was operative on primitive earth, before larger molecular structures were somehow formed,” says Grzybowski. “We see emergence of primitive metabolism, but we don’t see self-replication, so maybe self-replication appeared later in evolution.”
“If you asked me two years ago, I’d be thinking we’d need years for this type of work,” says Grzybowski. “But for a fraction of the cost, in two or three months, we finished a task of 10 billion reactions, 100k times bigger than we did previously.”
This work not only advances what we know about early prebiotic chemistry, but it also demonstrates how science can be made more accessible to researchers at smaller universities and institutions.
“Our system of education is based on elite universities mostly in the western world. It’s very hard for the developing world to even compete with these universities because they don’t have access to supercomputers,” says Grzybowski. “But if you can distribute computing in this way for a fraction of the cost, you can give other people opportunities to play.”
While the network generated in this work was performed on hundreds of computers around the world, Grzybowski suggests that this method can be used at institutions without having to pay out cryptocurrency tokens to the computers performing the calculations.
“With a platform like Golem you can connect your institution’s network and harness the entire idle power of its computers to perform calculations,” says Grzybowski. “You could create this computing infrastructure without any capital expenditure.”
Grzybowski hopes that repurposing the blockchain in this way can revolutionize the way we perform large scale calculations across the world and change how we see the value of cryptocurrency.
“I hope people in computer science can figure out how can we tokenize cryptocurrencies in some way that can benefit global science,” says Grzybowski. “Maybe society could be happier about using cryptocurrencies, if you could tell people that in the process we could discover new laws of biology or some new cancer drug,” says Grzybowski.
###
Development of all codes and algorithms described in this work described was supported by internal funds of Allchemy, Inc. and Golem Factory, GmbH. Analysis of pathways and writing of the paper by Bartosz Grzybowski was supported by the Institute for Basic Science, Korea. Grzybowski has no financial stake in Golem although he is a stakeholder of Allchemy. Additional information about declarations of interest can be found in the paper.
Chem, Roszak et al. “Emergence of metabolic-like cycles in blockchain-orchestrated reaction networks” https://cell.com/chem/fulltext/S2451-9294(23)00611-3
Chem (@Chem_CP) is the first physical science journal published by Cell Press. A sister journal to Cell, Chem, which is published monthly, provides a home for seminal and insightful research and showcases how fundamental studies in chemistry and its sub-disciplines may help in finding potential solutions to the global challenges of tomorrow. Visit https://www.cell.com/chem. To receive Cell Press media alerts, contact press@cell.com.
END
About The Study: This survey study found a reduced rate of overall fractures but an excess of vertebral fractures among living kidney donors compared with controls after a mean follow-up of 25 years. Treatment of excess vertebral fractures with dietary supplements such as vitamin D3 may reduce the numbers of vertebral fractures and patient morbidity.
Authors: Rajiv Kumar, M.B.B.S., of the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.53005)
Editor’s ...
About The Study: In this study of 4,360 patients with traumatic brain injury (TBI), functional limitations six months after injury were common after sports-related TBI, even mild sports-related TBI. Persisting impairment was evident in the sports-related TBI group despite better recovery compared with non–sports-related TBI on measures of mental health and post-concussion symptoms. These findings caution against taking an overoptimistic view of outcomes after sports-related TBI, even if the initial injury appears mild.
Authors: Lindsay Wilson, ...
Researchers at the Universities of Basel and Zurich have discovered the genetic material of the pathogen Treponema pallidum in the bones of people who died in Brazil 2,000 years ago. This is the oldest verified discovery of this pathogen thus far, and it proves that humans were suffering from diseases akin to syphilis – known as treponematoses – long before Columbus’s discovery of America. The new findings, published in the scientific journal Nature, call into question previous theories concerning the spread of syphilis ...
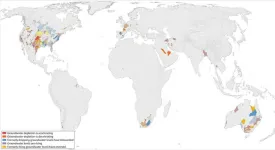
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — Groundwater is rapidly declining across the globe, often at accelerating rates. Writing in the journal Nature, UC Santa Barbara researchers present the largest assessment of groundwater levels around the world, spanning nearly 1,700 aquifers. In addition to raising the alarm over declining water resources, the work offers instructive examples of where things are going well, and how groundwater depletion can be solved. The study is a boon for scientists, policy makers and resource managers working to understand global groundwater dynamics.
“This study was driven by curiosity. We wanted to better understand the state of global ...
DALLAS, Jan. 24, 2024 — In an effort to identify effective food is medicine approaches for incorporating healthy food into health care delivery, the American Heart Association, the world’s leading voluntary organization focused on heart and brain health research, now celebrating 100 years of lifesaving work, today announced grants totaling $7.8 million to 19 research projects nationwide as part of its Health Care by Food™ initiative.
The research projects focus on areas including food resource coaching for patients of a safety-net clinic, delivering food is medicine interventions ...
The Krantz Family Center for Cancer Research at the Mass General Cancer Center today announced the selection of 17 scientists who have been awarded a combined $6 million in funding. These competitive awards, which will be granted annually, were established to recognize the trailblazing efforts of Krantz Center scientists and accelerate ideas, projects and initiatives with the potential to fundamentally change how cancer is diagnosed and treated.
Philanthropists Jason and Keely Krantz, who ...
Despite strict EU regulations on plastic recycling, there is little oversight on plastic waste shipped from the EU to Vietnam. A large percentage of the exported European plastic cannot be recycled and gets dumped in nature. That is what new research led by Utrecht University’s Kaustubh Thapa has found.
Following the recycling path
About half of Europe’s plastic waste is exported to a number of countries in the Global South, including Vietnam. A Dutch and Vietnamese research team ventured to Minh Khai Craft Village, the largest recycling hub ...
Cincinnati Children’s continues to be a cradle for great discoveries.
Our latest Research Annual Report, online now, recounts a remarkable year of scientific advancement supported by a record-high level of research funding from federal, state, industry and philanthropic sources.
Among the many accomplishments from more than 1,000 faculty working in 50 research areas:
Promising results from the world’s first clinical trial of FLASH proton therapy for cancer treatment
Developing the first intestine organoids with functional immune cells, a major step closer to testing potential treatments using these amazing lab-grown tissues
Completing ...
The American Meteorological Society continuously publishes research on climate, weather, and water in its 12 journals. Many of these articles are available for early online access–they are peer-reviewed, but not yet in their final published form.
Below is a selection of articles published early online recently. To view full article text, members of the media can contact kpflaumer@ametsoc.org for press login credentials.
Searching for the Most Extreme Temperature Events in Recent History
Bulletin ...
Researchers have developed a way to use ultrasound to predict whether a pregnant person is at risk of delivering a baby prematurely, which occurs in upward of 10% of pregnancies in the U.S.
The new method — the result of more than 20 years of collaboration between researchers in nursing and engineering at University of Illinois Chicago and University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign — measures microstructural changes in a woman’s cervix using quantitative ultrasound. The ultrasound method works as early as 23 weeks into a pregnancy, according to the research, which is published in ...